(Press-News.org)
“Our ultimate goal is to find existing FDA-approved drugs and dietary supplements that can not only increase lifespan but also improve healthspan.”
BUFFALO, NY- November 22, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 21, entitled, “Antibiotics that target mitochondria extend lifespan in C. elegans.”
Aging is a continuous degenerative process caused by a progressive decline of cell and tissue functions in an organism. It is induced by the accumulation of damage that affects normal cellular processes, ultimately leading to cell death. It has been speculated for many years that mitochondria play a key role in the aging process.
In this new study, researchers Gloria Bonuccelli, Darren R. Brooks, Sally Shepherd, Federica Sotgia, and Michael P. Lisanti from the University of Salford aimed to characterize the implications of mitochondria in aging using Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) as an organismal model. The C. elegans were treated with a panel of mitochondrial inhibitors and assessed for survival.
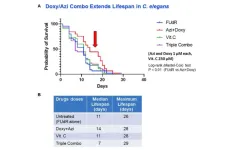
“In our study, we assessed survival by evaluating worm lifespan, and we assessed aging markers by evaluating the pharyngeal muscle contraction, the accumulation of lipofuscin pigment and ATP levels.”
Their results show that treatment of worms with either doxycycline, azithromycin (inhibitors of the small and the large mitochondrial ribosomes, respectively), or a combination of both, significantly extended median lifespan of C. elegans, enhanced their pharyngeal pumping rate, reduced their lipofuscin content and their energy consumption (ATP levels), as compared to control untreated worms, suggesting an aging-abrogating effect for these drugs. Similarly, DPI, an inhibitor of mitochondrial complex I and II, was capable of prolonging the median lifespan of treated worms. On the other hand, subjecting worms to vitamin C, a pro-oxidant, failed to extend C. elegans lifespan and upregulated its energy consumption, revealing an increase in ATP level.
“Therefore, our longevity study reveals that mitochondrial inhibitors (i.e., mitochondria-targeting antibiotics) could abrogate aging and extend lifespan in C. elegans.”
Read the full study: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.205229
Corresponding Authors: Michael P. Lisanti, Federica Sotgia
Corresponding Emails: m.p.lisanti@salford.ac.uk, f.sotgia@salford.ac.uk
Keywords: C. elegans, aging, lifespan, lipofuscin, antibiotics, mitochondria, metabolism, DPI
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article: https://aging.altmetric.com/details/email_updates?id=10.18632%2Faging.https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.205229
About Aging:
Launched in 2009, Aging publishes papers of general interest and biological significance in all fields of aging research and age-related diseases, including cancer—and now, with a special focus on COVID-19 vulnerability as an age-dependent syndrome. Topics in Aging go beyond traditional gerontology, including, but not limited to, cellular and molecular biology, human age-related diseases, pathology in model organisms, signal transduction pathways (e.g., p53, sirtuins, and PI-3K/AKT/mTOR, among others), and approaches to modulating these signaling pathways.
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
SoundCloud
Facebook
X, formerly known as Twitter
Instagram
YouTube
LabTube
LinkedIn
Reddit
Pinterest
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker Str., Suite 1B
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
###
END
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, NOVEMBER 22, 2022
MINNEAPOLIS – Black people who eat more foods with whole grains, including some breads and cereals, quinoa, and popcorn, may have a slower rate of memory decline compared to Black people who eat fewer whole grain foods, according to a study published in the November 22, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The researchers did not see a similar trend in white participants.
The study does not prove that eating more whole grains slows memory decline; it only shows an association.
The study found that among Black ...
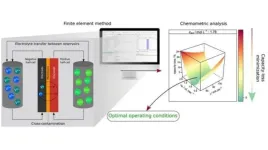
An article by researchers at the Center for Development of Functional Materials (CDMF) in Brazil describes a successful strategy to mitigate charge capacity loss in vanadium redox flow batteries, which are used by electric power utilities among other industries and can accumulate large amounts of energy. The article is published in the Chemical Engineering Journal.
CDMF is a Research, Innovation and Dissemination Center (RIDC) funded by FAPESP and hosted by the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar) in São Paulo state.
The study involved computer ...
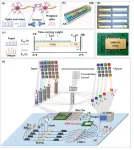
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances, 10.29026/oea.2023.230140 discusses photonic integrated neuro-synaptic core for convolutional spiking neural network.
Brain science and brain-like intelligence are the cutting-edge science and technology that countries all over the world compete to seize. The rapid rise and vigorous development of emerging fields such as artificial intelligence, 5G/6G, big data, autonomous driving, and the Internet of Things has led to the explosive growth of global data. Due to the memory wall effect, the conventional von Neumann architecture performs low energy efficiency. Electronic ...
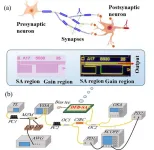
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Science; DOI 10.29026/oes.2023.230021 overviews multi-synaptic photonic SNN based on a DFB-SA chip.
Compared with traditional artificial neural networks, spiking neural networks (SNN) are more biologically authentic, more powerful, and less power-consuming due to their spatiotemporal coding and event-driven characteristics. In recent years, optical computing has been widely considered as a hardware acceleration platform, where nonlinear computing poses a challenge. Photonic SNN provides an ultra-fast and energy-efficient platform for high-performance ...
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Science; DOI 10.29026/oes.2023.230019 overviews optical trapping of optical nanoparticles.
This article reviews the fundamentals and applications of optically trapped optical nanoparticles. Optical nanoparticles are nowadays one of the key elements of photonics. They do not only allow optical imaging of a plethora of systems (from cells to microelectronics), but also behave as highly sensitive remote sensors. In recent years, it has been demonstrated the success of optical tweezers in isolating and manipulating individual optical nanoparticles. This has opened the door to high resolution single particle scanning ...
The Iron Age site of Casas del Turuñuelo was used repeatedly for ritualized animal sacrifice, according to a multidisciplinary study published November 22, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Mª Pilar Iborra Eres of the Institut Valencià de Conservació, Restauració i Investigació, Spain, Sebastián Celestino Pérez of Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas, Spain, and their colleagues.
Archaeological sites with evidence of major animal sacrifices are rarely ...
Modern hippos first dispersed in Europe during the Middle Pleistocene, according to a study published November 22, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Beniamino Mecozzi of the Sapienza University of Rome and colleagues.
Modern hippos, Hippopotamus amphibius, arose from African ancestors during the Quaternary, a time when hippos were widespread in Europe. However, the details of the modern species’ origin and dispersal into Europe are unclear and highly debated. In this study, Mecozzi and colleagues provide new insights via analysis of a fossil hippo skull from the study area of Tor di Quinto in Rome.
The skull of Tor di Quinto, currently housed at the ...
Status threat - the concern that outsiders will undermine your group's status - is associated with increased age, conservatism, conspiracy mentality, and paranoia, in study of 300 US adults
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0293930
Article Title: Conspiracy mentality, subclinical paranoia, and political conservatism are associated with perceived status threat
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
Transplanting gut microbes from an obesity-resistant shrew can improve microbiome diversity and decrease the weight of obese mice
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0293213
Article Title: Gut microbiota of Suncus murinus, a naturally obesity-resistant animal, improves the ecological diversity of the gut microbiota in high-fat-diet-induced obese mice
Author Countries: Japan, China
Funding: This work (PONE-D-23-21281) was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the ...
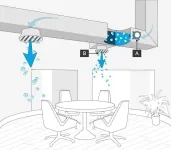
Airborne virus infectivity can be reduced by up to 99.98% by commercially available NPBI-based air purifiers, per experiment using real-world concentrations of COVID-19 strains, flu and RSV viruses
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0293504
Article Title: Bipolar ionization rapidly inactivates real-world, airborne concentrations of infective respiratory viruses
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. All research and 3rd party laboratory testing was funded entirely by GPS Air. Edward Sobek is an employee of GPS Air ...