(Press-News.org) University of Sussex researchers have developed a more energy-efficient alternative to transmit data that could potentially replace Bluetooth in mobile phones and other tech devices. With more and more of us owning smart phones and wearable tech, researchers at the University of Sussex have found a more efficient way of connecting our devices and improving battery life. Applied to wearable devices, it could even see us unlocking doors by touch or exchanging phone numbers by shaking hands.
Professor Robert Prance and Professor Daniel Roggen, of the University of Sussex, have developed the use of electric waves, rather than electromagnetic waves, for a low-power way to transmit data at close range, while maintaining the high throughput needed for multimedia applications.
Bluetooth, Wifi, and 5G currently rely on electromagnetic modulation, a form of wireless technology which was developed over 125 years ago. In the late 19th Century, the focus was to transmit data over long distances using electromagnetic waves. By contrast, electric field modulation uses short-range electric waves, which consumes much less power than Bluetooth.
As we tend to be in close proximity to our devices, electric field modulation offers a proven, more efficient method of connecting our devices, enabling longer lasting battery life when streaming music to headphones, taking calls, using fitness trackers, or interacting with smart home tech.
The development could advance how we use tech in our day to day lives and evolve a wide range of futuristic applications too. For example, a bracelet using this technology could enable phone numbers to be exchanged simply by shaking hands or a door could be unlocked just by touching the handle.
Daniel Roggen, Professor of Engineering and Design at the University of Sussex, explains:
“We no longer need to rely on electromagnetic modulation, which is inherently battery hungry. We can improve the battery life of wearable technology and home assistants, for example, by using electric field modulation instead of Bluetooth. This solution will not only make our lives much more efficient, but it also opens novel opportunities to interact with devices in smart homes.
“The technology is also low cost, meaning it could be rolled out to society quickly and easily. If this were mass produced, the solution can be miniaturised to a single chip and cost just a few pence per device, meaning that it could be used in all devices in the not-too-distant future.”
The University of Sussex researchers are now seeking industrial partnerships to help further miniaturize the technology for personal devices.
- Ends -
END
Day by day, we communicate with our office colleagues to accomplish tasks that are necessary to function. The more than 200 different types of cells in our bodies do the same thing, but the way they communicate with each other isn't as simple as sending an email.
Researchers like Ioannis Zervantonakis are still trying to understand how these cells actually communicate with each other. The assistant professor of bioengineering at the University of Pittsburgh Swanson School of Engineering recently received a National Institute of General Medical Sciences Maximizing Investigators' Research Award, and his project ...
Digital payment platforms such as Venmo work great for sharing a dinner bill with friends, buying gifts at a pop-up shop or making payments without cash or credit cards.
But these digital payment platforms have a dark side: They can be misused for drug dealing and other illicit activity, suggest researchers from the University of California, Davis. And social media apps such as TikTok and Instagram can act as marketing tools for digital drug dealing.
“While platforms like Venmo revolutionize financial interactions, they also highlight the need for ongoing vigilance and adaptive regulatory measures,” said Pantelis ...
The deep sea is home to one of the world's largest communities of animals about which we still know very little. Yet it is already subject to a growing number of human-induced environmental pressures. How do its inhabitants respond to these stressors? A new study led by researchers from the GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel, published today in the scientific journal Nature Communications, provides first insights into the stress response of a deep pelagic jellyfish to ocean warming and deep-sea mining induced sediment plumes.
One particular and potentially large environmental stressor for organisms in the deep ocean is the environmental ...
Female academics are significantly underrepresented in winning academic prizes and having awards named after them, a new study shows.
Analysis of nearly 9,000 awardees and 346 scientific prizes and medals published today (Tuesday 21 November) in Nature Human Behaviour has found that men win eight prizes for every one won by a woman if the award is named after a man. These awards represent almost two thirds of all scientific prizes.
Female academics are however more likely to win awards that have been named after other notable female scientists, with 47% of those awards going to women and 53% to men.
Dr Katja Gehmlich, Associate Professor in the Institute ...
Leipzig/Mainz. The extent to which aerosol particles affect the climate depends on how much water the particles can hold in the atmosphere. The capacity to hold water is referred to as hygroscopicity (K) and, in turn, depends on further factors – particularly the size and chemical composition of the particles, which can be extremely variable and complex. Through extensive investigations, an international research team under the leadership of the Max Planck Institute for Chemistry (MPIC) and the Leibniz Institute for Tropospheric Research ...
WASHINGTON – U.S. Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) researchers have discovered solar-wind hydrogen in lunar samples, which indicates that water on the surface of the Moon may provide a vital resource for future lunar bases and longer-range space exploration. Space-based resource identification is a key factor in planning for civilian- and government-led space exploration.
“Hydrogen has the potential to be a resource that can be used directly on the lunar surface when there are more regular or permanent ...
Scientists have identified the genes in the probiotic Bifidobacteria longum responsible for improving gut motility. A research team reporting November 21st in the journal Cell Host & Microbe found that B. longum strains possessing the abfA cluster of genes can ameliorate constipation through enhanced utilization of an indigestible fiber called arabinan in the gut.
“We established the causal link between a genetic variant—the abfA cluster—to the key functional difference of probiotic B. longum in multiple model organisms, including mice and humans, and provided mechanistic and ecological insights ...
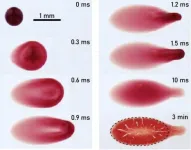
WASHINGTON, Nov. 21, 2023 – Forensic science has captured the public imagination by storm, as the profusion of “true crime” media in the last decade or so suggests. By now, most of us know that evidence left at a crime scene, such as blood, can often reveal information that is key to investigating and understanding the circumstances around a crime — and that scientific methods can help interpret that information.
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, a group of scientists from Boston University and the University of Utah demonstrated ...
About The Study: In this study of 25,000 veterans receiving dialysis, unstable housing experienced before starting dialysis was associated with increased risk of all-cause mortality, and risks increased with age. Further efforts are needed to understand the experiences of older adults with unstable housing and to estimate the scope of unstable housing among all individuals receiving dialysis.
Authors: Tessa K. Novick, M.D., M.S.W., M.H.S., of the University of Texas at Austin Dell Medical School in Austin, Texas is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit ...
About The Study: In this study of 7,000 older U.S. residents, food insecurity was associated with increased dementia risk, poorer memory function, and faster memory decline. Future studies are needed to examine whether addressing food insecurity may benefit brain health.
Authors: Aayush Khadka, Ph.D., of the University of California, San Francisco, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.44186)
Editor’s ...