(Press-News.org) Trans-vaccenic acid (TVA), a long-chain fatty acid found in meat and dairy products from grazing animals such as cows and sheep, improves the ability of CD8+ T cells to infiltrate tumors and kill cancer cells, according to a new study by researchers from the University of Chicago.
The research, published this week in Nature, also shows that patients with higher levels of TVA circulating in the blood responded better to immunotherapy, suggesting that it could have potential as a nutritional supplement to complement clinical treatments for cancer.
“There are many studies trying to decipher the link between diet and human health, and it’s very difficult to understand the underlying mechanisms because of the wide variety of foods people eat. But if we focus on just the nutrients and metabolites derived from food, we begin to see how they influence physiology and pathology,” said Jing Chen, PhD, the Janet Davison Rowley Distinguished Service Professor of Medicine at UChicago and one of the senior authors of the new study. “By focusing on nutrients that can activate T cell responses, we found one that actually enhances anti-tumor immunity by activating an important immune pathway.”
Finding nutrients that activate immune cells
Chen’s lab focuses on understanding how metabolites, nutrients and other molecules circulating in the blood influence the development of cancer and response to cancer treatments. For the new study, two postdoctoral fellows, Hao Fan, PhD and Siyuan Xia, PhD, both co-first authors, started with a database of around 700 known metabolites that come from food and assembled a “blood nutrient” compound library consisting of 235 bioactive molecules derived from nutrients. They screened the compounds in this new library for their ability to influence anti-tumor immunity by activating CD8+ T cells, a group of immune cells critical for killing cancerous or virally infected cells.
After the scientists evaluated the top six candidates in both human and mouse cells, they saw that TVA performed the best. TVA is the most abundant trans fatty acid present in human milk, but the body cannot produce it on its own. Only about 20% of TVA is broken down into other byproducts, leaving 80% circulating in the blood. “That means there must be something else it does, so we started working on it more,” Chen said.
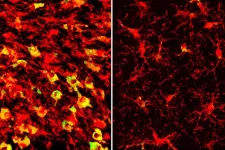
The researchers then conducted a series of experiments with cells and mouse models of diverse tumor types. Feeding mice a diet enriched with TVA significantly reduced the tumor growth potential of melanoma and colon cancer cells compared to mice fed a control diet. The TVA diet also enhanced the ability of CD8+ T cells to infiltrate tumors.
The team also performed a series of molecular and genetic analyses to understand how TVA was affecting the T cells. These included a new technique for monitoring transcription of single-stranded DNA called kethoxal-assisted single-stranded DNA sequencing, or KAS-seq, developed by Chuan He, PhD, the John T. Wilson Distinguished Service Professor of Chemistry at UChicago and another senior author of the study. These additional assays, done by both the Chen and He labs, showed that TVA inactivates a receptor on the cell surface called GPR43 which is usually activated by short-chain fatty acids often produced by gut microbiota. TVA overpowers these short-chain fatty acids and activates a cellular signaling process known as the CREB pathway, which is involved in a variety of functions including cellular growth, survival, and differentiation. The team also showed that mouse models where the GPR43 receptor was exclusively removed from CD8+ T cells also lacked their improved tumor fighting ability.
Finally, the team also worked with Justin Kline, MD, Professor of Medicine at UChicago, to analyze blood samples taken from patients undergoing CAR-T cell immunotherapy treatment for lymphoma. They saw that patients with higher levels of TVA tended to respond to treatment better than those with lower levels. They also tested cell lines from leukemia by working with Wendy Stock, MD, the Anjuli Seth Nayak Professor of Medicine, and saw that TVA enhanced the ability of an immunotherapy drug to kill leukemia cells.
Focus on the nutrients, not the food
The study suggests that TVA could be used as a dietary supplement to help various T cell-based cancer treatments, although Chen points out that it is important to determine the optimized amount of the nutrient itself, not the food source. There is a growing body of evidence about the detrimental health effects of consuming too much red meat and dairy, so this study shouldn’t be taken as an excuse to eat more cheeseburgers and pizza; rather, it indicates that nutrient supplements such as TVA could be used to promote T cell activity. Chen thinks there may be other nutrients that can do the same.
“There is early data showing that other fatty acids from plants signal through a similar receptor, so we believe there is a high possibility that nutrients from plants can do the same thing by activating the CREB pathway as well,” he said.
The new research also highlights the promise of this “metabolomic” approach to understanding how the building blocks of diet affect our health. Chen said his team hopes to build a comprehensive library of nutrients circulating in the blood to understand their impact on immunity and other biological processes like aging.
“After millions of years of evolution, there are only a couple hundred metabolites derived from food that end up circulating in the blood, so that means they could have some importance in our biology,” Chen said. “To see that a single nutrient like TVA has a very targeted mechanism on a targeted immune cell type, with a very profound physiological response at the whole organism level—I find that really amazing and intriguing.”
The study, “Trans-vaccenic acid reprograms CD8+ T cells and anti-tumor immunity,” was supported by the National Institutes of Health (grants CA140515, CA174786, CA276568, 1375 HG006827, K99ES034084), a UChicago Biological Sciences Division Pilot Project Award, the Ludwig Center at UChicago, the Sigal Fellowship in Immuno-oncology, the Margaret E. Early Medical Research Trust, the AASLD Foundation a Harborview Foundation Gift Fund, and the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
END
Nutrient found in beef and dairy improves immune response to cancer
Scientists at UChicago discover that trans-vaccenic acid (TVA), a fatty acid found in beef, lamb, and dairy products, improves the ability of immune cells to fight tumors
2023-11-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Overdose deaths increased in pregnant and postpartum women from early 2018 to late 2021
2023-11-22
Drug overdose deaths rose markedly between January to June 2018 and July to December 2021 among 10- to 44-year-old girls and women who were pregnant or pregnant within the previous 12 months, according to a new study by researchers at National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) at the National Institutes of Health. Overdose mortality more than tripled among those aged 35 to 44 during the study period, from 4.9 deaths per 100,000 mothers aged 35 to 44 with a live birth in the 2018 period to 15.8 in the 2021 period. Over 60% of these pregnancy-associated overdose deaths occurred outside healthcare settings, ...
Lowering a form of brain cholesterol reduces Alzheimer’s-like damage in mice
2023-11-22
In Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias, cognitive decline is driven by the overaccumulation of a normal brain protein known as tau. Wherever tau builds up, nearby brain tissue starts to degenerate and die.
Now, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have found — in mice — that Alzheimer’s-like tau deposits in the brain lead to the accumulation of a form of cholesterol known as cholesteryl esters, and that lowering cholesteryl ester levels ...
Segregated patterns of hospital care delivery and health outcomes
2023-11-22
About The Study: This study of Medicare claims data for 4,386 hospitals found that higher segregation of hospital care was associated with poorer health outcomes for both Black and white patients, with significantly greater negative health outcomes for Black populations, supporting racial segregation as a root cause of health disparities. Policymakers and clinical leaders could address this important public health issue through payment reform efforts and expansion of health insurance coverage, in addition to supporting upstream efforts to reduce racial segregation in hospital ...
Mortality and hospitalization risks in patients with cancer and the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant
2023-11-22
About The Study: This study showed that during the Omicron-dominant period, patients with solid cancer and COVID-19 had higher mortality and hospitalization risks following COVID-19 infection versus patients without solid cancer with COVID-19, and that COVID-19 vaccination in the patients with cancer mitigated this risk.
Authors: Salomon M. Stemmer, M.D., of Beilinson Hospital in Petah Tikva, Israel, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2023.5042)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional ...
ADHD medications and long-term risk of cardiovascular diseases
2023-11-22
About The Study: Longer cumulative duration of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) medication use was associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, particularly hypertension and arterial disease, compared with nonuse in this study of 278,000 individuals in Sweden ages 6 to 64 who had an incident ADHD diagnosis or ADHD medication dispensation. These findings highlight the importance of carefully weighing potential benefits and risks when making treatment decisions about ...
Racial and ethnic disparity in preoperative chemosensitivity and survival in patients with early-stage breast cancer
2023-11-22
About The Study: In this study of 103,000 individuals with early-stage breast cancer, Black patients had a higher mortality risk compared with white patients among those with residual disease after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. This highlights the need for personalized treatment strategies for Black patients to help them attain pathologic complete response.
Authors: Shipra Gandhi, M.D., of Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center in Buffalo, New York, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed ...
From the first bite, our sense of taste helps pace our eating
2023-11-22
When you eagerly dig into a long-awaited dinner, signals from your stomach to your brain keep you from eating so much you’ll regret it – or so it’s been thought. That theory had never really been directly tested until a team of scientists at UC San Francisco recently took up the question.
The picture, it turns out, is a little different.
The team, led by Zachary Knight, PhD, a UCSF professor of physiology in the Kavli Institute for Fundamental ...
Team discovers rules for breaking into Pseudomonas
2023-11-22
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Researchers report in the journal Nature that they have found a way to get antibacterial drugs through the nearly impenetrable outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a bacterium that – once it infects a person – is notoriously difficult to treat.
By bombarding P. aeruginosa with hundreds of compounds and using machine learning to determine the physical and chemical traits of those molecules that accumulated inside it, the team discovered how to penetrate the bacterium’s defenses. They used this information ...
Camouflaging stem cell-derived transplants avoids immune rejection
2023-11-22
Cell and organ transplants can be lifesaving, but patients often encounter long waiting lists due to the shortage of suitable donors. According to donatelife.net, in 2021 6,000 people died in the U.S. alone while waiting for a transplant. One day, transplants generated from stem cells may alleviate the constant organ donor shortage, making transplants available to a larger group of patients.
An issue with donation, whether it’s with solid tissues or cells from deceased or living donors, is immune rejection. Unless the donor material is carefully matched to the recipient’s immune system, the transplant will be rejected. However, stem cell research ...
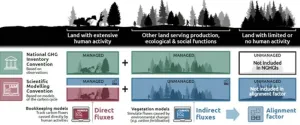
Mind the gap: Caution needed when assessing land emissions in the COP28 Global Stocktake
2023-11-22
Effective management of land, whether for agriculture, forests, or settlements, plays a crucial role in addressing climate change and achieving future climate targets. Land use strategies to mitigate climate change include stopping deforestation, along with enhancing forest management efforts. Countries have recognized the importance of the land use, land-use change, and forestry (LULUCF) sector, with 118 of 143 countries including land-based emissions reductions and removals in their Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs), which are at the heart of the Paris Agreement and the achievement of its long-term goals.
A new study, published in Nature, demonstrates that estimates of current land-based ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Tokyo Bay’s night lights reveal hidden boundaries between species
As worms and jellyfish wriggle, new AI tools track their neurons
ATG14 identified as a central guardian against liver injury and fibrosis
Research identifies blind spots in AI medical triage
$9M for exploring the fundamental limits of entangled quantum sensor networks
Study shows marine plastic pollution alters octopus predator-prey encounters
Night lights can structure ecosystems
A parasitic origin for the ribosome?
A gold-standard survey of the American mood
Tool for identifying children at risk of speech disorders
How Japanese medical trainees view artificial intelligence in medicine
MambaAlign fusion framework for detecting defects missed by inspection systems
Children born with upper limb difference show the incredible adaptability of the young brain
How bacteria can reclaim lost energy, nutrients, and clean water from wastewater
Fast-paced lives demand faster vision: ecology shapes how “quickly” animals see time
Global warming and heat stress risk close in on the Tour de France
New technology reveals hidden DNA scaffolding built before life ‘switches on’
New study reveals early healthy eating shapes lifelong brain health
Trashing cancer’s ‘undruggable’ proteins
Industrial research labs were invented in Europe but made the U.S. a tech superpower
Enzymes work as Maxwell's demon by using memory stored as motion
Methane’s missing emissions: The underestimated impact of small sources
Beating cancer by eating cancer
How sleep disruption impairs social memory: Oxytocin circuits reveal mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities
Natural compound from pomegranate leaves disrupts disease-causing amyloid
A depression treatment that once took eight weeks may work just as well in one
New study calls for personalized, tiered approach to postpartum care
The hidden breath of cities: Why we need to look closer at public fountains
Rewetting peatlands could unlock more effective carbon removal using biochar
Microplastics discovered in prostate tumors
[Press-News.org] Nutrient found in beef and dairy improves immune response to cancerScientists at UChicago discover that trans-vaccenic acid (TVA), a fatty acid found in beef, lamb, and dairy products, improves the ability of immune cells to fight tumors