(Press-News.org) Parents who send their children to child care can breathe a little easier – research published in JAMA Network Open from experts at Michigan Medicine, the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, and UPMC Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh shows that children in daycare were not significant spreaders of COVID-19.
The study found that transmission rates of SARS-CoV-2 within child care centers was only about 2% to 3%, suggesting that children and caregivers were not spreading COVID at significant rates to others in the centers.
The study also found low rates of infection among households that had kids attending child care centers, as only 17% of household infections resulted from children who caught COVID at their centers.
Overall, the study found that only 1 in 20 symptomatic children attending child care centers tested positive for the virus.
In contrast, once someone in a household tested positive for the coronavirus, transmission to other household members was high, at 50% for children and 67% for adults.
Young children frequently contracted COVID-19 from individuals outside their child care center.
Additional safety measures
Despite the low rates of transmission in child care centers, experts still highly recommend that families get themselves and their children vaccinated against COVID-19, as additional research shows that vaccines are a safe and effective way of preventing against serious infection.
“We strongly recommend the COVID-19 vaccine for young children to disrupt the high rates of transmission that we saw occur in households that can lead to missed work and school,” said Andrew Hashikawa, M.D., clinical professor of emergency medicine.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention currently advises that kids with congestion, runny noses or other respiratory symptoms get tested for COVID and stay home if positive.
The findings suggest that these recommendations could be revised to align with those of other serious respiratory viruses, like influenza and respiratory syncytial virus, commonly known as RSV.
"While it's crucial to remain vigilant in our efforts to manage the spread of SARS-CoV-2, it seems that prioritizing testing and extended exclusion periods for children in child care centers may not be the most practical approach, as it can place undue financial burden on families from frequent testing, result in missed work, and hinder children's critical access to quality care and education," said Hashikawa.
This study was supported by Merck Investigator Studies Program grant 60418, the Henry L. Hillman Foundation and Flu Lab.
Paper cited: “Incidence and Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in US Child Care Centers After COVID-19 Vaccines,” JAMA Network Open. DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.39355
END
Child care centers aren’t a likely source of COVID-19 spread, study says
Research sheds light on COVID in these child care settings
2023-11-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Next generation semiconductors: Diamond device shows highest breakdown voltage
2023-11-27
To reach the world’s goal of carbon neutrality by 2050, there must be a fundamental change in electronic materials to create a more reliable and resilient electricity grid. A diamond might be a girl’s best friend, but it might also be the solution needed to sustain the electrification of society needed to reach carbon neutrality in the next 30 years. Researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have developed a semiconductor device made using diamond, that has the highest breakdown voltage and lowest leakage current compared to previously reported diamond devices. Such a device will enable more efficient technologies needed as the world transitions to renewable energies.
It ...
Review article shows key role of Brazil in research on sugarcane for bioenergy
2023-11-27
Publications on sugarcane have increased exponentially since 2006 worldwide, and Brazil has had more articles published on the topic than any other country in the period, according to a review in BioEnergy Research.
The number of articles on the subject averaged about five per year between 1999 and 2006 but had reached 327 by 2021. Brazil has twice as many articles on sugarcane as the United States, which ranks first in the world for scientific publications in general. Brazil is also ahead of Australia, China and India, which are also major sugarcane growers.
According to the authors of the review, who are affiliated with the Laboratory of Plant Physiological Ecology (LAFIECO) ...
Cellular postal service delivers messages from non-human cells, too
2023-11-27
Messenger bubbles produced by human cells can pick up bacterial products and deliver them to other cells, University of Connecticut researchers report in the Nov. 16 issue of Nature Cell Biology. The discovery may explain a key mechanism by which bacteria, whether friendly or infectious, affect our health.
Extra-cellular vesicles (EVs) are like a postal service for our cells. Cells produce the EVs, tiny bubbles with a water-resistant shell made of fatty substances called lipids, and send them into the bloodstream. When another cell comes across an EV, it takes it inside itself ...
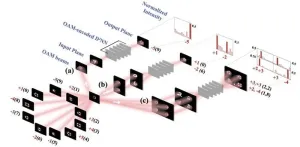
Orbital-angular-momentum-encoded diffractive networks for object classification tasks
2023-11-27
Deep learning has revolutionized the way we perceive and utilize data. However, as datasets grow and computational demands increase, we need more efficient ways to handle, store, and process data. In this regard, optical computing is seen as the next frontier of computing technology. Rather than using electronic signals, optical computing relies on the properties of light waves, such as wavelength and polarization, to store and process data.
Diffractive deep neural networks (D2NN) utilize various properties of light waves to perform tasks like image and object recognition. Such networks consist of two-dimensional pixel arrays as diffractive layers. Each pixel serves as an adjustable ...
Gig workers saw greater financial hardship during COVID-19 compared to other workers
2023-11-27
Many gig workers experienced financial hardships during the COVID-19 pandemic, including food insecurity and trouble paying bills, according to a recent study published in Work and Occupations.
“In a nutshell, our study shows gig workers were harmed more by the COVID-19 pandemic than any other workers,” said Dr. Mathieu Despard, a co-author on the paper and faculty member in UNC Greensboro’s Department of Social Work.
Despard – who collaborated closely with first author Daniel Auguste ...
CU Anschutz scientists create patch that may successfully treat congenital heart defects
2023-11-27
AURORA, Colo. (Nov. 27, 2023) – Using laboratory engineered tissue, scientists at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus have created a full thickness, biodegradable patch that holds the promise of correcting congenital heart defects in infants, limiting invasive surgeries and outlasting current patches.
The findings were published this week in the journal Materials Today.
“The ultimate goal is to make lab-grown heart tissue from a patient’s own cells that can be used to restructure the heart to correct for heart defects,” said the ...
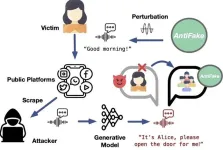
Defending your voice against deepfakes
2023-11-27
Recent advances in generative artificial intelligence have spurred developments in realistic speech synthesis. While this technology has the potential to improve lives through personalized voice assistants and accessibility-enhancing communication tools, it also has led to the emergence of deepfakes, in which synthesized speech can be misused to deceive humans and machines for nefarious purposes.
In response to this evolving threat, Ning Zhang, an assistant professor of computer science and engineering at the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University ...
Revolutionizing cancer treatment through programmable bacteria
2023-11-27
What if a single one-dollar dose could cure cancer?
A multi-university team of researchers, supported by federal funding, is developing a highly efficient bacterial therapeutic to target cancer more precisely to make treatment safer through a single $1 dose.
Traditionally, cancer therapies have been limited in their efficacy in treating patients. Some, like radiation and chemotherapy, cause harmful side effects, while others tend to result in low patient responsiveness, not to mention the cost it takes to receive treatment. Findings from the American Cancer Society Cancer Action Network recorded ...
One protein is key to the spread of lung cancer. Now, a new study has found a way to stop it
2023-11-27
A new study by Tulane University has uncovered a previously unknown molecular pathway that could be instrumental to halting lung cancer in its tracks.
Lung cancer is one of the most common cancers and the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the world. The research, published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, could lead to the development of a new anti-cancer drug and more personalized lung cancer treatment, said senior study author Dr. Hua Lu, the Reynolds and Ryan Families Chair in Translational Cancer at the Tulane University School of Medicine.
The study found ...
Study: Spike in premature births caused by COVID, halted by vaccines
2023-11-27
MADISON, Wis. — COVID-19 caused an alarming surge in premature births, but vaccines were key to returning the early birth rate to pre-pandemic levels, according to a new analysis of California birth records.
“The effect of maternal COVID infection from the onset of the pandemic into 2023 is large, increasing the risk of preterm births over that time by 1.2 percentage points,” says Jenna Nobles, a University of Wisconsin–Madison sociology professor. “To move the needle on preterm birth that much is akin to a disastrous ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
[Press-News.org] Child care centers aren’t a likely source of COVID-19 spread, study saysResearch sheds light on COVID in these child care settings