(Press-News.org) Washington, D.C.—The American Academy of Microbiology, the scientific think tank and honorific leadership group at the American Society for Microbiology (ASM), has released a new report, The Role of Microbes in Mediating Methane Emissions. The report highlights recommendations to further the scientific community’s understanding of microbial processes of methane production and consumption to mitigate methane emissions and address climate change.
Microbes can influence climate change through biogeochemical cycles that consume or produce greenhouse gases. Increased levels of methane are a main driver of rising global temperatures. Methane’s warming power is about 80 times more potent than carbon dioxide over a 20-year period. Reducing methane is an effective way to slow the rise of global temperatures in the near term. Microbes are major consumers and producers of methane, so understanding the diverse metabolic capabilities of microbes can help scientists better develop microbial solutions that address the issue of methane emissions.
“By understanding the roles of microbes in mediating methane emissions, we open up a wide range of promising solutions to address the climate challenge,” said Vanessa Sperandio, Chair of the Academy Governors. “More than ever, the scientific community needs to work together to urgently bring forward these solutions.”
The report is the result of the discussions and deliberations of participating experts at the colloquium on May 31 and June 1, 2023, organized by ASM and the American Geophysical Union with additional support from the Soil Science Society of America. The participants’ expertise covered a variety of disciplines and sectors, and they identified gaps in knowledge that must be explored further and highlighted potential strategies to address methane emissions. The recommendations in the report aim to help advance the development of solutions that leverage microbes to mediate methane emissions from 4 main sources: enteric fermentation in ruminant animals (such as cows or sheep), animal wastes, rice paddies and landfills.
Read the Recommendations
This colloquium is part of the Academy’s 5-year Climate Change and Microbes Portfolio that focuses on furthering scientific understanding of climate change and microbes. To complement the new report and serve as a practical next step, ASM will release a Microbial Methane Mitigation research roadmap in December, outlining current knowledge gaps and first-order research priorities for experts to use microbes to combat increasing methane emissions. Learn more about the impact of microbes on climate change on ASM’s Microbes and Climate Change resource page.
###
The American Society for Microbiology is one of the largest professional societies dedicated to the life sciences and is composed of 36,000 scientists and health practitioners. ASM's mission is to promote and advance the microbial sciences.
ASM advances the microbial sciences through conferences, publications, certifications, educational opportunities and advocacy efforts. It enhances laboratory capacity around the globe through training and resources. It provides a network for scientists in academia, industry and clinical settings. Additionally, ASM promotes a deeper understanding of the microbial sciences to diverse audiences.
END
New report outlines microbial solutions to mediate methane emissions
2023-11-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NYU Tandon takes a quantum leap with new minor
2023-11-15
NYU Tandon School of Engineering is poised to become one of an extremely select group of American universities offering an undergraduate program in quantum technology, situating it at the forefront of a fast-growing field in which high employer demand significantly outpaces available talent.
Beginning in the spring 2024 semester, NYU Tandon students can start earning credits towards the new quantum tech minor, offered through the Department of Applied Physics.
In the past decade, quantum technology – the use of ...
Stand Up To Cancer announces three teams focused on gastroesophageal cancer
2023-11-15
LOS ANGELES – Nov. 15, 2023 – Stand Up To Cancer® (SU2C) today announced three Research Teams focused on bringing new therapies to clinical trials for the treatment of gastroesophageal cancer (GEC). The Research Teams, a part of a Dream Team Collective supported by the Torrey Coast Foundation, will unite top researchers from 11 institutions to address critical problems in GEC prevention, diagnosis and treatment. The Dream Team Collective aims to foster new and inclusive cancer research on the causes and treatments of GEC, mentor a new generation of scientists focused on GEC, bring ...
Should a hospital invest toward specializing in an area? Or diversify? The impact of a hospital’s portfolio strategy on patient demand
2023-11-15
Researchers from Indiana University and Texas Christian University published a new Journal of Marketing study that examines the impact of a hospital’s portfolio strategy on patient demand.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “Hospital Portfolio Strategy and Patient Choice” and is authored by Sarang Sunder and Sriram Thirumalai.
Structural changes in the healthcare industry (e.g., the institution of the Affordable ...
Surveilling wetlands for infectious bird flu — and finding it
2023-11-15
Recently, morning omelets and holiday dinners have gotten more expensive. One likely cause is bird flu, outbreaks of which led to the deaths of millions of chickens and turkeys from infection or culling in 2022, according to the U.S. Department of Agriculture, and which still demands rigorous monitoring of wild populations. Now, reporting in Environmental Science & Technology Letters, researchers have developed a method that detected infectious bird flu virus in wetlands frequented by waterfowl.
Wild birds represent a significant reservoir of avian influenza ...
Not so silver lining: Microplastics found in clouds could affect the weather
2023-11-15
From the depths of the seas to snow on mountains and even the air above cities, microplastics are turning up increasingly often. Now, in ACS’ Environmental Science & Technology Letters, researchers have analyzed microplastics in clouds above mountains. They suggest that these tiny particles could play a role in cloud formation and, in turn, affect weather.
Microplastics — plastic fragments smaller than five millimeters — originate from a myriad of items used daily, such as clothing, packaging and car tires. As research in the field evolves, scientists are not only detecting microplastics in the atmosphere but also investigating how they may play a role in cloud formation. ...
Association of molecular subtypes in bladder cancer with response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy, progression, and survival
2023-11-15
Considering the molecular subtype of muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC) based on differences in tumor RNA expression can improve the ability of an existing tumor biomarker such as the COXEN score to predict which patients’ tumors are likely to respond to chemotherapy given before surgery. Individual molecular subtypes, however, were not associated with significant differences in patients’ overall survival (OS) or progression-free survival (PFS) times.
Those are the conclusions from a secondary analysis of data from the S1314 clinical trial, a large study in patients with MIBC that was conducted by the SWOG Cancer Research Network, a clinical trials group funded by ...
Colliding ribosomes activate RNA repair
2023-11-15
Aldehydes are toxic compounds that are produced in the body by metabolic processes, especially upon alcohol consumption. They are dangerous because they bind to cellular macromolecules such as DNA, RNA, and proteins, and crosslink them.
Crosslinking damage to DNA must be repaired by the cell to prevent premature aging and cancer. However, it was previously unknown whether and how cells sense and resolve crosslinking damage to single-stranded RNA. A team led by Professor Julian Stingele from ...
On two small islands in the Indian Ocean, an endangered palm with the world’s largest seed sows a lesson about landscape restoration
2023-11-15
Every tree species has its story. Unraveling all 73,000 of them is a significant undertaking for science, in no small part because a considerable proportion of tree biodiversity is tropical, rare, remote and subject to the ravages of deforestation. And an estimated 9,200 tree species have yet to be discovered.
Even trees well-known to science have mysteries. One is the Seychelles’ endangered coco de mer, or sea coconut palm tree, which is now relegated to parts of two small Indian Ocean islands and in decline. Only some 8,200 individuals remain.
What Lodoicea madivica lacks in range it makes ...
New scientific study reveals the crucial role of herbivorous fishes and sea urchins in restoring Caribbean coral reefs
2023-11-15
A new study by Dr. Lindsay Spiers (Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission) and Professor Thomas Frazer (College of Marine Science at the University of South Florida), published in PeerJ Life & Environment, presents crucial findings on the feeding preferences of herbivorous fishes and the sea urchin Diadema antillarum in Little Cayman. The study, titled "Comparison of feeding preferences of herbivorous fishes and the sea urchin Diadema antillarum in Little Cayman," sheds new light on the dynamics of these herbivores and their impact on the resilience of Caribbean coral reefs.
Caribbean coral reefs face significant challenges, ...
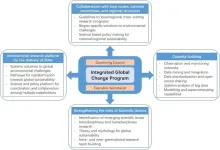
The Future of Future Earth: How global science programs can navigate the complex, shifting challenges in sustainability science
2023-11-15
The global change program Future Earth is an international alliance of organizations and agencies that was launched by the UN in June 2012. The Future Earth 2025 Vision identified eight global challenges for scientific research to accelerate progress in sustainability, improve collaboration, and mobilize resources.
After more than a decade of this global change program, researchers are analyzing the challenges Future Earth has faced and the path forward. Discussion presented in a recently published paper reviews these challenges faced by the coalition and proposes solutions to help these programs meet the many needs of the global community.
The paper was published on ...