(Press-News.org) Aldehydes are toxic compounds that are produced in the body by metabolic processes, especially upon alcohol consumption. They are dangerous because they bind to cellular macromolecules such as DNA, RNA, and proteins, and crosslink them.
Crosslinking damage to DNA must be repaired by the cell to prevent premature aging and cancer. However, it was previously unknown whether and how cells sense and resolve crosslinking damage to single-stranded RNA. A team led by Professor Julian Stingele from the Gene Center Munich has now shown that RNA crosslinking damage is toxic because it impairs protein synthesis.
“It was previously difficult to study specifically RNA crosslinking damage, as most chemicals also damage DNA,” says lead author Jacqueline Cordes. “We therefore utilized a new approach to induce and study RNA damage in the absence of DNA damage,” adds Dr. Shubo Zhao, also lead author of the study. Using this novel experimental system, the researchers uncovered a previously unknown mechanism by which the ribosome can act as a sensor for crosslinking damage. Ribosomes run along the messenger molecule mRNA to translate the information stored in the mRNA into proteins. As the researchers demonstrate, the ribosome gets stuck as soon as it encounters a lesion. This leads to collisions with subsequent ribosomes, triggering removal of the damage.
“Our new findings indicate that compounds commonly considered solely as DNA-damaging agents challenge cellular homeostasis on a much broader level. Given that such agents are often used for chemotherapy, our work has imminent implications for the mechanisms of action of frequently-used anti-cancer drugs,” says Stingele.
Aldehydes are toxic compounds that are produced in the body by metabolic processes, especially upon alcohol consumption. They are dangerous because they bind to cellular macromolecules such as DNA, RNA, and proteins, and crosslink them.
Crosslinking damage to DNA must be repaired by the cell to prevent premature aging and cancer. However, it was previously unknown whether and how cells sense and resolve crosslinking damage to single-stranded RNA. A team led by Professor Julian Stingele from the Gene Center Munich has now shown that RNA crosslinking damage is toxic because it impairs protein synthesis.
“It was previously difficult to study specifically RNA crosslinking damage, as most chemicals also damage DNA,” says lead author Jacqueline Cordes. “We therefore utilized a new approach to induce and study RNA damage in the absence of DNA damage,” adds Dr. Shubo Zhao, also lead author of the study. Using this novel experimental system, the researchers uncovered a previously unknown mechanism by which the ribosome can act as a sensor for crosslinking damage. Ribosomes run along the messenger molecule mRNA to translate the information stored in the mRNA into proteins. As the researchers demonstrate, the ribosome gets stuck as soon as it encounters a lesion. This leads to collisions with subsequent ribosomes, triggering removal of the damage.
“Our new findings indicate that compounds commonly considered solely as DNA-damaging agents challenge cellular homeostasis on a much broader level. Given that such agents are often used for chemotherapy, our work has imminent implications for the mechanisms of action of frequently-used anti-cancer drugs,” says Stingele.
END
Colliding ribosomes activate RNA repair
LMU researchers discover how ribosomes contribute to the recognition and removal of RNA crosslinking damage
2023-11-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
On two small islands in the Indian Ocean, an endangered palm with the world’s largest seed sows a lesson about landscape restoration
2023-11-15
Every tree species has its story. Unraveling all 73,000 of them is a significant undertaking for science, in no small part because a considerable proportion of tree biodiversity is tropical, rare, remote and subject to the ravages of deforestation. And an estimated 9,200 tree species have yet to be discovered.
Even trees well-known to science have mysteries. One is the Seychelles’ endangered coco de mer, or sea coconut palm tree, which is now relegated to parts of two small Indian Ocean islands and in decline. Only some 8,200 individuals remain.
What Lodoicea madivica lacks in range it makes ...
New scientific study reveals the crucial role of herbivorous fishes and sea urchins in restoring Caribbean coral reefs
2023-11-15
A new study by Dr. Lindsay Spiers (Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission) and Professor Thomas Frazer (College of Marine Science at the University of South Florida), published in PeerJ Life & Environment, presents crucial findings on the feeding preferences of herbivorous fishes and the sea urchin Diadema antillarum in Little Cayman. The study, titled "Comparison of feeding preferences of herbivorous fishes and the sea urchin Diadema antillarum in Little Cayman," sheds new light on the dynamics of these herbivores and their impact on the resilience of Caribbean coral reefs.
Caribbean coral reefs face significant challenges, ...
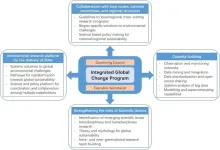
The Future of Future Earth: How global science programs can navigate the complex, shifting challenges in sustainability science
2023-11-15
The global change program Future Earth is an international alliance of organizations and agencies that was launched by the UN in June 2012. The Future Earth 2025 Vision identified eight global challenges for scientific research to accelerate progress in sustainability, improve collaboration, and mobilize resources.
After more than a decade of this global change program, researchers are analyzing the challenges Future Earth has faced and the path forward. Discussion presented in a recently published paper reviews these challenges faced by the coalition and proposes solutions to help these programs meet the many needs of the global community.
The paper was published on ...
Georgetown Global Health Center launches first open-access wildlife disease database
2023-11-15
WASHINGTON (November 15, 2023) – Georgetown University Medical Center’s Center for Global Health Science and Security (GHSS) today announces the launch of a first-of-its-kind wildlife disease database -- a system for collecting records of viruses, bacteria, fungi, parasites, etc. -- designed to support an early warning system for potential viral emergence. The Pathogen Harmonized Observatory, or PHAROS, is open to the global community and free to access.
Scientists in GHSS’ Verena program, a collaborative ...
University of Basel delivers first biological implants for treatment of cartilage lesions and osteoarthritis in humans
2023-11-15
The Department of Biomedicine at the University of Basel and the University Hospital Basel, today announced that it delivered the first surgical procedure to treat Osteoarthritis (OA) in humans. The procedure called Nasal Chondrocyte Tissue-Engineered Cartilage, or N-TEC, provides an innovative alternative to cure confined knee cartilage lesions as well as to address degenerative OA cases that have to date required knee joint replacements – prosthetics that routinely need replacing after 15-20 years.
The team at Basel is spearheading the next-generation human clinical trials that will ...
From 2018 to 2022, eating disorder claim lines increased 65 percent nationally as a percentage of all medical claim lines
2023-11-15
NEW YORK, NY—November 15, 2023—From 2018 to 2022, eating disorder claim lines increased 65 percent nationally as a percentage of all medical claim lines.[1] All eating disorders studied increased during this period, but at different rates: avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder (ARFID) by 305 percent,[2] binge-eating disorder by 81 percent, anorexia nervosa (anorexia) by 73 percent and bulimia nervosa (bulimia) by 3 percent. These and other findings on eating disorders are reported in a FAIR Health white paper released today: Spotlight on Eating Disorders: An Analysis of Private Healthcare Claims.
Eating ...
NTU Singapore’s strength in research excellence sees it ranked 22nd globally and first in Singapore with most number of highly cited researchers
2023-11-15
Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) is up one spot to 22nd globally in this year’s Highly Cited Researchers list by Clarivate, a United Kingdom-based data company.
For the sixth year running, the University has the largest number of influential scientists among Singapore institutions recognised, with 42 NTU researchers that have significant and broad influence in their fields of research named.
These 42 scientists account for 44 mentions in the list, with two individuals recognised more ...
New study finds association between insecticide exposure and lower sperm concentration in adult men
2023-11-15
EMBARGOED until November 15, 2023
Contact: Michelle Thompson
George Mason University
mthomp7@gmu.edu
703-993-3485
New study finds association between insecticide exposure and lower sperm concentration in adult men
Comprehensive systematic review of 25 studies over nearly 50 years reveals consistent evidence of associations between insecticide exposure and lower sperm concentration
FAIRFAX, Va – Melissa J. Perry, Sc.D., MHS, dean of the George Mason University ...
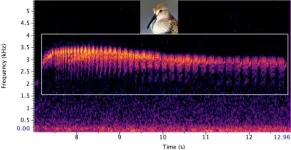
New deep learning AI tool helps ecologists monitor rare birds through their songs
2023-11-15
Researchers have developed a new deep learning AI tool that generates life-like birdsongs to train bird identification tools, helping ecologists to monitor rare species in the wild. The findings are presented in the British Ecological Society journal, Methods in Ecology and Evolution.
Identifying common bird species through their song has never been easier, with numerous phone apps and software available to both ecologists and the public. But what if the identification software has never heard a particular bird before, or only has a small sample of recordings to reference? This is a problem facing ...
Study finds increasingly popular oral nicotine pouches do little to curb smokers’ cravings
2023-11-15
Oral nicotine pouches, a tobacco-leaf-free product marketed as an alternative to cigarettes, do little to curb current smokers’ nicotine cravings, according to a new study. Public health scientists with The Center for Tobacco Research at The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center – Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute report these findings in the medical journal Addiction.
Nicotine pouches are small pre-portioned bags filled with nicotine powder, flavorings, artificial sweeteners and other chemicals that extend shelf life. Marketed ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
[Press-News.org] Colliding ribosomes activate RNA repairLMU researchers discover how ribosomes contribute to the recognition and removal of RNA crosslinking damage