(Press-News.org) Change in clinical practice would have clear benefits for patients undergoing major bowel surgery, according to analysis conducted by researchers from UCL and the Royal Devon and Exeter Hospital.
The study, published in The British Journal of Surgery, provides evidence that giving iron intravenously before colorectal surgery improves outcomes for patients, reducing the need for blood transfusion by 33%.
Anaemia is a common problem in patients undergoing bowel surgery due to bleeding from the gut and blood loss during the operation. Anaemia is also associated with feeling tired and unwell, a slower recovery and other complications after surgery.
Blood transfusion is used when blood levels are low, but there has been concern that colorectal cancer patients may have higher rates of complications and cancer recurrence if they’ve had a blood transfusion. Iron is commonly used to treat anaemia, with a full course of treatment being administered intravenously in 15-30 minutes. To date intravenous iron infusion has been used sparingly, with a question remaining whether treating patients before major surgery would reduce the need for blood transfusion.
In this study, a meta-analysis of five randomised controlled trials was conducted by researchers from UCL, focusing on a subset of patients from those trials who had undergone bowel surgery. In these trials, patients were split into two groups, a control group and a group who received iron intravenously prior to surgery.
The analysis showed that patients who had received iron infusion were 33% less likely to require a blood transfusion during or after surgery.
Professor Toby Richards, senior author of the study from UCL Division of Surgery & Interventional Sciences, said: “This is the first time that clinical trials have shown a patient benefit from treatment with an iron infusion before surgery, which has the potential to treat anaemia and reduce the need for blood transfusion. Previous studies had not shown this benefit for all patients undergoing surgery in the NHS, but this analysis identifies a subset of patients undergoing bowel surgery who will see a benefit.”
Professor Neil Smart, colorectal surgeon from the Royal Devon and Exeter Hospital and co-lead of the study, said: "With over 20,000 major colorectal cancer resections per year in the UK, the findings of this study have the potential to improve outcomes for the second most common cause of cancer mortality. In the past, surgeons were uncertain whether the benefits of iron infusion could be realised in the short time frames of cancer care and consequently the uptake of this treatment was limited. Our findings show that improved outcomes can be achieved if iron infusion is given in the period between cancer diagnosis and surgery."
As well as reducing the risk for patients, fewer blood transfusions would be good news at a time when there are blood supply shortages in the UK.
Sue Pavord, Vice President of British Society for Haematology, said: “The recent shortage of blood supply in the UK means it is more important than ever to focus on ways to avoid blood transfusions and their associated risks. This analysis shows a reduction of over one-third in blood transfusions when anaemic patients are treated with intravenous iron before their colorectal surgery. If we could combine this insight with others from the previous PREVENTT study, then hospital readmissions could potentially be cut even more, which would be important for both patients and the NHS.”
Notes to Editors:
For more information, please contact:
Dr Matt Midgley
+44 (0)20 7679 9064
m.midgley@ucl.ac.uk
Publication:
Hans Lederhuber et al. ‘Preoperative intravenous iron and the risk of blood transfusion in colorectal cancer surgery: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials’ will be published in The British Journal of Surgery and is strictly embargoed until 23 November 2023 at 00:01 GMT / 22 November 2023 19:01 ET.
DOI: https://academic.oup.com/bjs/article-lookup/doi/10.1093/bjs/znad320
About UCL – London’s Global University
UCL is a diverse global community of world-class academics, students, industry links, external partners, and alumni. Our powerful collective of individuals and institutions work together to explore new possibilities.
Since 1826, we have championed independent thought by attracting and nurturing the world's best minds. Our community of more than 50,000 students from 150 countries and over 16,000 staff pursues academic excellence, breaks boundaries and makes a positive impact on real world problems.
The Times and Sunday Times University of the Year 2024, we are consistently ranked among the top 10 universities in the world and are one of only a handful of institutions rated as having the strongest academic reputation and the broadest research impact.
We have a progressive and integrated approach to our teaching and research – championing innovation, creativity and cross-disciplinary working. We teach our students how to think, not what to think, and see them as partners, collaborators and contributors.
For almost 200 years, we are proud to have opened higher education to students from a wide range of backgrounds and to change the way we create and share knowledge.
We were the first in England to welcome women to university education and that courageous attitude and disruptive spirit is still alive today. We are UCL.
www.ucl.ac.uk | Follow @uclnews on Twitter | Read news at www.ucl.ac.uk/news/ | Listen to UCL podcasts on SoundCloud | View images on Flickr | Find out what’s on at UCL Mind
END
Iron infusion before bowel surgery reduces need for blood transfusion
2023-11-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The first report on telomere-to-telomere gap-free reference genome of wild blueberry (Vaccinium duclouxii)
2023-11-23
Blueberry, a common Vaccinium species with small-sized berries, is known for its delicious taste, balanced sweetness and acidity, and rich nutritional content. It is abundant in various vitamins and antioxidants. However, the limited genetic resources for cultivated blueberries have significantly hindered their development and utilization. Therefore, utilizing wild blueberries' genetic resources for breeding is paramount to enhancing the resilience and quality of cultivated varieties.
Vaccinium duclouxii, native to the southwestern region of China, is an endemic wild blueberry ...
Chinese-Russian cooperation has strengthened significantly in the past 30 years, analysis shows
2023-11-22
Chinese and Russian cooperation has grown significantly in the past three decades thanks to joint work on energy trade, politics and official visits, analysis shows.
There was a ‘limited’ Sino–Russian cooperation intensity in 1992–1995, which grew from then until 2007 and then rose. The bilateral relationship grew progressively, with no exponential growth or peaks, according to the study.
There were no or dramatic changes following Russia’s 2014 annexation of Crimea.
The ...
Researchers develop new method for prenatal genetic testing
2023-11-22
A team of investigators from Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), Brigham and Women’s Hospital (BWH), and the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard have developed a non-invasive genetic test that can screen the blood of pregnant individuals to survey all genes for fetal DNA sequence variants. The team evaluated the test by examining blood samples from 51 pregnant persons, finding that the test was able to capture variants that were inherited from the mother as well as new variants that were not present in the mother and associated with prenatal diagnoses. ...
Genetic predisposition to early breast cancer in Kazakh women
2023-11-22
“Our study may reveal previously uncharacterized population-specific variants that may increase the risk of BC in the Kazakh population.”
BUFFALO, NY- November 22, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on October 4, 2023, entitled, “Determination of genetic predisposition to early breast cancer in women of Kazakh ethnicity.”
Breast cancer (BC) is the most common type of cancer among women in Kazakhstan. To date, little data are available on the spectrum of genetic variation in Kazakh women with BC.
In this new study, researchers Gulnur Zhunussova, Nazgul Omarbayeva, ...
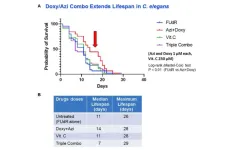
Mitochondria-targeting antibiotics extend lifespan in C. elegans
2023-11-22
“Our ultimate goal is to find existing FDA-approved drugs and dietary supplements that can not only increase lifespan but also improve healthspan.”
BUFFALO, NY- November 22, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 21, entitled, “Antibiotics that target mitochondria extend lifespan in C. elegans.”
Aging is a continuous degenerative process caused by a progressive decline of cell and tissue functions in an organism. It is induced by the accumulation of damage that affects normal cellular processes, ...
Adding a few servings of whole grains linked to slower memory decline in Black people
2023-11-22
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, NOVEMBER 22, 2022
MINNEAPOLIS – Black people who eat more foods with whole grains, including some breads and cereals, quinoa, and popcorn, may have a slower rate of memory decline compared to Black people who eat fewer whole grain foods, according to a study published in the November 22, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The researchers did not see a similar trend in white participants.
The study does not prove that eating more whole grains slows memory decline; it only shows an association.
The study found that among Black ...
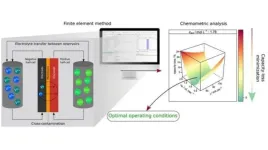
Researchers obtain promising results against capacity loss in vanadium batteries
2023-11-22
An article by researchers at the Center for Development of Functional Materials (CDMF) in Brazil describes a successful strategy to mitigate charge capacity loss in vanadium redox flow batteries, which are used by electric power utilities among other industries and can accumulate large amounts of energy. The article is published in the Chemical Engineering Journal.
CDMF is a Research, Innovation and Dissemination Center (RIDC) funded by FAPESP and hosted by the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar) in São Paulo state.
The study involved computer ...
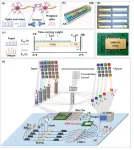
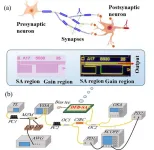
Photonic integrated neuro-synaptic core for convolutional spiking neural network
2023-11-22
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances, 10.29026/oea.2023.230140 discusses photonic integrated neuro-synaptic core for convolutional spiking neural network.
Brain science and brain-like intelligence are the cutting-edge science and technology that countries all over the world compete to seize. The rapid rise and vigorous development of emerging fields such as artificial intelligence, 5G/6G, big data, autonomous driving, and the Internet of Things has led to the explosive growth of global data. Due to the memory wall effect, the conventional von Neumann architecture performs low energy efficiency. Electronic ...
Multi-synaptic photonic SNN based on a DFB-SA chip
2023-11-22
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Science; DOI 10.29026/oes.2023.230021 overviews multi-synaptic photonic SNN based on a DFB-SA chip.
Compared with traditional artificial neural networks, spiking neural networks (SNN) are more biologically authentic, more powerful, and less power-consuming due to their spatiotemporal coding and event-driven characteristics. In recent years, optical computing has been widely considered as a hardware acceleration platform, where nonlinear computing poses a challenge. Photonic SNN provides an ultra-fast and energy-efficient platform for high-performance ...
Optical trapping of optical nanoparticles: fundamentals and applications
2023-11-22
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Science; DOI 10.29026/oes.2023.230019 overviews optical trapping of optical nanoparticles.
This article reviews the fundamentals and applications of optically trapped optical nanoparticles. Optical nanoparticles are nowadays one of the key elements of photonics. They do not only allow optical imaging of a plethora of systems (from cells to microelectronics), but also behave as highly sensitive remote sensors. In recent years, it has been demonstrated the success of optical tweezers in isolating and manipulating individual optical nanoparticles. This has opened the door to high resolution single particle scanning ...