(Press-News.org) About The Study: Longer cumulative duration of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) medication use was associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, particularly hypertension and arterial disease, compared with nonuse in this study of 278,000 individuals in Sweden ages 6 to 64 who had an incident ADHD diagnosis or ADHD medication dispensation. These findings highlight the importance of carefully weighing potential benefits and risks when making treatment decisions about long-term ADHD medication use. Clinicians should regularly and consistently monitor cardiovascular signs and symptoms throughout the course of treatment.
Authors: Zheng Chang, Ph.D., and Le Zhang, Ph.D., of the Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm, are the corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2023.4294)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapsychiatry/fullarticle/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2023.4294?guestAccessKey=381db621-a5e7-4bdb-b2ee-ae9791f8e599&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=112223
END
ADHD medications and long-term risk of cardiovascular diseases
JAMA Psychiatry
2023-11-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Racial and ethnic disparity in preoperative chemosensitivity and survival in patients with early-stage breast cancer
2023-11-22
About The Study: In this study of 103,000 individuals with early-stage breast cancer, Black patients had a higher mortality risk compared with white patients among those with residual disease after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. This highlights the need for personalized treatment strategies for Black patients to help them attain pathologic complete response.
Authors: Shipra Gandhi, M.D., of Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center in Buffalo, New York, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed ...
From the first bite, our sense of taste helps pace our eating
2023-11-22
When you eagerly dig into a long-awaited dinner, signals from your stomach to your brain keep you from eating so much you’ll regret it – or so it’s been thought. That theory had never really been directly tested until a team of scientists at UC San Francisco recently took up the question.
The picture, it turns out, is a little different.
The team, led by Zachary Knight, PhD, a UCSF professor of physiology in the Kavli Institute for Fundamental ...
Team discovers rules for breaking into Pseudomonas
2023-11-22
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Researchers report in the journal Nature that they have found a way to get antibacterial drugs through the nearly impenetrable outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a bacterium that – once it infects a person – is notoriously difficult to treat.
By bombarding P. aeruginosa with hundreds of compounds and using machine learning to determine the physical and chemical traits of those molecules that accumulated inside it, the team discovered how to penetrate the bacterium’s defenses. They used this information ...
Camouflaging stem cell-derived transplants avoids immune rejection
2023-11-22
Cell and organ transplants can be lifesaving, but patients often encounter long waiting lists due to the shortage of suitable donors. According to donatelife.net, in 2021 6,000 people died in the U.S. alone while waiting for a transplant. One day, transplants generated from stem cells may alleviate the constant organ donor shortage, making transplants available to a larger group of patients.
An issue with donation, whether it’s with solid tissues or cells from deceased or living donors, is immune rejection. Unless the donor material is carefully matched to the recipient’s immune system, the transplant will be rejected. However, stem cell research ...
Mind the gap: Caution needed when assessing land emissions in the COP28 Global Stocktake
2023-11-22
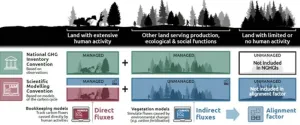
Effective management of land, whether for agriculture, forests, or settlements, plays a crucial role in addressing climate change and achieving future climate targets. Land use strategies to mitigate climate change include stopping deforestation, along with enhancing forest management efforts. Countries have recognized the importance of the land use, land-use change, and forestry (LULUCF) sector, with 118 of 143 countries including land-based emissions reductions and removals in their Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs), which are at the heart of the Paris Agreement and the achievement of its long-term goals.
A new study, published in Nature, demonstrates that estimates of current land-based ...
Developing a new perspective for the EU beekeeping sector: B-GOOD legacy booklet
2023-11-22
The aim of the B-GOOD project (Giving Beekeeping Guidance By Computational-Assisted Decision Making) was to pave the way towards healthy and sustainable beekeeping within the European Union by following a collaborative and interdisciplinary approach. By merging data from within and around beehives, as well as wider socioeconomic conditions and by developing and testing innovative tools to perform risk assessments, B-GOOD provided guidance for beekeepers and helped them make better and more informed decisions.
The communication of scientific information and the transformation of scientific ...
How do temperature extremes influence the distribution of species?
2023-11-22
As the planet gets hotter, animal and plant species around the world will be faced with new, potentially unpredictable living conditions, which could alter ecosystems in unprecedented ways. A new study from McGill University researchers, in collaboration with researchers in Spain, Mexico, Portugal, Denmark, Australia, South Africa and other universities in Canada, investigates the importance of temperature in determining where animal species are currently found to better understand how a warming climate ...
New remote sensing dataset improves global land change tracking
2023-11-22
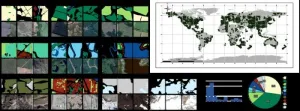
Tracking unprecedented changes in land use over the past century, global land cover maps provide key insights into the impact of human settlement on the environment. Researchers from Sun Yat-sen University created a large-scale remote sensing annotation dataset to support Earth observation research and provide new insight into the dynamic monitoring of global land cover.
In their study, published Oct 16 in the Journal of Remote Sensing, the team examined how global land use/landcover (LULC) has undergone dramatic changes with the advancement of industrialization and urbanization, including deforestation and flooding.
“We ...
A Special Collection collaboration between SLAS and SBI2
2023-11-22
Oak Brook, IL – The latest issue of SLAS Discovery is a joint Special Collection between SLAS and the Society of Biomolecular Imaging and Informatics (SBI2) to celebrate the 10th Annual SBI2 High-Content Imaging and Informatics meeting. This collaboration features a curated special collection of articles that highlight the significant impact of high-content imaging in basic and translational research. Volume 28, Issue 7 features one perspective, four original research articles and one short communication.
Perspective
Evolution and Impact of High Content Imaging
This ...
A new diagnostic tool to identify and treat pathological social withdrawal, Hikikomori
2023-11-22
Fukuoka, Japan—Researchers at Kyushu University have developed a new tool to help clinicians and researchers assess individuals for pathological social withdrawal, known as Hikikomori. The tool, called Hikikomori Diagnostic Evaluation, or HiDE, can be a practical guide on collecting information on this globally growing pathology.
Hikikomori is a condition characterized by sustained physical isolation or social withdrawal for a period exceeding six months. It was first defined in Japan in 1998, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] ADHD medications and long-term risk of cardiovascular diseasesJAMA Psychiatry