(Press-News.org) HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP), a daily dose of two medications meant to prevent HIV infection in high-risk people, has changed public health dramatically in recent years. Yet, adolescents and young adults, one high-risk group, have shown slower uptake in using this prevention method.
Despite accounting for around 20 percent of new HIV infections, adolescents and young adults between the ages of 13 and 24 are still largely not being prescribed PrEP. Research has described physician intentions to prescribe PrEP to at-risk young people, but no studies until now have focused on factors that may affect actual prescribing of this evidence-based practice.
In a new study published in the Nature journal Scientific Reports, Christopher Owens, PhD, assistant professor in the Department of Health Behavior at the Texas A&M University School of Public Health, and colleagues analyzed characteristics of primary care physicians to see how demographic, clinical care, and implementation factors influence prescribing of PrEP to adolescents.
The researchers used an approach known as the Theoretical Domains Framework for their analysis. This framework is commonly used in research about physicians using evidence-based practices. Additionally, it was used in a prior study of physician intent to prescribe PrEP to adolescents.
Researchers found that providers who were assigned male at birth, practiced in the Western region of the United States, and had more knowledge about the PrEP prescribing guidelines were more likely to prescribe PrEP.
Differences in prescribing rates between genders could be due to male adolescents, who are more affected by HIV, seeking male providers, differences in adoption of new treatments by male and female providers, or proportions of male and female providers in different practices. Geographic differences could be due to availability of providers specializing in PrEP or differences in state policies that allow minors to access HIV-related care without parental permission. Further research into these areas could be beneficial. These findings also indicate the potential value of programs to educate providers on PrEP and its prescribing guidelines. Additionally, geographic differences in prescribing behaviors indicate that changes to laws that allow adolescents to seek HIV-related care without parental consent could further improve PrEP uptake.
“Most PrEP research focuses on providers’ intentions to prescribe while we looked at the determinants of prior prescribing PrEP, finding two main points. First, knowledge is important in better understanding providers’ behaviors in delivering this HIV preventive evidence-based practice. Also, structural factors like laws and access to care—that vary widely between states and regions—might be important in mediating or moderating providers’ prescription habits,” Owens said.
END
What factors influence PrEP prescribing behavior in health care providers?
Analysis found male providers in the western U.S. who knew PrEP prescribing guidelines were more likely to prescribe this HIV prevention method
2023-11-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
ASCE establishes Dan M. Frangopol Medal for Life-Cycle Civil Engineering of Civil Structures
2023-11-14
The American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE) recently instituted the Dan M. Frangopol Medal for Life-Cycle Engineering of Civil Structures in recognition of the Lehigh Engineering professor’s contributions as a pioneering researcher and educator and leading authority in the fields of life-cycle civil engineering and life-cycle cost optimization.
The award pays tribute to Frangopol, the inaugural Fazlur R. Khan Endowed Chair of Structural Engineering and Architecture in the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering ...
Webb Telescope’s Marcia Rieke awarded Catherine Wolfe Bruce Gold Medal
2023-11-14
Dr. Marcia Rieke, principal investigator for the Near-Infrared Camera on NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope is the Astronomical Society of the Pacific’s (ASP) 2023 recipient of its most prestigious award. ASP’s Catherine Wolfe Bruce Gold Medal honors Rieke, a Regents Professor of astronomy and Elizabeth Roemer Endowed Chair, Steward Observatory, at the University of Arizona. Rieke’s award and achievements was recognized at the ASP Awards Gala on Saturday, Nov. 11, in Redwood City, California.
Groundbreaking Contributions
Rieke’s research has focused on infrared observations of ...
Galactic ‘lightsabers’: Answering longstanding questions about jets from black holes
2023-11-14
The one thing everyone knows about black holes is that absolutely everything nearby gets sucked into them.
Almost everything, it turns out.
“Even though black holes are defined as objects from which nothing can escape, one of the astonishing predictions of Einstein’s theory of relativity is that black holes can actually lose energy,” says astrophysicist Eliot Quataert, Princeton’s Charles A. Young Professor of Astronomy on the Class of 1897 Foundation. “They ...
Researchers identify unexpected twist while developing new polymer-based semiconductors
2023-11-14
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — A new study led by chemists at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign brings fresh insight into the development of semiconductor materials that can do things their traditional silicon counterparts cannot – harness the power of chirality, a non-superimposable mirror image.
Chirality is one of nature’s strategies used to build complexity into structures, with the DNA double helix perhaps being the most recognized example – two molecule chains connected by a molecular “backbone” ...
Immigrants living in the U.S. have fewer preterm births
2023-11-14
Preterm birth predicts lifelong health outcomes
Worsening preterm birth rates in the U.S. represent a ‘key metric to target to improve overall societal health’
Study identifies key differences among Asian and Hispanic subgroups
Minority stress could contribute to inequities that begin at birth between populations in the U.S.
CHICAGO --- Preterm birth rates are an important marker in assessing a country’s overall health. And the United States isn’t fairing very well.
Individuals born in the U.S. had an overall higher rate (9.7%) of giving birth prematurely compared to U.S. immigrants (9%), a new Northwestern Medicine ...
When we see what others do, our brain sees not what we see, but what we expect
2023-11-14
When we see what others do, our brain sees not what we see, but what we expect
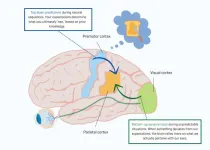
When we engage in social interactions, like shaking hands or having a conversation, our observation of other people’s actions is crucial. But what exactly happens in our brain during this process: how do the different brain regions talk to each other? Researchers at the Netherlands Institute for Neuroscience provide an intriguing answer: our perception of what others do depends more on what we expect to happen than previously believed.
For some time, researchers have been trying to understand how our brains process other people’s ...
Great results with emergency care adapted for pregnant women
2023-11-14
Increased vigilance for high blood pressure and diffuse stomach pain. These are some of the characteristics of emergency care adapted for pregnant women and new mothers. The model, which could become clinical routine throughout Sweden, is described in a thesis at the University of Gothenburg.
The aim of the thesis was to reduce morbidity and mortality among pregnant women and new mothers seeking emergency care. Sweden has relatively low rates of pregnancy-related morbidity and mortality, but pregnant women and new mothers do not currently receive ...
Vegan diet fosters changes in gut microbiome that reduce hot flashes by 95%, finds new study
2023-11-14
A low-fat vegan diet that includes soy fosters changes in the gut microbiome that decrease postmenopausal vasomotor symptoms, or hot flashes, overall by 95%, according to a new study by the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine. A vegan diet also eliminated severe hot flashes, led to a 96% decrease in moderate-to-severe hot flashes, and reduced daytime and nighttime hot flashes by 96% and 94%, respectively. Participants also lost 6.4 pounds on average.
“Women who want to fight hot flashes should feed the bacteria in their gut a vegan diet rich in fruits, vegetables, grains, and beans, which also leads to weight loss and protects against heart disease and type 2 diabetes,” ...
Drug that kills off sleeping bone cells could treat lower back pain
2023-11-14
An existing drug that targets senescent, or sleeping cells could provide the answer to treating lower back pain, according to a new study.
The research, published today as a Reviewed Preprint in eLife, advances our understanding of the role of senescent osteoclasts – cells that break down and remove damaged bone tissue – in the development of lower back pain, which affects 8 in 10 people at some point in their lives. eLife’s editors say the study provides compelling evidence that an existing drug, Navitoclax, can eliminate senescent osteoclasts in mice and, in doing so, markedly reduce spinal pain.
Osteoclasts resorb ...
Inflammation and loss of protective mechanisms in the brain linked to suicide risk
2023-11-14
GRAND RAPIDS, Mich. (Nov. 14, 2023) — A first-of-its-kind study has identified overactive inflammation and loss of critical protection mechanisms in the brain as potential contributors to suicide risk.
The findings support further exploration of anti-inflammatory medications to reduce risk, especially in situations where suicidal ideation can be ascertained early.
The study was published in the journal Molecular Psychiatry and led by Van Andel Institute’s Lena Brundin, M.D., Ph.D., Columbia ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
Psilocybin trends in states that decriminalized use
New data signals high demand in aesthetic surgery in southern, rural U.S. despite access issues
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
[Press-News.org] What factors influence PrEP prescribing behavior in health care providers?Analysis found male providers in the western U.S. who knew PrEP prescribing guidelines were more likely to prescribe this HIV prevention method