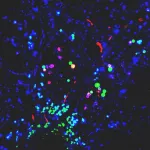
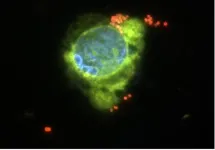
(Press-News.org) A new understanding of lung cancer cells’ “memories” suggests a new strategy for improving treatment, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK) researchers have found.
Research from the lab of cancer biologist Tuomas Tammela, MD, PhD shows that some lung cancer cells retain a “memory” of the healthy cell where they came from — one that might be exploited to make an emerging type of lung cancer treatment called KRAS inhibition more effective.
The study looked specifically at lung adenocarcinoma, a type of non-small cell lung cancer that is the most common type of lung cancer in the U.S. and responsible for 7% of all cancer deaths. This cancer is frequently driven by mutations in the KRAS gene.
“For a long time, cancer-driving KRAS proteins were considered ‘undruggable,’” says study co-first author Zhuxuan “Zoe” Li, a doctoral student in the Tammela Lab at MSK’s Sloan Kettering Institute. “Within the last few years, however, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved the first KRAS inhibitors, with quite a few more in clinical trials. But they don’t work for everyone, and most patients’ cancers eventually acquire resistance to the drugs and come back.”
The team’s findings — co-led by postdoctoral fellow Xueqian Zhuang, PhD — shed important light on lung cancer cells that linger after treatment with a KRAS inhibitor. Importantly, they suggest that separately targeting these cells alongside treatment with a KRAS inhibitor could help prevent recurrence. The study was recently published in Cancer Discovery, a leading journal for biological insights that have important implications for clinical care.
Stem Cells With a Day Job’
To understand the MSK discovery and its implications, it’s helpful to know a little lung biology.
Within the lungs, oxygen is absorbed and carbon dioxide released via air sacs called alveoli. The lining of the alveoli is made of two distinct types of cells — alveolar type 1 (AT1) and alveolar type 2 (AT2).
And while they’re similarly named, these two cells couldn’t be more different.
AT1 cells are long and thin, with a large surface to facilitate gas exchange between the lungs and the bloodstream.
AT2 cells, meanwhile, play a caretaking role, secreting compounds that are important for the health and function of the lungs, as well as helping maintain and repair the lungs by dividing to create replacement AT1 cells.
“You can think of them as stem cells with a day job,” Dr. Tammela says.
The big problem comes when lung cancer cells — which typically develop from AT2 cells — take on some “remembered” properties of the AT1 cells that AT2 cells differentiate into when they’re playing their stem cell role. Scientists call these cancer cells “AT1-like” cells.
Eliminating AT1-Like Cells Improves Response to KRAS Inhibition
In healthy cells, KRAS plays a key role in regulating cell growth and division. But when the gene becomes mutated, it can lead to runaway cell proliferation.
KRAS inhibitors can switch off this explosive growth, greatly diminishing tumors, but they still leave behind pockets of cancer cells that aren’t sensitive to the drug, and that also give the cancer a chance to develop new mutations to resist the drugs’ effects.
The research team painstakingly studied these residual cancer cells to uncover the mechanisms of this resistance using genetically engineered mouse models, mice implanted with patient-derived tumors, and tumor samples from patients.
They discovered that the cancer cells that remained after treatment were these AT1-like cells. They also found these cells have the capacity to reignite the cancer’s runaway growth.
“Importantly, we found that if you get rid of these AT1-like cells, it greatly improves the treatment response to KRAS inhibitors,” Dr. Tammela says.
Eliminating those cells in experimental models is relatively easy, but doing so in the clinic will require further research.
“We actually live in a very exciting time with fantastic pharmacology,” Dr. Tammela says. “We can engineer molecules to bind to a certain cell type and kill them — this is how CAR T cell therapy and antibody drug conjugates work.
“Now that we’ve done these proof-of-concept experiments, the next step would be to find surface proteins that are unique to these AT1-like cells and then develop a therapeutic that can bind to them and kill them,” he adds.
Only at a Place Like MSK
Collaborations with other labs were essential to the research, Dr. Tammela says.
“This is the type of research that can really only happen at a place like MSK,” he says. “We had really important collaborations with other labs at MSK that shared animal models and patient samples that were integral to the study, and we worked closely with several of MSK’s core facilities — the Antitumor Assessment Core, Integrated Genomics Operation, Flow Cytometry Core, and Molecular Cytology Core.”
MSK investigators Scott Lowe, PhD and Charles Rudin, MD, PhD were key contributors, Dr. Tammela notes.
“And the study would not have been possible without Zoe’s dedication, and the model systems and initial insights developed by Dr. Zhuang,” he adds.
Additional Authors, Funding, and Disclosures
Additional authors include Chun-Hao Pan, Yan Yan, Rohit Thummalapalli, Stefan Torborg, Anupriya Singhal, Jason Chang, and Rona Yaeger of MSK; Simon Joost, formerly of MSK and now at GC Therapeutics; Eusebio Manchado, formerly of MSK, now at the Novartis Institute for Biomedical Research; Jill Hallin and James Christensen of Mirati Theraputics; and Lukas Dow of Weill Cornell Medicine.
The work was supported by an American Cancer Society Research Scholar Grant (R01-CA270116), the National Institutes of Health and National Cancer Institute (R01-CA233944, P30-CA08748, F30-CA254120, T32GM007739), the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, New York Stem Cell Science (C32559GG), Hope Funds for Cancer Research, and a Josie Robertson Scholarship.
Dr. Tammela reports an advisory role and equity interests in Lime Therapeutics; and he receives research support to his laboratory from Ono Pharmaceuticals (unrelated to this work). Dr. Rudin consults on oncology drug development with AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, D2G, Daiichi Sankyo, Epizyme, Genentech/Roche, Ipsen, Jazz, Kowa, Lilly, Merck, and Syros; he also serves on the scientific advisory boards of Auron, Bridge Medicines, Earli, and Harpoon Therapeutics. Dr. Lowe is a founder and member of the scientific advisory board of Blueprint Medicines, Mirimus, ORIC Pharmaceuticals, and Faeth Therapeutics; he also has advisory role and equity interests in Constellation Pharmaceuticals and PMV Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Yaeger has served as an advisor for Amgen, Array BioPharma/Pfizer, Mirati Therapeutics, and Zai Lab; she has received research support from Array BioPharma/Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Daiichi Sankyo, and Mirati Therapeutics.
END
Lung cancer cells’ ‘memories’ suggest new strategy for improving treatment
2023-11-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Idai vs. Impalas: New study shows in real-time what helps mammals survive a natural disaster
2023-11-17
When Cyclone Idai swept through Mozambique’s Gorongosa National Park in May 2019, one of nature‘s deadliest forces encountered one of the most technologically sophisticated wildlife parks on the planet. Princeton researchers and colleagues from around the world documented the effects using trail cameras and animal-tracking devices that had been in use before the storm.
Thanks to the extensive network of cameras, GPS collars and other instruments, park staff and ...
Nanoplastics promote conditions for Parkinson’s across various lab models
2023-11-17
DURHAM, N.C. – Nanoplastics interact with a particular protein that is naturally found in the brain, creating changes linked to Parkinson’s disease and some types of dementia.
In a Duke-led study appearing Nov. 17 in Science Advances, the researchers report that the findings create a foundation for a new area of investigation, fueled by the timely impact of environmental factors on human biology.
“Parkinson’s disease has been called the fastest growing neurological disorder in the world,” said principal investigator, Andrew West, Ph.D., professor in the Department of Pharmacology and Cancer Biology at ...
New research suggests plants might be able to absorb more CO2 from human activities than previously expected
2023-11-17
New research published today in leading international journal Science Advances paints an uncharacteristically upbeat picture for the planet. This is because more realistic ecological modelling suggests the world’s plants may be able to take up more atmospheric CO2 from human activities than previously predicted.
Despite this headline finding, the environmental scientists behind the research are quick to underline that this should in no way be taken to mean the world’s governments can take their foot off the brake in their obligations to reduce carbon ...
In the fight against malaria-carrying mosquitoes, just add soap
2023-11-17
EL PASO, Texas (Nov. 17, 2023) – Could the solution to the decades-long battle against malaria be as simple as soap? In a new study published in PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases, scientists at The University of Texas at El Paso have made a compelling case for it.
The team has found that adding small quantities of liquid soap to some classes of pesticides can boost their potency by more than ten-fold.
The discovery is promising news as malaria-carrying mosquitoes display ...
Deep dive on sea level rise: new modelling gives better predictions on Antarctic ice sheet melt
2023-11-17
Using historical records from around Australia, an international team of researchers have put forward the most accurate prediction to date of past Antarctic ice sheet melt, providing a more realistic forecast of future sea level rise.
The Antarctic ice sheet is the largest block of ice on earth, containing over 30 million cubic kilometers of water.
Hence, its melting could have a devasting impact on future sea levels. To find out just how big that impact might be, the research team, including Dr Mark Hoggard from The Australian National University, turned to the past.
“If ...
Crime-free housing policies increase evictions among minorities, but do not cut crime
2023-11-17
Policies that encourage landlords to evict tenants who have involvement with the criminal justice system do not appear to reduce crime, while increasing evictions among Black residents and people with lower incomes, according to a new RAND Corporation report.
Studying “crime-free housing policies” adopted by cities in California over a decade-long period, researchers found no meaningful statistical evidence that the policies reduce crime.
The study also found that crime-free housing policies significantly increased ...
Consumption of antibiotics in the community back to pre-pandemic levels in the European Union and European Economic Area
2023-11-17
This year’s European Antibiotic Awareness Day (EAAD) focuses on the targets outlined in the 2023 Council Recommendation to step up efforts in the European Union (EU) against antimicrobial resistance in a One Health approach. [1] Those recommendations formulate the 2023 goal to reduce total antibiotic consumption (community and hospital sectors combined) by 20%, using consumption data from 2019 as baseline.
Consumption of antibiotics in the community accounts for around 90% of the total use. This means, that a substantial and consistent decline in the use of antibiotics in this sector will be key on the way towards reaching ...
LSU Health’s Bailey to receive prestigious national award
2023-11-17
New Orleans, LA – The American Psychiatric Association (APA) Foundation has selected Rahn Baily, MD, DLFAPA, ACP, Professor and Chair of Psychiatry at LSU Health New Orleans School of Medicine, as the recipient of the 2024 Solomon Carter Fuller Award.
According to the APA Foundation, “The Solomon Carter Fuller Award—established in 1969 and named for Dr. Solomon Carter Fuller, recognized as the first Black psychiatrist in America—honors a Black citizen who has pioneered in ...
Significant "post-COVID" resurgence in invasive meningococcal disease
2023-11-17
A team of scientists from the Institut Pasteur has used the database of the National Reference Center for Meningococci to trace the evolution of invasive meningococcal disease cases in France between 2015 and 2022, revealing an unprecedented resurgence in the disease after the easing of control measures imposed during the COVID-19 epidemic. Recently reported cases have mainly been caused by meningococcal serogroups that were less frequent before the pandemic, and there has been a particular uptick in cases among people aged 16 to 24. The results, published in the Journal of Infection and Public Health on October 12, ...
Scientists produce human norepinephrine neurons from stem cells, with significant implications for researching diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s
2023-11-17
Researchers at the University of Wisconsin–Madison have identified a protein key to the development of a type of brain cell believed to play a role in disorders like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases and used the discovery to grow the neurons from stem cells for the first time.
The stem-cell-derived norepinephrine neurons of the type found in a part of the human brain called the locus coeruleus may enable research into many psychiatric and neurodegenerative diseases and provide a tool for developing ...