(Press-News.org) A third of users on a popular breast cancer support forum describe using peer-recommended or self-discovered techniques to improve sexual functioning, according to a study published November 15, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Christiana von Hippel from the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, USA, and colleagues.
Over 75 percent of breast cancer survivors describe experiencing some degree of sexual dysfunction. Commonly prescribed interventions such as vaginal lubricants or numbing creams are only moderately effective, and many women report difficulty in discussing sexual dysfunction with their healthcare provider.
von Hippel and colleagues reached out to members of the popular Breastcancer.org online forum community who were women over 18 years old and diagnosed with Stage I-IV breast cancer. The study survey sought to quantify the frequency of sexual dysfunction in participants and investigate their techniques for improving sexual function.
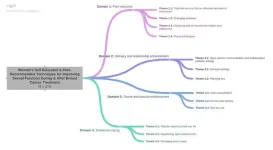
501 women with a median age of 53 years completed the authors’ online survey. Participants were 70 percent sexually active at the time of survey completion, 69 percent heterosexual, 65 percent partnered, and 71 percent white (though about a quarter of participants provided no information regarding partner status, sexual orientation, or race/ethnicity). 47 percent reported being very or extremely satisfied with their sex lives prior to cancer treatment, and 44 percent reported having a significantly worsened sex life post-diagnosis. Though a quarter of participants reported discussing sexual function concerns with their providers, with vaginal dryness and pain with penetration the most common issues, the majority (57 percent) reported never discussing sexual side effects of breast cancer treatment with their clinicians. 35 percent of participants reported using techniques recommended by a peer or that they discovered themselves in order to improve sexual functioning. The authors found these techniques tended to fall into four main domains: pain reduction (e.g. using coconut oil for lubricant or choosing new positions); intimacy and relationship enhancement (e.g more open communication with partners); desire and arousal enhancement (e.g. solo masturbation or using erotica before partnered sex); and emotional coping (e.g. mindset shifts). 46 percent of participants rated their techniques as moderately or more effective when used in addition to or instead of standard techniques offered by clinicians.
Though the authors note their study may not be widely generalizable because of a lack of diversity in their sample, they encourage providers to initiate conversations around sex with their breast cancer patients and share coping techniques discussed by the participants here.
The authors add: “Women with breast cancer are taking the initiative to fill the gap in their care for sexual symptoms by seeking, innovating, and sharing solutions amongst themselves.”
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0293298
Citation: von Hippel C, Dibble KE, Rosenberg SM, Bollman-Jenkins M, Weiss M, Partridge AH (2023) Taking their wellbeing into their own hands: Self-educated and peer-recommended techniques used by women with breast cancer to improve sexual functioning during treatment and in survivorship. PLoS ONE 18(11): e0293298. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0293298
Author Countries: USA
Funding: Dr. von Hippel was supported by the National Cancer Institute (NCI 3R25CA057711). Dr. Dibble was supported by the Helen Gurley Brown Foundation (Helen Gurley Brown Presidential Initiative) at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Harvard Medical School. Dr. Partridge receives support from Susan G. Komen and the Breast Cancer Research Foundation (BCRF). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
Women with breast cancer take sexual health into their own hands
A third of users on online breast cancer support forum describe using peer-recommended or self-discovered techniques to improve sexual functioning
2023-11-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Australian footprints are the oldest known evidence of birds from southern regions
2023-11-15
Early birds had made it to southern polar environments by 120 million years ago, according to a study published November 15, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Anthony Martin of Emory University, USA and colleagues.
Cretaceous bird fossils are abundant and diverse in northern continents, but extremely rare in southern continents, regions that were once part of the landmass of Gondwana. This presents a challenge for paleontologists trying to understand the distribution of early birds. In this study, Martin and colleagues report ...
Treatment strategy for certain advanced prostate cancers shows promise in preclinical models
2023-11-15
Study Title: Targeting DNA methylation and B7-H3 in RB1-deficient and neuroendocrine prostate cancer
Publication: Science Translational Medicine [10.1126/scitranslmed.adf6732]
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute author: Himisha Beltran, MD
Summary: Epigenetic changes can cause prostate cancer to resist treatment by switching genes on or off. One epigenetic mechanism tags genes with DNA methylation marks. This process is mediated by molecules called DNA methyltransferases. These tags can alter gene expression in ways that promote tumors to grow and transition ...
Devil in the detail – What corporations aren’t disclosing about their C02 emissions
2023-11-15
A new study estimates most corporations are not reporting the full scope of their carbon footprint with many claiming to be ‘green’ despite a lack of reporting on Scope 3 key categories.
Though CO2 reporting is currently voluntary for most firms, corporations are under pressure from investors, regulators, politicians, non-profit organisations and other stakeholders to disclose and reduce greenhouse gas emissions (GHG).
The standard for greenhouse gas accounting, the Greenhouse Gas Protocol, is used worldwide to measure a company’s total carbon footprint with three levels of reporting.
The first measures the GHG emissions directly produced by a company ...
New ‘patch’ uses natural body motion to fix disc herniation
2023-11-15
PHILADELPHIA— A new biologic “patch” that is activated by a person’s natural motion could be the key to fixing herniated discs in people’s backs, according to researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania and the CMC VA Medical Center (CMCVAMC). Combining years of work from many different projects, the “tension-activated repair patches” (TARPs) provide controlled release of an anti-inflammatory molecule called anakinra from microcapsules over time, which helped ...
The liking gap is real for second language English speakers, new Concordia research shows
2023-11-15
A new study from Concordia’s Applied Linguistics Lab suggests that most people are usually overly harsh on themselves when speaking in a second language.
Writing in the journal Languages, PhD student Rachael Lindberg and her co-authors build on the previous understanding of individuals’ metaperception—a person’s idea of how they are perceived by others.
The idea that people frequently underestimate how likeable they are, known as the Liking Gap, ...
Study reveals link between neighborhood environmental burden and risk of cardiovascular disease
2023-11-15
BOSTON – A national study led by investigators at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) demonstrates that neighborhood exposure to environmental hazards is significantly associated with poor cardiovascular health across the United States. The study, presented at the American Heart Association Scientific Sessions and simultaneously published in JAMA Cardiology, found that greater cumulative environmental burden (e.g., air pollution, nearby hazardous/toxic sites, poor built environment) was linked ...
Cancer: Discovery of the mechanisms regulating cancer formation
2023-11-15
To form a cancer, cells need to accumulate oncogenic mutations that confer tumor-initiating properties. However, recent evidence has shown that oncogenic mutations occur at a surprisingly high frequency in normal tissues, suggesting that mutations alone are not sufficient to drive cancer formation and that other mechanisms should promote or restrain oncogene-expressing cells from progressing into invasive tumors.
In a study published in Nature, researchers led by Prof. Cédric Blanpain, MD/PhD, investigator of the WEL Research Institute, Director of the Stem Cells and Cancer Laboratory and Professor at the Université ...
Researchers halt progression in Parkinson's disease mouse model
2023-11-15
BOSTON – In a study published in Nature Communications, investigators at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) shed new light on key cellular processes involved in the progression of Parkinson’s disease (PD). Affecting around 10 million people worldwide, Parkinson's disease is a neurodegenerative disorder caused by the progressive loss of the group of brain cells responsible for producing dopamine, a neurotransmitter that plays a critical role in regulating movement and coordination. As these neurons degenerate and dopamine levels decrease, individuals with Parkinson's disease experience a wide range of symptoms, including ...
Study: People with obesity burn less energy during day
2023-11-15
PORTLAND, Oregon – Weight influences how and when bodies burn energy, new research indicates.
An Oregon Health & Science University study published in the journal Obesity found people who have a healthy weight use more energy during the day, when most people are active and eat, while those who have obesity spend more energy during the night, when most people sleep. The study also found that during the day, those with obesity have higher levels of the hormone insulin — a sign that the body is working harder to use glucose, an energy-packed sugar.
“It was surprising to learn how dramatically the timing of when our bodies burn energy differed in ...
Female MP pioneers lost unique appeal to voters because of increasing party control over campaigning, study shows
2023-11-15
Early women parliamentary candidates found it harder to make unique appeals to represent the ‘woman’s point of view’ over time because of increasing national control over campaigning, a new study shows.
The increasing trend for men to present themselves as diligent workers for their constituents’ welfare and keen supporters for social reform also meant they challenged the idea that only female politicians could represent their sex properly in parliament, researchers have found.
The first women parliamentary candidates built on the suffrage campaigners’ argument that there was a distinctive woman’s point of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Lifestyle medicine experts call meaning, purpose, and spirituality foundational to evidence-based, whole-person lifestyle change
Significant acceleration of global warming since 2015
FAU awarded $2.4M NIH grant to study immune signaling and social behavior
Deep learning-enabled virtual multiplexed immunostaining of label-free tissue for vascular invasion assessment
New PET imaging study reveals how ketamine relieves treatment-resistant depression
New study reveals differences between anime bamboo muzzle and actual bamboo
The ‘Great Texas Freeze’ killed thousands of purple martins; biologists worry recovery could take decades
Cancer has a unique nuclear metabolic fingerprint
Tiny thermometers offer on-chip temperature monitoring for processors
New compound stops common complications after intestinal surgery
Breaking through water treatment limits with defect-free, high-efficiency next-generation ceramic filters!
Researchers determine structural motifs of water undecamer cluster
Researchers enhance photocatalytic hydrogen evolution performance of covalent organic frameworks by constitutional isomer strategy
Molecular target drives immunogenicity in cancer immunotherapy
Plant cell structure could hold key to cancer therapies and improved crops
Sustainable hydrogen peroxide production: Breakthroughs in electrocatalyst design for on-site synthesis
Cash rewards for behavior change: A review of financial incentives science in one health contexts and implications
One Health antimicrobial resistance modelling: from science to policy
Artificial feeding platform transforms study of ticks and their diseases
Researchers uncover microscopic mechanism of alkali species dissolution in water clusters
Methionine restriction for cancer therapy: A comprehensive review of mechanisms and clinical applications
White House autism briefing linked to swift shifts in prescribing patterns, study finds
Specialist palliative care can save the NHS up to £8,000 per person and improves quality of life
New research warns charities against ‘AI shortcut’ to empathy
Cannabis compounds show promise in fighting fatty liver disease
Study in mice reveals the brain circuits behind why we help others
Online forum to explore how organic carbon amendments can improve soil health while storing carbon
Turning agricultural plastic waste into valuable chemicals with biochar catalysts
Hidden viral networks in soil microplastics may shape the future of sustainable agriculture
Americans don’t just fear driverless cars will crash — they fear mass job losses
[Press-News.org] Women with breast cancer take sexual health into their own handsA third of users on online breast cancer support forum describe using peer-recommended or self-discovered techniques to improve sexual functioning