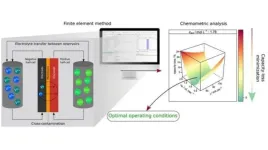
(Press-News.org) An article by researchers at the Center for Development of Functional Materials (CDMF) in Brazil describes a successful strategy to mitigate charge capacity loss in vanadium redox flow batteries, which are used by electric power utilities among other industries and can accumulate large amounts of energy. The article is published in the Chemical Engineering Journal.
CDMF is a Research, Innovation and Dissemination Center (RIDC) funded by FAPESP and hosted by the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar) in São Paulo state.
The study involved computer simulations designed to find out how ion leakage between the anolyte and catholyte, called transport loss, leads to battery deactivation, and how to mitigate this loss so as to keep ion concentration constant over time. Initially, the researchers estimated the effects of current density, active species concentration and volumetric flow on capacity loss. The second stage sought optimal conditions to minimize capacity loss based on the flow between electrolyte tanks in the opposite direction to cross-contamination (transport of electroactive species through the membrane).
The results showed current density and active species concentration to be the main variables affecting capacity loss. According to the researchers, their approach successfully mitigated cross-contamination in different combinations of the two variables, providing an optimal flow between electrolyte tanks under different operating conditions.
Ernesto Pereira, last author of the article and a professor at UFSCar, noted that the main advantage of redox flow batteries is lack of electrode aging as the electroactive components are dissolved in solutions instead of being coated onto electrodes.
Commercial vanadium redox flow batteries are expected to have a longer lifetime than other types, although the study was conducted on a small scale. “Energy efficiency loss due to aging is minimal, given the slow pace of aging,” he said.
The researchers explained that they are exploring and analyzing flow batteries computationally, with commercial batteries as a model, as part of a broader strategy that includes the development of novel organic substances for this type of battery.
About São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP)
The São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) is a public institution with the mission of supporting scientific research in all fields of knowledge by awarding scholarships, fellowships and grants to investigators linked with higher education and research institutions in the State of São Paulo, Brazil. FAPESP is aware that the very best research can only be done by working with the best researchers internationally. Therefore, it has established partnerships with funding agencies, higher education, private companies, and research organizations in other countries known for the quality of their research and has been encouraging scientists funded by its grants to further develop their international collaboration. You can learn more about FAPESP at www.fapesp.br/en and visit FAPESP news agency at www.agencia.fapesp.br/en to keep updated with the latest scientific breakthroughs FAPESP helps achieve through its many programs, awards and research centers. You may also subscribe to FAPESP news agency at http://agencia.fapesp.br/subscribe.
END
Researchers obtain promising results against capacity loss in vanadium batteries
A computational study conducted in Brazil could help extend the working lives of these batteries, which are widely used by utilities and manufacturers.
2023-11-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Photonic integrated neuro-synaptic core for convolutional spiking neural network
2023-11-22
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances, 10.29026/oea.2023.230140 discusses photonic integrated neuro-synaptic core for convolutional spiking neural network.
Brain science and brain-like intelligence are the cutting-edge science and technology that countries all over the world compete to seize. The rapid rise and vigorous development of emerging fields such as artificial intelligence, 5G/6G, big data, autonomous driving, and the Internet of Things has led to the explosive growth of global data. Due to the memory wall effect, the conventional von Neumann architecture performs low energy efficiency. Electronic ...
Multi-synaptic photonic SNN based on a DFB-SA chip
2023-11-22
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Science; DOI 10.29026/oes.2023.230021 overviews multi-synaptic photonic SNN based on a DFB-SA chip.
Compared with traditional artificial neural networks, spiking neural networks (SNN) are more biologically authentic, more powerful, and less power-consuming due to their spatiotemporal coding and event-driven characteristics. In recent years, optical computing has been widely considered as a hardware acceleration platform, where nonlinear computing poses a challenge. Photonic SNN provides an ultra-fast and energy-efficient platform for high-performance ...
Optical trapping of optical nanoparticles: fundamentals and applications
2023-11-22
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Science; DOI 10.29026/oes.2023.230019 overviews optical trapping of optical nanoparticles.
This article reviews the fundamentals and applications of optically trapped optical nanoparticles. Optical nanoparticles are nowadays one of the key elements of photonics. They do not only allow optical imaging of a plethora of systems (from cells to microelectronics), but also behave as highly sensitive remote sensors. In recent years, it has been demonstrated the success of optical tweezers in isolating and manipulating individual optical nanoparticles. This has opened the door to high resolution single particle scanning ...
Casas del Turuñuelo, a site of repeated animal sacrifice in Iron Age Spain
2023-11-22
The Iron Age site of Casas del Turuñuelo was used repeatedly for ritualized animal sacrifice, according to a multidisciplinary study published November 22, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Mª Pilar Iborra Eres of the Institut Valencià de Conservació, Restauració i Investigació, Spain, Sebastián Celestino Pérez of Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas, Spain, and their colleagues.
Archaeological sites with evidence of major animal sacrifices are rarely ...
Earliest known European common hippopotamus fossil reveals their Middle Pleistocene dispersal
2023-11-22
Modern hippos first dispersed in Europe during the Middle Pleistocene, according to a study published November 22, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Beniamino Mecozzi of the Sapienza University of Rome and colleagues.
Modern hippos, Hippopotamus amphibius, arose from African ancestors during the Quaternary, a time when hippos were widespread in Europe. However, the details of the modern species’ origin and dispersal into Europe are unclear and highly debated. In this study, Mecozzi and colleagues provide new insights via analysis of a fossil hippo skull from the study area of Tor di Quinto in Rome.
The skull of Tor di Quinto, currently housed at the ...
Status threat - the concern that outsiders will undermine your group's status - is associated with increased age, conservatism, conspiracy mentality, and paranoia, in study of 300 US adults
2023-11-22
Status threat - the concern that outsiders will undermine your group's status - is associated with increased age, conservatism, conspiracy mentality, and paranoia, in study of 300 US adults
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0293930
Article Title: Conspiracy mentality, subclinical paranoia, and political conservatism are associated with perceived status threat
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
Transplanting gut microbes from an obesity-resistant shrew can improve microbiome diversity and decrease the weight of obese mice
2023-11-22
Transplanting gut microbes from an obesity-resistant shrew can improve microbiome diversity and decrease the weight of obese mice
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0293213
Article Title: Gut microbiota of Suncus murinus, a naturally obesity-resistant animal, improves the ecological diversity of the gut microbiota in high-fat-diet-induced obese mice
Author Countries: Japan, China
Funding: This work (PONE-D-23-21281) was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the ...
Airborne virus infectivity can be reduced by up to 99.98% by commercially available NPBI-based air purifiers, per experiment using real-world concentrations of COVID-19 strains, flu and RSV viruses
2023-11-22
Airborne virus infectivity can be reduced by up to 99.98% by commercially available NPBI-based air purifiers, per experiment using real-world concentrations of COVID-19 strains, flu and RSV viruses
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0293504
Article Title: Bipolar ionization rapidly inactivates real-world, airborne concentrations of infective respiratory viruses
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. All research and 3rd party laboratory testing was funded entirely by GPS Air. Edward Sobek is an employee of GPS Air ...
7 in 8 homicide victims in South Africa are male
2023-11-22
7 in 8 homicide victims in South Africa are male, with homicide rates peaking on weekends and holidays, and firearms and sharp items being the most common murder weapons, in analysis of almost 20,000 2017 post-mortems. END ...
In Nepalese survey, 1 in 5 men who have sex with men report having attempted suicide, with over 40 percent experiencing some suicidal ideation
2023-11-22
In Nepalese survey, 1 in 5 men who have sex with men report having attempted suicide, with over 40 percent experiencing some suicidal ideation.
####
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/globalpublichealth/article?id=10.1371/journal.pgph.0002348
Article Title: Suicidal ideation, plan, and attempt among men who have sex with men in Nepal: Findings from a cross-sectional study
Author Countries: Nepal, USA
Funding: RS received funding from the National Institute on Drug Abuse (Award Number: K01DA051346). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
[Press-News.org] Researchers obtain promising results against capacity loss in vanadium batteriesA computational study conducted in Brazil could help extend the working lives of these batteries, which are widely used by utilities and manufacturers.