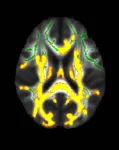
(Press-News.org) CHICAGO – Higher amounts of visceral abdominal fat in midlife are linked to the development of Alzheimer’s disease, according to research being presented next week at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA). Visceral fat is fat surrounding the internal organs deep in the belly. Researchers found that this hidden abdominal fat is related to changes in the brain up to 15 years before the earliest memory loss symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease occur.
According to the Alzheimer’s Association, there are more than 6 million Americans living with Alzheimer’s disease. By 2050, this number is projected to rise to nearly 13 million. One in every five women and one out of 10 men will develop Alzheimer’s disease in their lifetime.
To try and identify Alzheimer’s risks earlier, researchers assessed the association between brain MRI volumes, as well as amyloid and tau uptake on positron emission tomography (PET) scans, with body mass index (BMI), obesity, insulin resistance and abdominal adipose (fatty) tissue in a cognitively normal midlife population. Amyloid and tau are proteins thought to interfere with the communication between brain cells.
“Even though there have been other studies linking BMI with brain atrophy or even a higher dementia risk, no prior study has linked a specific type of fat to the actual Alzheimer’s disease protein in cognitively normal people,” said study author Mahsa Dolatshahi, M.D., M.P.H., post-doctoral research fellow with Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology (MIR) at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. “Similar studies have not investigated the differential role of visceral and subcutaneous fat, especially in terms of Alzheimer’s amyloid pathology, as early as midlife.”
For this cross-sectional study, researchers analyzed data from 54 cognitively healthy participants, ranging in age from 40 to 60 years old, with an average BMI of 32. The participants underwent glucose and insulin measurements, as well as glucose tolerance tests. The volume of subcutaneous fat (fat under the skin) and visceral fat were measured using abdominal MRI. Brain MRI measured the cortical thickness of brain regions that are affected in Alzheimer’s disease. PET was used to examine disease pathology in a subset of 32 participants, focusing on amyloid plaques and tau tangles that accumulate in Alzheimer’s disease.
The researchers found that a higher visceral to subcutaneous fat ratio was associated with higher amyloid PET tracer uptake in the precuneus cortex, the region known to be affected early by amyloid pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. This relationship was worse in men than in women. The researchers also found that higher visceral fat measurements are related to an increased burden of inflammation in the brain.
“Several pathways are suggested to play a role,” Dr. Dolatshahi said. “Inflammatory secretions of visceral fat—as opposed to potentially protective effects of subcutaneous fat—may lead to inflammation in the brain, one of the main mechanisms contributing to Alzheimer’s disease.”
Senior author Cyrus A. Raji, M.D., Ph.D., associate professor of radiology and neurology, and director of neuromagnetic resonance imaging at MIR, noted that the findings have several key implications for earlier diagnosis and intervention.
“This study highlights a key mechanism by which hidden fat can increase the risk of Alzheimer’s disease,” he said. “It shows that such brain changes occur as early as age 50, on average—up to 15 years before the earliest memory loss symptoms of Alzheimer’s occur.”
Dr. Raji added that the results may point to visceral fat as a treatment target to modify risk of future brain inflammation and dementia.
“By moving beyond body mass index in better characterizing the anatomical distribution of body fat on MRI, we now have a uniquely better understanding of why this factor may increase risk for Alzheimer’s disease,” he said.
Additional co-authors are Paul K. Commean, B.E.E., Joseph E. Ippolito, M.D., Ph.D., Tammie L. S. Benzinger, M.D., Ph.D., and John C. Morris, M.D.
###
Note: Copies of RSNA 2023 news releases and electronic images will be available online at RSNA.org/press23.
RSNA is an association of radiologists, radiation oncologists, medical physicists and related scientists promoting excellence in patient care and health care delivery through education, research and technologic innovation. The Society is based in Oak Brook, Illinois. (RSNA.org)
Editor’s note: The data in these releases may differ from those in the published abstract and those actually presented at the meeting, as researchers continue to update their data right up until the meeting. To ensure you are using the most up-to-date information, please call the RSNA Newsroom at 1-312-791-6610.
For patient-friendly information on MRI and PET, visit RadiologyInfo.org.
END
CHICAGO – Using an image-guided minimally invasive procedure, researchers may be able to restore the sense of smell in patients who have suffered with long-COVID, according to research being presented next week at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Parosmia, a condition where the sense of smell no longer works correctly, is a known symptom of COVID-19. Recent research has found that up to 60% of COVID-19 patients have been affected. While most patients do recover their sense of smell over time, some patients with long COVID continue to have these symptoms for months, or even years, after ...
A red wine may pair nicely with the upcoming Thanksgiving meal. But for some people, drinking red wine even in small amounts causes a headache. Typically, a “red wine headache” can occur within 30 minutes to three hours after drinking as little as a small glass of wine.
What in wine causes headaches?
In a new study, scientists at the University of California, Davis, examined why this happens – even to people who don’t get headaches when drinking small amounts of other alcoholic beverages. Researchers think that a flavanol found naturally in red wines can interfere with the proper metabolism of alcohol and can lead to a headache. The study was published in ...
New research led by Griffith University on Australia’s Gold Coast and Andrés Bello University in Chile, has shown that surfing contributes about US$1 trillion a year to the global economy, by improving the mental health of surfers.
For the Gold Coast alone, the research team estimated the benefits to be valued at ~US$1.0–3.3 billion per year. Mental health benefits from surfing comprise 57–74% of the total economic benefits of surfing. The mental health benefits are 4.4–13.5 times direct expenditure by surfers, and 4–12 times economic effects via property and inbound tourism.
The research ...
Proof of concept of new material for long lasting relief from dry mouth conditions
A novel aqueous lubricant technology designed to help people who suffer from a dry mouth is between four and five times more effective than existing commercially available products, according to laboratory tests.
Developed by scientists at the University of Leeds, the saliva substitute is described as comparable to natural saliva in the way it hydrates the mouth and acts as a lubricant when food is chewed.
Under a powerful microscope, the molecules in the substance - known as a microgel - appear as a lattice-like ...
PRESS RELEASE FROM THE UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE
EMBARGOED UNTIL 10:00 LONDON TIME (GMT) ON 20 NOVEMBER, 2023
[Photographs and a copy of the paper are available here]
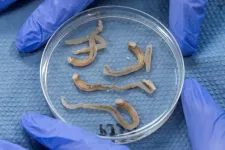
These long, white saltwater clams are the world’s fastest-growing bivalve and can reach 30cm long in just six months. They do this by burrowing into waste wood and converting it into highly-nutritious protein.
The researchers found that the levels of Vitamin B12 in the Naked Clams were higher than in most other bivalves – and almost twice the amount found in blue mussels.
And with the addition of an algae-based feed to the system, the Naked Clams can be fortified with omega-3 polyunsaturated ...
Associative learning was always thought to be regulated by the cortex of the cerebellum, often referred to as the “little brain". However, new research from a collaboration between the Netherlands Institute for Neuroscience, Erasmus MC, and Champalimaud Center for the Unknown reveals that actually the nuclei of the cerebellum make a surprising contribution to this learning process.
If a teacup is steaming, you’ll wait a bit longer before drinking from it. And if your fingers get caught in the door, you'll be more careful next time. These are forms of associative ...
New research reveals that with each subsequent generation of Mexican Americans, the risk of developing liver cancer has climbed. Although Mexican Americans have experienced a growing trend in modifiable risk factors—such as increased alcohol consumption, higher smoking rates, and elevated body mass index—these factors alone do not entirely account for the increased risk of liver cancer as generations progress. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
US-born Latinos have a higher incidence of liver cancer than foreign-born Latinos, and a possible ...
In the United States, liver cancer rates have more than tripled since 1980. Some groups, including Latinos, face an even higher risk than the general population—but researchers do not fully understand why.
A study from the Keck School of Medicine of USC, funded by the National Cancer Institute, has shed new light on those disparities. Researchers found that among Mexican Americans, liver cancer risk rises the longer a person’s family has lived in the U.S. That increased risk primarily affected men. The ...
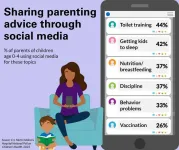
ANN ARBOR, Mich. – Potty training, getting kids to sleep and toddler tantrums are just some of the challenges parents of young children face.
And four in five parents in a new national poll say they go to the same place to discuss such parenting issues: social media.
Nearly half of parents rate social media as very useful for getting new ideas to try, according to the University of Michigan Health C.S. Mott Children’s Hospital National Poll on Children’s Health.
“Many parents turn to online communities ...
Cyberattacks targeting health information systems can cause considerable damage and stress, but there are ways to reduce the risk of these events, write authors in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.230436.
"With respect to cybersecurity, a bit of prevention is worth a terabyte of cure," writes Vinyas Harish, MD/PhD candidate at the University of Toronto's Temerty Faculty of Medicine, with coauthors, in an article outlining the impact of cyberattacks on Canadian health information ...