(Press-News.org) A new artificial intelligence computer program created by researchers at the University of Florida and NVIDIA can generate doctors’ notes so well that two physicians couldn’t tell the difference, according to an early study from both groups.
In this proof-of-concept study, physicians reviewed patient notes — some written by actual medical doctors while others were created by the new AI program — and the physicians identified the correct author only 49% of the time.
A team of 19 researchers from NVIDIA and the University of Florida said their findings, published Nov. 16 in the Nature journal npj Digital Medicine, open the door for AI to support health care workers with groundbreaking efficiencies.
The researchers trained supercomputers to generate medical records based on a new model, GatorTronGPT, that functions similarly to ChatGPT. The free versions of GatorTron™ models have more than 430,000 downloads from Hugging Face, an open-source AI website. GatorTron™ models are the site’s only models available for clinical research, according to the article’s lead author Yonghui Wu, Ph.D., from the UF College of Medicine’s department of health outcomes and biomedical informatics.
“In health care, everyone is talking about these models. GatorTron™ and GatorTronGPT are unique AI models that can power many aspects of medical research and health care. Yet, they require massive data and extensive computing power to build. We are grateful to have this supercomputer, HiPerGator, from NVIDIA to explore the potential of AI in health care,” Wu said.
UF alumnus and NVIDIA co-founder Chris Malachowsky is the namesake of UF’s new Malachowsky Hall for Data Science & Information Technology. A public-private partnership between UF and NVIDIA helped to fund this $150 million structure. In 2021, UF upgraded its HiPerGator supercomputer to elite status with a multimillion-dollar infrastructure package from NVIDIA, the first at a university.
For this research, Wu and his colleagues developed a large language model that allows computers to mimic natural human language. These models work well with standard writing or conversations, but medical records bring additional hurdles, such as needing to protect patients’ privacy and being highly technical. Digital medical records cannot be Googled or shared on Wikipedia.
To overcome these obstacles, the researchers stripped UF Health medical records of identifying information from 2 million patients while keeping 82 billion useful medical words. Combining this set with another dataset of 195 billion words, they trained the GatorTronGPT model to analyze the medical data with GPT-3 architecture, or Generative Pre-trained Transformer, a form of neural network architecture. That allowed GatorTronGPT to write clinical text similar to medical doctors’ notes.
“This GatorTronGPT model is one of the first major products from UF’s initiative to incorporate AI across the university. We are so pleased with how the partnership with NVIDIA is already bearing fruit and setting the stage for the future of medicine,” said Elizabeth Shenkman, Ph.D., a co-author and chair of UF’s department of health outcomes and biomedical informatics.
Of the many possible uses for a medical GPT, one idea involves replacing the tedium of documentation with notes recorded and transcribed by AI. Wu says that UF has an innovation center that is pursuing a commercial version of the software.
For an AI tool to reach such parity with human writing, programmers spend weeks programming supercomputers with clinical vocabulary and language usage based on billions upon billions of words. One resource providing the necessary clinical data is the OneFlorida+ Clinical Research Network, coordinated at UF and representing many health care systems.
“It’s critical to have such massive amounts of UF Health clinical data not only available but ready for AI. Only a supercomputer could handle such a big dataset of 277 billion words. We are excited to implement GatorTron™ and GatorTronGPT models to real-world health care at UF Health,” said Jiang Bian, Ph.D., a co-author and UF Health’s chief data scientist and chief research information officer.
A cross-section of 14 UF and UF Health faculty contributed to this study, including researchers from Research Computing, Integrated Data Repository Research Services within the Clinical and Translational Science Institute, and from departments and divisions within the College of Medicine, including neurosurgery, endocrinology, diabetes and metabolism, cardiovascular medicine, and health outcomes and biomedical informatics.
The study was partially funded by grants from the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute, the National Cancer Institute and the National Institute on Aging.
Here are two paragraphs that reference two patient cases one written by a human and one created by GatorTronGPT — can you tell whether the author was machine or human?
END
Medical AI tool from UF, NVIDIA gets human thumbs-up in first study
2023-11-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Getting to the root of visceral gut pain
2023-11-21
MSU has a satellite uplink/LTN TV studio and Comrex line for radio interviews upon request.
Researchers at Michigan State University may have discovered why visceral pain is so common in people who have experienced inflammation in their guts, including patients with irritable bowel syndrome, or IBS.
Working with mouse models, MSU physiologists showed that nervous system cells known as glia can sensitize nearby neurons, causing them to send pain signals more easily than they did prior to inflammation.
“The glia drop the threshold for activating a neuron,” said MSU Research Foundation Professor Brian Gulbransen, whose research team authored the new report in the ...
How AI could help optimize nutrient consistency in donated human breast milk
2023-11-21
A team of University of Toronto Engineering researchers, led by Professor Timothy Chan, is leveraging machine learning to optimize the macronutrient content of pooled human donor milk recipes.
The researchers introduce their data-driven optimization model in a new paper published in Manufacturing and Systems Operations Management.
Chan and his team worked with Mount Sinai Hospital’s Rogers Hixon Ontario Human Milk Bank — which provides donor milk to preterm and sick babies who are hospitalized across Ontario — as well as Dr. Debbie O’Connor, a professor at the Temerty ...
Dwarf galaxies use 10-million-year quiet period to churn out stars
2023-11-21
Contact: Morgan Sherburne, morganls@umich.edu
Images
ANN ARBOR—If you look at massive galaxies teeming with stars, you might be forgiven in thinking they are star factories, churning out brilliant balls of gas. But actually, less evolved dwarf galaxies have bigger regions of star factories, with higher rates of star formation.
Now, University of Michigan researchers have discovered the reason underlying this: These galaxies enjoy a 10-million-year delay in blowing out the gas cluttering up their environments. Star-forming regions are able to hang on to their gas and dust, allowing more stars to coalesce ...
New report highlights vital contribution of ‘virtual schools’ for children in care
2023-11-21
A new study highlights the vital contribution of ‘virtual schools’ for children in care and recommends ten ways to improve their educational outcomes.
The research, by the University of Exeter and the National Association of Virtual School Heads (NAVSH), shows strong disparities in progress and attainment for children in care depending on where they live. They found these differences are not driven by neighbourhood deprivation but by patchy distribution of school places, confused funding policies and variable regulation.
As a result, some virtual schools have difficulty ...
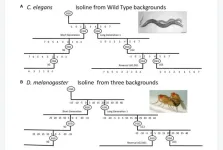
Parental age effect on the longevity and healthspan of flies and worms
2023-11-21
“[...] little work [has been] published on the effect of parental age in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, a common model organism for aging studies.”
BUFFALO, NY- November 16, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 21, entitled, “Parental age effect on the longevity and healthspan in Drosophila melanogaster and Caenorhabditis elegans.”
Several studies have investigated the effect of parental age on biological ...
Two new UW–Madison-led studies inform outlook on scaling of carbon removal technologies
2023-11-21
MADISON, Wis., - Carbon dioxide removal (CDR) technologies that could be critical tools to combat climate change have developed in line with other technologies from the last century. However, according to new studies led by Gregory Nemet, a professor at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, these technologies need to develop faster to meet policy targets aimed at limiting global warming.
As policymakers, researchers and climate activists from around the world prepare to meet for the UN Climate Change Conference beginning on ...
Nuclear physics traineeship program offers launchpad for research careers
2023-11-21
Associate Professor of physics Benjamin Jones has received a $341,571 grant from the U.S. Department of Energy to continue his successful traineeship program at The University of Texas at Arlington.
The program exposes undergraduate students to opportunities in particle and nuclear physics, which offer key components in many diverse careers, such as nuclear medicine, radiation therapy, archaeology, precision management and astrophysics.
UTA’s Nuclear Research Experiences for Minority Students (NREMST) started in 2021 with the goal of immersing students from historically underrepresented populations in nuclear physics.
“We know that many students ...
Experts from the UK and South America join forces for major new study of mental health reform
2023-11-21
A major new research project will explore the impact of transformational changes to mental health treatment in South America.
Community-based care for people with psychosocial disabilities began in the region in the 1960s and 1970s, when a minority of people were moved from large and isolated psychiatric hospitals to residential alternatives in the community.
This policy was promoted by the World Health Organization and the Pan America Health Organization and is considered a defining element of the modernisation of mental health systems. But in current analysis of this process the ethical, social and political tensions associated ...
Bacteria store memories and pass them on for generations
2023-11-21
Scientists have discovered that bacteria can create something like memories about when to form strategies that can cause dangerous infections in people, such as resistance to antibiotics and bacterial swarms when millions of bacteria come together on a single surface. The discovery — which has potential applications for preventing and combatting bacterial infections and addressing antibiotic-resistant bacteria — relates to a common chemical element bacterial cells can use to form and pass along these memories to their progeny over later generations.
Researchers ...
Forest modeling shows which harvest rotations lead to maximum carbon sequestration
2023-11-21
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Forest modeling by Oregon State University scientists shows that a site’s productivity – an indicator of how fast trees grow and how much biomass they accumulate – is the main factor that determines which time period between timber harvests allows for maximum above-ground carbon sequestration.
The findings, published in the journal Forests, are important for Pacific Northwest forest managers seeking to strike an optimal balance between harvesting and carbon sequestration, an important tool in the fight against climate change.
The study by Catherine Carlisle, Temesgen Hailemariam ...