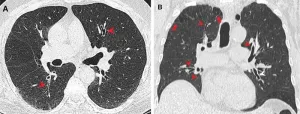
(Press-News.org) CHICAGO – Smoking marijuana in combination with cigarettes may lead to increased damage of the lung’s air sacs, according to research being presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
It is commonly believed that smoking marijuana is not harmful to the lungs. There is an abundance of established research that identifies the harms of cigarette smoking. In contrast, very little is known about the effects of marijuana smoking, and even less research has been done on the combined effects of smoking marijuana and cigarettes.
“Marijuana is the most widely used illicit psychoactive substance in the world, and its use has increased in Canada since the legalization of non-medical marijuana in 2018,” said study co-author Jessie Kang, M.D., cardiothoracic radiologist and assistant professor in the Department of Diagnostic Radiology at Dalhousie University in Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada. “Currently, not much research exists on the effects of marijuana smoking on the lungs.”
To determine the effects of marijuana and cigarette smoking, researchers for the multicenter prospective study examined the chest CT images of four patient groups: non-smokers, cigarette smokers, marijuana smokers, and combined marijuana and cigarette smokers. Marijuana smokers included in the study had smoked marijuana at least four times a month for two years. Patients who ingested marijuana via edibles or oral drops were excluded from the study.
The researchers found that people who combined marijuana and cigarettes were 12 times more likely to have centrilobular emphysema than non-smokers. Centrilobular emphysema is a type of pulmonary emphysema where the air sacs within the lungs are damaged. This can lead to breathing difficulties and other serious respiratory symptoms.
“The mean number of marijuana smoking years was less than compared to cigarette smokers and combined marijuana and cigarette smokers,” Dr. Kang said. “However, marijuana that is smoked is often unfiltered, which can potentially lead to more damaging particles entering the airways and lungs.”
Combined marijuana and cigarette smokers were three to four times more likely to have airway wall thickening, which can lead to infections, scarring and further airway damage. Association with marijuana only and smoking only with bronchial wall thickening was not as significant. Similar results were seen with centrilobular and paraseptal emphysema, suggesting that the combination of cigarette and marijuana smoking may have a synergistic role on the lungs and airways.
“With our study, we show that there are physical effects of marijuana smoking on the lungs and that cigarette smoking and marijuana smoking may have a combined damaging effect on the lungs,” Dr. Kang said.
According to Dr. Kang, further research is needed to identify the long-term effects of smoking marijuana.
“There is a common public misconception that marijuana smoking is not harmful,” Dr. Kang said. “More research needs to be done in this area, so the public can make an informed decision on their recreational usage of marijuana.”
Co-authors are Sebastian Karpinski, B.Sc., Paul Sathiadoss, M.B.B.S., Eric Lam, M.Sc., Eric Hutfluss, M.D., O. Osorio, M.D., D. A. Hashem, M.D., Matthew D. F. McInnes, M.D., and Giselle Y. Revah, M.D.
###
Note: Copies of RSNA 2023 news releases and electronic images will be available online at RSNA.org/press23.
RSNA is an association of radiologists, radiation oncologists, medical physicists and related scientists promoting excellence in patient care and health care delivery through education, research and technologic innovation. The Society is based in Oak Brook, Illinois. (RSNA.org)
Editor’s note: The data in these releases may differ from those in the published abstract and those actually presented at the meeting, as researchers continue to update their data right up until the meeting. To ensure you are using the most up-to-date information, please call the RSNA Newsroom at 1-312-791-6610.
For patient-friendly information on chest CT, visit RadiologyInfo.org.
END
Essential features of the cortex, an important part of the human brain and its development, are more accurately captured in organoids generated by researchers of the Princess Máxima Center for pediatric oncology and the Hubrecht Institute. The scientists developed mini-organs with features like cell organization, stem cell expansion and cell identity that more closely mimic the real-life situation. These novel organoids can be used as a basis to model pediatric brain tumors.
Multiple childhood brain tumors, like cortical gliomas, arise from the cortex, the outer layer of the largest part of the brain and the brain’s ...
Concerted efforts and commitments are needed to solve the complex trade-offs involved in reducing the impact of aviation on the climate, according to new research.
Non-CO2 emissions from aircraft - largely of nitrogen oxides, soot and water vapour – are known to add to global warming effects alongside the aviation sector’s other CO2 emissions.
Soot triggers the formation of contrails and ‘contrail cirrus’, which are line-shaped clouds produced by aircraft engine exhaust. This causes an increase in high clouds that can warm the Earth’s atmosphere.
In a comprehensive assessment ...
Statement Highlights:
Intensive care management of cardiac arrest survivors is important and influences survival and neurological outcomes.
This collaborative statement from a diverse group with expertise in post-cardiac arrest care identifies current knowledge gaps and provides guidance about care in topics where research and existing guidelines were not able to provide solid evidence.
This statement calls for more research into neurological, cardiac, pulmonary, hematologic, infectious, gastrointestinal, endocrine and general critical care management after cardiac arrest.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT / 5 a.m. ET Tuesday, ...
The Supply Chain Intelligence Institute Austria (ASCII) advocates for a revision of the EU Corporate Sustainable Due Diligence Directive (CS3D). The proposed amendments focus on direct monitoring of suppliers – instead of bilateral supply links – and the introduction of negative and positive lists to streamline due diligence processes, improving effectiveness and reducing costs for EU importers.
The Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CS3D), currently under negotiation by EU institutions with a potential adoption in 2024, aligns with international norms to cover both human rights and environmental ...
IOP Publishing (IOPP) is launching Sustainability Science and Technology, an interdisciplinary, open access journal dedicated to advancing sustainability through cutting-edge research in science, technology, and engineering. The new journal will bring together researchers from diverse disciplines across engineering, chemistry, physics, materials science and environmental science to address global challenges and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Sustainability Science and Technology sets itself apart by focussing on the critical importance of sustainable impact. ...
Tetrodotoxin, the neurotoxin that makes a blue-ringed octopus deadly, also protects Taricha newts — but we don’t understand how they produce it, or what purposes it serves for them. A first step to answering these questions is understanding whether different levels appear in males and females. In sexually reproducing animals, dimorphic traits such as color or canine tooth size can be key for survival and reproductive fitness. Investigating whether toxin production is a sexually dimorphic trait in newts gets us closer to understanding it.
“It had long been considered that newts’ ...
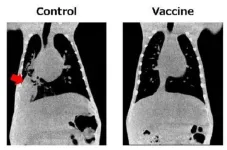
Osaka, Japan – The global impact of the coronavirus pandemic has ignited a renewed focus on emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases. Researchers at Osaka Metropolitan University are making great strides in combating pneumococcal pneumonia, one of the leading causes of respiratory deaths worldwide.
Despite the existence of vaccines against pneumococcal infections such as otitis media, sinusitis, and meningitis, the prevalence of pneumococcal pneumonia remains high. Currently, around 100 new serotypes of Streptococcus pneumoniae have been identified, and ...
Image
A new kind of "wire" for moving excitons, developed at the University of Michigan, could help enable a new class of devices, perhaps including room temperature quantum computers.
What's more, the team observed a dramatic violation of Einstein's relation, used to describe how particles spread out in space, and leveraged it to move excitons in much smaller packages than previously possible.
"Nature uses excitons in photosynthesis. We use excitons in OLED displays and some LEDs and solar cells," said Parag Deotare, ...
Machine learning is now helping researchers analyze the makeup of unfamiliar cells, which could lead to more personalized medicine in the treatment of cancer and other serious diseases.
Researchers at the University of Waterloo developed GraphNovo, a new program that provides a more accurate understanding of the peptide sequences in cells. Peptides are chains of amino acids within cells and are building blocks as important and unique as DNA or RNA.
In a healthy person, the immune system can correctly identify the peptides of irregular or foreign cells, such as cancer cells or harmful bacteria, and then target those cells for destruction. For people whose immune system is ...
Adaptive optics (AO) is a technique used for real-time correction of phase aberrations by employing feedback to adjust the optical system. Polarization aberrations represent another significant type of distortion that can impact optical systems. Various factors, such as stressed optical elements, Fresnel effects, and polarizing effects in materials or biological tissues, can induce polarization aberrations. These aberrations affect both system resolution and the accuracy of vector information.
Vectorial aberrations result from the ...