Survey: from inflation to world affairs, stressors pile up for Americans this holiday season
A new survey commissioned by The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and College of Medicine finds Americans are feeling the strain from inflation and world affairs this year, in addition to other stressors that often come with the holidays
2023-11-20
(Press-News.org)
EMBARGOED UNTIL MONDAY, NOVEMBER 20 AT 12:01 A.M. EST
COLUMBUS, Ohio – The season of comfort and joy is upon us, but a new survey finds that for many Americans, it’s the season of stress and worry. A new survey commissioned by The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and College of Medicine finds Americans are feeling the strain from inflation and world affairs this year, in addition to other stressors that often come with the holidays.
Of the 1,007 survey respondents, 81% said that national issues and world affairs are causing them stress. In addition, 75% of respondents are experiencing stress from rising prices and holiday spending and 53% are stressed from increasing cases of respiratory illnesses across the nation such as the flu and COVID-19. Memories of last year’s holiday travel meltdown have 44% of survey respondents stressed out.
While they can be stressful, the holidays are supposed to be a time for families and friends to connect and recharge, said Nicole Hollingshead, PhD, a psychologist in the Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Health at the Ohio State Wexner Medical Center.
“The holidays kind of bring on this feeling of sadness and struggle when we really want it to be more of a joyous time,” said Hollingshead. “I encourage people to reflect on what the holidays meant for you growing up. And most of the time I don't hear people reflect on, ‘I loved having all the presents, or I remember every single thing that someone gave me.’ Instead, it's more of the feeling of the holidays.”
People who are stressed out should take a step back and tackle holiday stress by taking charge of what they can control.
When someone is feeling overwhelmed, Hollingshead says it’s time to STOP:
Slow down.
Take a few deep breaths.
Observe the issue.
Proceed with a rational plan.
The survey asked questions about these specific topics, and Hollingshead offers tips to help cope with each stressor:
Inflation and holiday spending: Rising prices are out of your control, but you can discuss your budget with your family or partner ahead of time and make plans to reduce spending.
National/World affairs: The constant stream of headlines about violent crime, political controversy and escalating international conflicts is negatively affecting Americans’ mental health. While there’s not much we can do to control these things, we can control our exposure to it. Limit the time spent watching TV news and avoid doom scrolling through online news stories and social media.
Rise in seasonal respiratory diseases: Mitigating your risk is the best way to protect you and your family from illnesses like COVID and the flu. Make sure you are caught up on recommended vaccinations, set clear boundaries about being around people who are feeling sick and wash your hands frequently.
Unreliable travel industry - When it comes to travel, hope for the best, but prepare for the worst. You can’t control traffic jams or flight delays, but you can ensure all your phones and devices are charged up in case you’re stranded for a while. Always have a plan B in case things go wrong. Be flexible and find ways to enjoy your time together even if your travel doesn’t go as planned.
While it’s common to feel stress around the holidays, Hollingshead encourages people to avoid emotional spending fueled by advertising messages that tap into desires for a picture-perfect holiday. That desire for perfection often deters from holiday joy, she said.
“It gets close to the holidays, and I worry: ‘Did I buy enough for my family? Did I do enough?’ And so we can lose sight of the importance of having too many gifts or making sure everybody has enough to unwrap. Then we lose sight of the big picture, which is that time together.”
# # #
Study results and methodology
This study was conducted on behalf of The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center by SSRS on its Opinion Panel Omnibus platform. The SSRS Opinion Panel Omnibus is a national, twice-per-month, probability-based survey. Data collection was conducted from Oct. 20-23 among a sample of 1,007 respondents. The survey was conducted via web (n=977) and telephone (n=30) and administered in English. The margin of error for total respondents is +/-3.6 percentage points at the 95% confidence level. All SSRS Opinion Panel Omnibus data are weighted to represent the target population of U.S. adults ages 18 or older.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-11-18
When we point at an object, the toddler focuses on the object, while the dog usually takes the gesture as a directional cue. In a recent study, researchers from the Department of Ethology at Eötvös Loránd University find explanations for this phenomenon. It appears that the discrepancy is not only due to how dogs see, but may, in fact, reflect how they think. For "smarter" dogs, the appearance of an object matters as much as its location, suggesting that their information processing is more similar to that of humans.
Spatial bias is the phenomenon of interpreting information in relation to space, location ...
2023-11-17
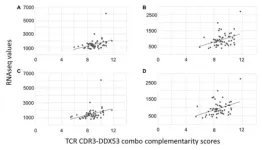
“In this ESCA study, the possibility of an immune response that selected for tumor cells lacking the DDX53 CTA is discussed.”
BUFFALO, NY- November 17, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncoscience (Volume 10) on November 10, 2023, entitled, “An immunoinformatics assessment of the cancer testis antigen, DDX53, as a potential early esophageal cancer antigen.”
T-lymphocytes have been implicated in facilitating a pro-inflammatory, pro-tumorigenic microenvironment that worsens prognosis for esophageal carcinoma (ESCA). In their new study, researchers ...
2023-11-17
To reduce the side effects associated with chemotherapy treatments, researchers have investigated the use of delivery systems that can take more drugs directly to the tumor. Ninh (Irene) La-Beck, Pharm.D., from the Department of Immunotherapeutics and Biotechnology at the Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center (TTUHSC) Jerry H. Hodge School of Pharmacy is one of those researchers.
La-Beck recently received a five-year, $2.49 million grant (“Cholesterol Metabolism in the Pharmacology of Liposomal ...
2023-11-17
Earth science researcher Dr. Antonia Gambacorta earned the 2023 Goddard IRAD Technology Leadership award for pioneering new ways to measure lower layers of Earth’s atmosphere from space.
The award from the chief technologist of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, recognizes Gambacorta’s work demonstrating how hyperspectral microwave sounding, the measurement of hundreds of thousands of wavelengths of microwave light, could dissect Earth’s atmospheric planetary boundary layer (PBL). She also ...
2023-11-17
BOSTON – Glaucoma is one of the leading causes of blindness worldwide, and vision loss, due to the loss of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs), cannot currently be reversed with any treatment. Some studies have looked at replacing RGCs through cell transplants, but this process is still in the research and development stage and fraught with limitations that highlight a need for a more precise manner of effectively repopulating these cells in the retina. Now, a multidisciplinary team led by researchers at the Schepens Eye Research Institute of Mass Eye and Ear has ...
2023-11-17
Rochester Institute of Technology’s Emiliano Brini, assistant professor in the School of Chemistry and Materials Science, has received an award from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to support his research on building the next generation of drugs.
Brini and his team of students will develop computational tools that can predict the strength of the interaction between two proteins and how drugs will modify this interaction. Physics-based methodologies will quickly and accurately provide such predictions.
Designing a new ...
2023-11-17
Small molecules called immunomodulators can help create more effective vaccines and stronger immunotherapies to treat cancer.
But finding the molecules that instigate the right immune response is difficult —the number of drug-like small molecules has been estimated to be 1060, much higher than the number of stars in the visible universe.
In a potential first for the field of vaccine design, machine learning guided the discovery of new immune pathway-enhancing molecules and found one particular small molecule that could outperform the best immunomodulators on the market. The ...
2023-11-17
Seven scientists from the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory have been named among the world’s most influential researchers on the 2023 Highly Cited Researchers list, produced by Clarivate, a data analytics firm that specializes in scientific and academic research.
"These scientists have delivered significant impact for the scientific community and nation," said ORNL Director Stephen Streiffer. "This honor highlights their commitment, hard work and leadership in their respective fields.”
The ORNL researchers named to the list are:
Miaofang Chi, Center for Nanophase Materials Sciences
David A. Cullen, Center for Nanophase Materials ...
2023-11-17
A new understanding of lung cancer cells’ “memories” suggests a new strategy for improving treatment, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK) researchers have found.
Research from the lab of cancer biologist Tuomas Tammela, MD, PhD shows that some lung cancer cells retain a “memory” of the healthy cell where they came from — one that might be exploited to make an emerging type of lung cancer treatment called KRAS inhibition more effective.
The study looked specifically at lung adenocarcinoma, a type of non-small ...
2023-11-17
When Cyclone Idai swept through Mozambique’s Gorongosa National Park in May 2019, one of nature‘s deadliest forces encountered one of the most technologically sophisticated wildlife parks on the planet. Princeton researchers and colleagues from around the world documented the effects using trail cameras and animal-tracking devices that had been in use before the storm.
Thanks to the extensive network of cameras, GPS collars and other instruments, park staff and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Survey: from inflation to world affairs, stressors pile up for Americans this holiday season
A new survey commissioned by The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and College of Medicine finds Americans are feeling the strain from inflation and world affairs this year, in addition to other stressors that often come with the holidays