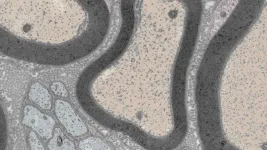
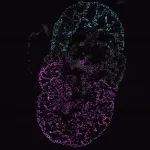
(Press-News.org) CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Researchers report that they have developed a new composite material designed to change behaviors depending on temperature in order to perform specific tasks. These materials are poised to be part of the next generation of autonomous robotics that will interact with the environment.
The new study conducted by University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign civil and environmental engineering professor Shelly Zhang and graduate student Weichen Li, in collaboration with professor Tian Chen and graduate student Yue Wang from the University of Houston, uses computer algorithms, two distinct polymers and 3D printing to reverse engineer a material that expands and contracts in response to temperature change with or without human intervention.
The study findings are reported in the journal Science Advances.
“Creating a material or device that will respond in specific ways depending on its environment is very challenging to conceptualize using human intuition alone – there are just so many design possibilities out there,” Zhang said. “So, instead, we decided to work with a computer algorithm to help us determine the best combination of materials and geometry.”
The team first used computer modeling to conceptualize a two-polymer composite that can behave differently under various temperatures based on user input or autonomous sensing.
“For this study, we developed a material that can behave like soft rubber in low temperatures and as a stiff plastic in high temperatures,” Zhang said.
Once fabricated into a tangible device, the team tested the new composite material’s ability to respond to temperature changes to perform a simple task – switch on LED lights.
Click here for a video explanation of this research.
“Our study demonstrates that it is possible to engineer a material with intelligent temperature sensing capabilities, and we envision this being very useful in robotics,” Zhang said. “For example, if a robot’s carrying capacity needs to change when the temperature changes, the material will ‘know’ to adapt its physical behavior to stop or perform a different task.”
Zhang said that one of the hallmarks of the study is the optimization process that helps the researchers interpolate the distribution and geometries of the two different polymer materials needed.
“Our next goal is to use this technique to add another level of complexity to a material’s programmed or autonomous behavior, such as the ability to sense the velocity of some sort of impact from another object,” she said. “This will be critical for robotics materials to know how to respond to various hazards in the field.”
The National Science Foundation supported this research.
Editor’s notes:
To reach Shelly Zhang, call 217-300-1815; email zhangxs@illinois.edu.
The paper “Algorithmic encoding of adaptive responses in temperature-sensing
multimaterial architectures” is available online. DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adk0620
END
Researchers engineer a material that can perform different tasks depending on temperature
2023-11-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
MU fish ecologist’s research indicates need to conserve iconic migratory snook in Mexico
2023-11-28
Allison Pease grew up fascinated by river fish, spending countless summers in a mask beneath the surface of Texas creeks. Now a fish ecologist in the College of Agriculture, Food and Natural Resources at the University of Missouri, Pease is studying the common snook — an iconic game fish that has filled an important cultural, ecological and economic niche in Mexico for centuries. Her latest study focuses on this species’ migration patterns and the effects of proposed hydrodams on their population in southern Mexico.
For the study, Pease traveled to the states of Tabasco and Chiapas, where she investigated the snook’s almost ...
Two biomedical sciences researchers named among world’s most highly cited scientists for 2023
2023-11-28
ATLANTA — Two leading researchers in the Institute for Biomedical Sciences at Georgia State University have been ranked in the top 1 percent worldwide by citations for their field and publication year in the Web of Science database, according to the Highly Cited Researchers 2023 list by Clarivate.
The annual Highly Cited Researchers list has identified global research scientists and social scientists who have demonstrated significant and broad influence in their fields of research since 2001.
The ...
NYU Abu Dhabi researchers develop first-of-its-kind woven material made entirely from flexible organic crystals
2023-11-28
Fast facts:
Weaving is one of the oldest crafts known to humankind, with the earliest textiles dating back to about 5,000 years ago.
Organic crystals, long thought to be stiff and brittle, are now known to have extraordinary elastic properties, revealing an unexplored new direction in materials science.
Abu Dhabi, UAE, November 28, 2023: Applying simple, ancient weaving techniques to newly recognized properties of organic crystals, researchers with the Smart Materials Lab (SML) and the Center for Smart Engineering Materials (CSEM) at NYU Abu Dhabi (NYUAD) have, for the first time, developed a unique form of woven “textile.” These new fabric ...
St. Jude revealed functional targets of oncogenic HOXA9 in high-risk pediatric leukemia
2023-11-28
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. – November 28, 2023) Scientists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital comprehensively identified genes directly regulated by a protein associated with high-risk pediatric leukemias. High-risk leukemias, particularly MLL-rearranged (MLL-r) leukemia, often overexpress the homeodomain transcription factor HOXA9 protein, which cannot currently be targeted with drugs. This study provides a foundation for revealing the HOXA9 regulation network and finding novel drug targets downstream of HOXA9 that can form the basis of new treatments. The findings were published today in Nature Communications.
HOXA9 ...
Human rights are a low priority for many national climate change adaptation policies, new Concordia research finds
2023-11-28
The link between human rights and climate change adaptation policy has not been a major source of discussion in national policies, according to a new Concordia-led study. Moreover, the researchers say the topic should play a bigger role in the upcoming COP28 conference, opening this week in Dubai.
The paper was published in the journal Climate Policy. Assistant professor in Concordia’s Department of Geography, Planning and Environment Alexandra Lesnikowski co-authored the study with researchers from McGill University’s Faculty ...
Want school kids to eat more vegetables? Don’t forget about the power of potatoes on the plate
2023-11-28
A new study published in Nutrients illustrates how potatoes may play a beneficial role in encouraging school aged children to eat more vegetables. The Dietary Guidelines for Americans currently recommends children ages 3-18 consume between 2.5-3 cups of vegetables per day to meet their total vegetable goals. Yet, the average school-age child eats only about 1 cup daily. “That’s why we wanted to learn more about how school meal offerings may influence kids’ eating behavior and possibly encourage greater vegetable consumption,” explains principal ...
Repairing nerve cells after injury and in chronic disease
2023-11-28
LA JOLLA (November 28, 2023)—Each year in the United States there are more than 3 million cases of peripheral neuropathy, wherein nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord are damaged and cause pain and loss of feeling in the affected areas. Peripheral neuropathy can occur from diabetes, injury, genetically inherited disease, infection, and more. Salk scientists have now uncovered in mice a mechanism for repairing damaged nerves during peripheral neuropathy. They discovered that the protein Mitf helps turn on the repair function of specialized nervous system Schwann cells.
The findings, published in Cell Reports ...
First multi-chamber heart organoids unravel human heart development and disease
2023-11-28
Heart disease kills 18 million people each year, but the development of new therapies faces a bottleneck: no physiological model of the entire human heart exists – so far. A new multi-chamber organoid that mirrors the heart’s intricate structure enables scientists to advance screening platforms for drug development, toxicology studies, and understanding heart development. The new findings, using heart organoid models developed by Sasha Mendjan’s group at the Institute of Molecular ...
Race and ethnicity and emergency department discharge against medical advice
2023-11-28
About The Study: The findings of this study of 33.1 million visits to 989 U.S. hospitals suggest that Black and Hispanic patients are more likely to receive care in hospitals with higher overall discharge against medical advice (DAMA) rates, suggesting interventions should address medical segregation. Structural racism may contribute to emergency department DAMA disparities via unequal allocation of health care resources in hospitals that disproportionately treat racial and ethnic minoritized groups. Monitoring variation in DAMA by race and ethnicity and hospital suggests ...
Strategies to increase cervical cancer screening with mailed HPV self-sampling kits
2023-11-28
About The Study: Direct-mail human papillomavirus (HPV) self-sampling increased cervical cancer screening by more than 14% in individuals who were due or overdue for cervical cancer screening in this randomized clinical trial of 31,000 individuals. The opt-in approach minimally increased screening. To increase screening adherence, systems implementing HPV self-sampling should prioritize direct-mail outreach for individuals who are due or overdue for screening. For individuals with unknown screening history, ...