(Press-News.org)
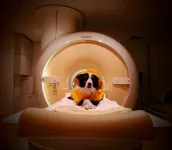
Dogs’ food preferences are mirrored in their brain activity, particularly within their caudate nuclei -a brain region associated with reward processing, a new study combining behavioural and neuroimaging data by researchers from the Department of Ethology, Eötvös Loránd University (Hungary) and Symrise Pet Food (France) finds. The study, which seamlessly blends behavioral observations with advanced neuroimaging techniques, offers novel insights into the influence of food quality on dogs' motivation. This work has been published in Scientific Reports.
Similar to people, when it comes to food, some dogs are pickier, while others are more easygoing. However, even food that may not be the tastiest is still motivating. Through two experiments, this study tested the influence of food quality on dogs' motivation to solve a problem, as well as their corresponding brain representations.
In the first experiment, a cohort of twenty family dogs was trained to unwrap a box. Subsequently, these dogs were taught to associate specific tones with two distinct food types: smoked ham, a highly rewarding treat, and fiber cookies, a less rewarding option. Finally, dogs unwrapped a box while one of the sounds played, and we used the unwrapping time as a measure of their motivation to obtain the associated food. The results showed that the dogs unwrapped the box quicker when the sound associated with the higher quality food, the smoked ham, was played.
VIDEOABSTRACT: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UgMtJszHSBg
The second experiment involved another group of twenty family dogs, which were trained to remain still in a brain scanner. Initially, a scanning session exposed the dogs to both sounds, which held no meaning at this stage. Following this, the dogs participated in the wrapped box experiment. Finally, the dogs underwent another scanning session during which they listened to the sounds again, but this time, each sound had an association with either smoked ham or fiber cookies.
The focus of the brain analysis centered on observing changes in the caudate nucleus, a brain region linked to reward processing across species. Compared to the first session, the caudate nucleus exhibited a heightened response in the second session, responding more strongly to both sounds. Remarkably, it displayed an even more pronounced response to the sound associated with the highly rewarding smoked ham. "While prior research has primarily focused on how the dog brain responds to rewards versus non-rewards, our study takes a step further, delving into the representation of two food rewards varying in quality. Our findings highlight that the caudate nuclei not merely process rewards, but also distinguish between rewards based on their quality." — explains Dorottya Ujfalussy, senior author of the study.
Of course, not all showed the same performance. The greater the discrepancy in the speed at which dogs unwrapped the two boxes, the more discernible their brain response patterns became for the two sounds in their right caudate nucleus. "It is exciting to be able to 'see' how dogs represent different foods in their brains and observe how the quality of the food influences their motivation. We were surprised to discover a distinct positive correlation between the behavior of the dogs and their brain representations. The direction of this relationship still intrigues us; based on our data, we cannot determine whether a more distinct brain representation of both sounds enables a better behavioral performance or if it operates in the reverse. It’s likely that this process is not solely unidirectional." — says Laura V. Cuaya, first author of the study.
END
Four in five primary caregivers of nine-month-old babies reported cuddling, talking and playing with their little one several times a day, in England's first national long-term study of babies in over two decades, led by UCL (University College London).
More than half engaged in physical or turn-taking play, singing, pretend games and noisy play with their babies several times a day – activities which were linked to improved early language development. Around three quarters showed their babies picture ...
The increased legalization of cannabis over the past several years can potentially increase its co-use with alcohol. Concerningly, very few studies have looked at the effects of these two drugs when used in combination. In a series of new studies, researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign used rats to understand how brain structure and behavior can change when cannabis and alcohol are taken together.
Most researchers have studied the effects of either alcohol or THC (delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol), the primary psychoactive drug in cannabis, alone. However, when people, especially adolescents, use these drugs, ...
Scientists are working to protect the unique qualities of cacao beans grown in the Buenaventura region on the Pacific coast of Colombia.
In a study published in the Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, researchers from the Colombian Corporation for Agricultural Research (AGROSAVIA) have examined a wealth of metrics to uncover the complex interactions between environmental factors and cacao quality.
In a pioneering move, they have proposed that Buenaventura should be designated as a new Denomination of Origin (DO) for cacao trees. This is a legal recognition given to products that originate ...
By strategically straining materials that are as thin as a single layer of atoms, University of Rochester scientists have developed a new form of computing memory that is at once fast, dense, and low-power. The researchers outline their new hybrid resistive switches in a study published in Nature Electronics.
Developed in the lab of Stephen M. Wu, an assistant professor of electrical and computer engineering and of physics, the approach marries the best qualities of two existing forms of resistive switches used for memory: memristors and phase-change materials. Both forms have been explored for their advantages over ...
MADISON – Nineteen million years ago, during a time known as the early Miocene, massive ice sheets in Antarctica rapidly and repeatedly grew and receded. The Miocene is widely considered a potential analog for Earth's climate in the coming century, should humanity remain on its current carbon emissions trajectory.
Identifying how and why Antarctica's major ice sheets behaved the way they did in the early Miocene could help inform understanding of the sheets' behavior under a warming climate. Together, the ice sheets lock a volume of water equivalent to more than 50 meters of sea level rise and influence ocean currents that affect marine food webs and regional climates. ...
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. – November 30, 2023) Immunotherapy using modified chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells has greatly improved survival rates for pediatric patients with relapsed and recurrent leukemia. However, these therapies are not as effective in treating solid tumors and can have significant toxicity. Findings from St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital showed that adding a modular chimeric cytokine receptor to CAR T cells increased their efficacy in multiple solid tumor models. The study was published today in Nature Biomedical Engineering.
“We designed modular chimeric cytokine receptors and showed that ...
Melting of glaciers, rising sea levels, extreme heat waves: the consequences of climate change are more visible than ever, and the scientific community has confirmed that humans are responsible. Yet studies show that a third of the population still doubts or disputes these facts. The cause is disinformation spread by certain vested interests. To try and prevent this phenomenon, a team from the University of Geneva (UNIGE) has developed and tested six psychological interventions on nearly 7,000 participants from twelve countries. The research, published in ...
Skin-to-skin contact between parent and infant during the first hours after a very premature birth helps develop the child's social skills. This is according to a new study published in JAMA Network Open by researchers from Karolinska Institutet and others. The study also shows that fathers may play a more important role than previous research has shown.
In current practice, very premature babies are usually placed in an incubator to keep them warm and to stabilize them during the first hours after birth. In the “Immediate parent-infant skin-to-skin study” (IPISTOSS), 91 premature babies born at 28 to 33 weeks were randomized to either ...
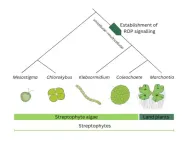
Plants regulate their development with a distinct group of molecular players. ROP proteins, a group of plant-specific proteins, are known to control plant tissue formation. Now, Hugh Mulvey and Liam Dolan at the GMI show that ROP proteins evolved at the transition between unicellular and multicellular plant life. The findings are published on November 30 in the journal Current Biology.
Being non-mobile, plants follow a very different lifestyle from us animals. To grow and develop, plants also need a distinct ...
In a study with 22 pairs of identical twins, Stanford Medicine researchers and their colleagues have found that a vegan diet improves cardiovascular health in as little as eight weeks.
Although it’s well-known that eating less meat improves cardiovascular health, diet studies are often hampered by factors such as genetic differences, upbringing and lifestyle choices. By studying identical twins, however, the researchers were able to control for genetics and limit the other factors, as the twins grew up in the same households ...