A research team, led by Tokyo Medical and Dental University(TMDU), identifies disease-associated variants in a rare case of RAD50 deficiency/Nijmegen breakage syndrome-like disorder
Tokyo, Japan – Many disorders are caused by genetic variants; to make matters worse, the genetic origin of most disorders remains unknown. Now, in a study recently published in the Journal of Clinical Immunology, researchers have shed light on the specific variants responsible for one rare and serious disorder: ‘RAD50 deficiency/Nijmegen breakage syndrome-like disorder’.
Together with MRE11 and NBN, RAD50 is one of three proteins that make up the ‘MRN complex’, which detects breaks in DNA and helps to initiate DNA repair. Because each of the three proteins is encoded by a separate gene, variants in any of the three genes can lead to altered functioning of the MRN complex. However, although MRE11 and NBN gene variants are known to cause other disorders, ataxia telangiectasia-like disorder and Nijmegen breakage syndrome, respectively, the pathological effects of RAD50 gene variants have remained somewhat unclear – until now.
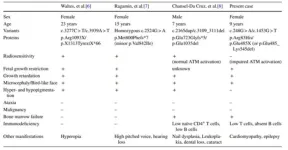
“When we looked at the literature, we realized that only three cases of RAD50 deficiency, which leads to symptoms similar to those of Nijmegen breakage syndrome, had been reported,” explains Masatoshi Takagi, lead author of the study. “Of these three, just one was reported to have RAD50 variants, with associated bone marrow failure and immunodeficiency.”
When the research team came across a patient with progressive bone marrow failure and immunodeficiency combined with Nijmegen breakage syndrome-like manifestations, they decided to perform whole-exome sequencing to see if they could identify any gene variants that might lead to the observed symptoms.
“We found two different RAD50 variants in our patient, each of which was inherited from one of her parents,” states Takagi. “We then tested the functional effects of these combined variants using fibroblast cells from the patient, which we grew in the lab.”
The functional experiments suggested that the patient’s RAD50 variants led to a loss of function of the RAD50 protein, and thus of the MRN complex. They also resulted in slower cell replication (i.e., mitosis), as expected. Interestingly, however, these variants did not cause hypersensitivity to radiation, unlike other known RAD50 variants.
“Together, the findings from our case and the three previously reported cases suggest that RAD50 deficiency/Nijmegen breakage syndrome-like disorder is characterized by growth retardation and microcephaly, which may coexist with bone marrow failure and immunodeficiency in some patients,” says senior author of the study Hirokazu Kanegane. “This disorder may therefore increase susceptibility to infectious diseases and immune-related conditions.”
Given the rarity of this disorder and our lack of knowledge about its genetic causes, the findings from this case are important. A better understanding of RAD50 and its effects on immunity can lead to improved diagnosis and treatment of patients with RAD50 deficiency.
###
The article, “Bone Marrow Failure and Immunodeficiency Associated with Human RAD50 Variants,” was published in the Journal of Clinical Immunology at DOI: 10.1007/s10875-023-01591-8
END
Researchers identify the variants responsible for a rare and serious disorder
2023-11-15
(Press-News.org)
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Do extracurricular activities always give children a head start? Research says maybe not
2023-11-15
In China, there is an old saying: "Don't let your children lose on the starting line." It highlights parents' desire to jumpstart their child's early development. Especially in recent years, parents have become increasingly anxious about their children's education, making it a trend to encourage children to participate in extracurricular activities from an early age. But is participating in extracurricular classes always advantageous for young children?
Recently, a study published in the Journal of School Psychology found that extracurricular activities don't always improve a child's skills or behaviour.
The ...
$3.37 million NIH grant backs effort to optimize online obesity programs for rural residents
2023-11-15
University of Virginia School of Medicine public health researchers, together with colleagues at the University of South Carolina, have received a $3.37 million grant from the National Institutes of Health to determine if online behavioral weight-management programs for rural residents can be improved by adding a human touch.
Online obesity programs have typically failed to yield the same benefits as in-person programs, the researchers note, so they will test three approaches to add human involvement. More than 600 volunteer participants will be enrolled in a core online 24-week weight-loss ...
The American Pediatric Society names Dr. Rachel Katzenellenbogen as the recipient of the 2024 Norman J. Siegel New Member Outstanding Science Award
2023-11-15
The American Pediatric Society (APS) is pleased to announce Rachel Katzenellenbogen, MD, as the 2024 Norman J. Siegel New Member Outstanding Science Award recipient for her considerable contributions to pediatric science. The award will be presented to Dr. Katzenellenbogen during the APS Presidential Plenary at the Pediatric Academic Societies 2024 Meeting.
The award was created in honor of one of the world’s leading nephrologists, Norman J. Siegel, MD, FASN. Dr. Siegel was an outstanding teacher and mentor, nurturing the early careers of numerous fellows and residents. He was a leader within the medical community and educated the ...
Climate engineering could slow Antarctic ice loss, study shows
2023-11-15
Scattering sunlight-reflecting particles in the atmosphere could slow rapid melting in West Antarctica and reduce the risk of catastrophic sea-level rise, according to a study led by Indiana University researchers.
The study, one of the first to look at how climate engineering might impact Antarctica, comes as scientists sound the alarm over the increasing likelihood of accelerated ice loss in West Antarctica this century. The work appears in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres.
“Even if the world meets the ambitious target of limiting global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels — which we are not on track ...
New report outlines microbial solutions to mediate methane emissions
2023-11-15
Washington, D.C.—The American Academy of Microbiology, the scientific think tank and honorific leadership group at the American Society for Microbiology (ASM), has released a new report, The Role of Microbes in Mediating Methane Emissions. The report highlights recommendations to further the scientific community’s understanding of microbial processes of methane production and consumption to mitigate methane emissions and address climate change.
Microbes can influence climate change through biogeochemical cycles that ...
NYU Tandon takes a quantum leap with new minor
2023-11-15
NYU Tandon School of Engineering is poised to become one of an extremely select group of American universities offering an undergraduate program in quantum technology, situating it at the forefront of a fast-growing field in which high employer demand significantly outpaces available talent.
Beginning in the spring 2024 semester, NYU Tandon students can start earning credits towards the new quantum tech minor, offered through the Department of Applied Physics.
In the past decade, quantum technology – the use of ...
Stand Up To Cancer announces three teams focused on gastroesophageal cancer
2023-11-15
LOS ANGELES – Nov. 15, 2023 – Stand Up To Cancer® (SU2C) today announced three Research Teams focused on bringing new therapies to clinical trials for the treatment of gastroesophageal cancer (GEC). The Research Teams, a part of a Dream Team Collective supported by the Torrey Coast Foundation, will unite top researchers from 11 institutions to address critical problems in GEC prevention, diagnosis and treatment. The Dream Team Collective aims to foster new and inclusive cancer research on the causes and treatments of GEC, mentor a new generation of scientists focused on GEC, bring ...
Should a hospital invest toward specializing in an area? Or diversify? The impact of a hospital’s portfolio strategy on patient demand
2023-11-15
Researchers from Indiana University and Texas Christian University published a new Journal of Marketing study that examines the impact of a hospital’s portfolio strategy on patient demand.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “Hospital Portfolio Strategy and Patient Choice” and is authored by Sarang Sunder and Sriram Thirumalai.
Structural changes in the healthcare industry (e.g., the institution of the Affordable ...
Surveilling wetlands for infectious bird flu — and finding it
2023-11-15
Recently, morning omelets and holiday dinners have gotten more expensive. One likely cause is bird flu, outbreaks of which led to the deaths of millions of chickens and turkeys from infection or culling in 2022, according to the U.S. Department of Agriculture, and which still demands rigorous monitoring of wild populations. Now, reporting in Environmental Science & Technology Letters, researchers have developed a method that detected infectious bird flu virus in wetlands frequented by waterfowl.
Wild birds represent a significant reservoir of avian influenza ...
Not so silver lining: Microplastics found in clouds could affect the weather
2023-11-15
From the depths of the seas to snow on mountains and even the air above cities, microplastics are turning up increasingly often. Now, in ACS’ Environmental Science & Technology Letters, researchers have analyzed microplastics in clouds above mountains. They suggest that these tiny particles could play a role in cloud formation and, in turn, affect weather.
Microplastics — plastic fragments smaller than five millimeters — originate from a myriad of items used daily, such as clothing, packaging and car tires. As research in the field evolves, scientists are not only detecting microplastics in the atmosphere but also investigating how they may play a role in cloud formation. ...