(Press-News.org) As the use of wearable technology grows, smart watches are marketed across the globe to consumers as a way to monitor health.
For some, they’re told by these devices that they have atrial fibrillation, an irregular heartbeat, which is known to increase the risk of heart attack and stroke.
“Unfortunately, this has led to a tsunami of healthy patients coming to clinics complaining about having atrial fibrillation, and we see many false positives without really having a way to use these devices clinically,” said Hamid Ghanbari, M.D., M.P.H., a cardiac electrophysiologist the University of Michigan Health Frankel Cardiovascular Center.
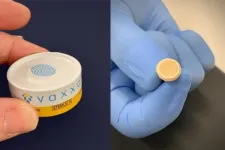
To address the clinical gap, a research team led by Ghanbari developed a prescription wristwatch that continuously monitors the wearer’s heart rhythm and uses a unique algorithm to detect atrial fibrillation.
The clinical-grade device, called the Verily Study Watch, proved very accurate at identifying atrial fibrillation in participants.
The results are published in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
“Right now, we typically manage patients with atrial fibrillation using electrocardiogram, or ECG, patches that we put on the chest, but the future of Afib management will be on the wrist,” said Ghanbari, lead author of the study and an assistant professor of internal medicine-cardiology at U-M Medical School.
Much like consumer wearable devices, the Verily Study Watch detects subtle changes in heart rhythm by sending light pulses through the skin into the blood vessels, a process known as photoplethysmography.
If it suspected atrial fibrillation, the device would prompt a user to take a single-lead ECG to determine if the algorithm correctly identified to Afib.
The results would then be reviewed by a cardiographic technician before it was reported to the participant’s physician.
The device analyzed data every 15 minutes, and its deep neural network algorithm determined whether over 100 participants had atrial fibrillation between September 2020 and May 2021.
The study watch correctly identified atrial fibrillation in the vast majority of participants, with levels of false negatives and positives that was similar to other devices for detection of Afib using similar photoplethysmography technology.
Although there was a decrease in performance of the device for some episodes of atrial fibrillation for participants with darker skin tones, it was still able to detect Afib in those patients.
Researchers say this is the first study to report the performance of the photoplenthysmography-based algorithm for participants at all levels of physical activity.
The device’s accuracy of detecting atrial fibrillation was comparable during low and moderate levels of activity.
Consumer-facing devices, like Apple Watch and Fitbit, are cleared by the United States Food and Drug Administration for pre-diagnostic purposes but are not intended for clinical decision making.
This device, Ghanbari says, could provide the link that allows providers to effectively use data from wearables to manage patients with Afib.
“The prescription Study Watch bridges the gap between long term, continuous monitoring that is currently more invasive and the consumer space with a practical solution for Afib detection and burden assessment,” he said.
“It is not intended to replace interval ECG monitoring for patients who need it. However, the multistage system may also limit the burden on clinicians and avoid the deluge of notifications generated by other wrist-worn devices that rarely result in clinically actionable findings.”
The creator of the watch, Verily Life Sciences, received 510(k) clearance from the FDA, a premarket submission to demonstrate the product’s efficacy and similarity to a legally marketed device.
“There is a need for clinical grade wrist-worn wearable that is affordable and can be prescribed by clinicians for the long term, personalized and continuous management of patients with Afib,” Ghanbari said.
Additional authors include Ming‐Zher Poh, Ph.D., of Google, Li-Fang Cheng, Ph.D., Janice Lin, Ph.D., Anil Patwardhan, Ph.D., R. Scooter Plowman, M.D., M.B.A., MHSA, M.Sc., all of Verily Life Sciences, Anthony J. Battisti, Ph.D., Lori A. Crosson, Ph.D., Jeffrey T. Ellis, Ph.D., Yuriko Tamura, and Mintu P. Turakhia, M.D., all of iRhythm Technologies, Ganesh S. Venkataraman, M.D., of Colorado Heart and Vascular, Charles A. Athill, M.D., of San Diego Cardiac Center, Nimesh S. Patel, M.D., of University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Chinmay P. Patel, M.D., of University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, and Christian E. Machado, M.D., of Ascension Providence Hospital.
Ghanbari is a paid consultant for Verily Life Sciences, Boston Scientific, Johnson and Johnson and Huxley Medical Inc.
Paper cited: “Validation of a Deep Learning Algorithm for Continuous, Real‐Time Detection of Atrial Fibrillation Using a Wrist‐Worn Device in an Ambulatory Environment,” Journal of the American Heart Association. DOI: 0.1161/JAHA.123.03054
END
Clinical smart watch finds success at identifying atrial fibrillation
The device would be the first clinical-grade, diagnostic wrist-worn device for long term Afib monitoring
2023-12-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Why reading nursery rhymes and singing to babies may help them to learn language
2023-12-01
PRESS RELEASE FROM THE UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE
EMBARGOED UNTIL 10 AM LONDON TIME (GMT) ON FRIDAY 1 DECEMBER 2023
Images and paper available at: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1JRhAD1ESL6NZN7acEoZQcXCA9w50Gczr?usp=drive_link
Phonetic information – the smallest sound elements of speech – may not be the basis of language learning in babies as previously thought
Babies don’t begin to process phonetic information reliably until seven months old – which researchers say is too late to form the foundation of language
Instead, babies learn from rhythmic information – the changing emphasis of syllables in speech – which unlike phonetic ...
Brace for a potentially record-breaking winter after sweltering summer and autumn
2023-12-01
The scorching heatwaves of 2023's summer and autumn shook the world, raising a pertinent question: Will this lead into the warmest winter the globe has ever witnessed?
After a summer and autumn marked by extreme temperatures and a consistent global warming trend across oceans and landmasses, concerns mounted about what might follow. The global average temperature during June to October 2023 surpassed the 1991-2020 average by 0.57℃. August and September soared even higher, surpassing historical averages by 0.62℃ and 0.69℃, respectively, eclipsing the records set in 2016.
From hottest ...
Scientists raise alarm as bacteria are linked to mass death of sea sponges weakened by warming Mediterranean
2023-12-01
Vibrio bacteria, named for their vibrating swimming motion, span approximately 150 known species. Most Vibrio live in brackish or salt water, either swimming free or living as pathogens or symbionts in fish, crustaceans, molluscs, and corals. Because Vibrio thrive at relatively high temperatures, outbreaks in marine animals are expected to become ever more frequent under global warming. For example, over the past few decades, Vibrio have been implicated in the ‘bleaching’ of subtropical and tropical corals around the world.
Now, researchers from Spain and Turkey have shown that Vibrio bacteria also play a role in outbreaks of mortality of an unrelated ...
Mass General-developed brain care score (BCS) is a scientifically validated way to assess current health habits and risk to future brain health
2023-12-01
BOSTON – Individuals can improve their brain care and reduce their risk of developing brain diseases such as dementia and stroke by focusing on a list of 12 steps covering modifiable physical, lifestyle, and social-emotional components of health.
The list was developed and validated in research published in Frontiers in Neurology by investigators from the McCance Center for Brain Health at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and their collaborators in the United States and Europe.
For the study, the scientists ...
Exercise training improves obesity-related dementia
2023-12-01
Obesity is a major risk factor for cardiovascular metabolic diseases and neurodegenerative diseases such as dementia. Long-term exercise improves memory and spatial cognition, reduces age-related cognitive decline, and maintains brain volume, but the mechanisms are not fully understood.
Recently, a study from Febbraio lab at Monash University reported that voluntary exercise training (VET) improves long-term memory in high-fat diet (HFD)-induced obese mice, increases hippocampal neurogenesis ...
Paleolithic humans may have understood the properties of rocks for making stone tools
2023-12-01
A research group led by the Nagoya University Museum and Graduate School of Environmental Studies in Japan has clarified differences in the physical characteristics of rocks used by early humans during the Paleolithic. They found that humans selected rock for a variety of reasons and not just because of how easy it was to break off. This suggests that early humans had the technical skill to discern the best rock for the tool. The researchers published the results in the Journal of Paleolithic Archaeology.
As Homo sapiens moved from Africa to Eurasia, they used stone tools made of rocks, such as obsidian and flint, to cut, slice, and craft ranged weapons. Because ...
A patch of protection against Zika virus
2023-12-01
A simple-to-apply, needle-free vaccine patch is being developed to protect people from the potentially deadly mosquito-borne Zika virus.
A prototype using The University of Queensland-developed and Vaxxas-commercialised high-density microarray patch (HD-MAP) has delivered a University of Adelaide-developed vaccine and elicited an effective immune response to Zika virus in mice.
UQ alum and Vaxxas researcher Dr Danushka Wijesundara said Zika virus was a risk to people across the Pacific, Southeast Asia, India, Africa and South and Central America.
“We can change the way we combat Zika virus with the ...
ORNL supports executive order for safe, secure and trustworthy AI
2023-12-01
As artificial intelligence technologies improve, they increase the efficiency and capabilities of research across the scientific spectrum. Because of the rapid pace of the field, AI tools must be developed sustainably, a guiding principle for the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory throughout its 40 years of AI research. Now, its extensive array of resources are supporting the nation as it harnesses the power of these transformative technologies.
In October, President Biden ...
Photonic chip that ‘fits together like Lego’ opens door to semiconductor industry
2023-12-01
Researchers at the University of Sydney Nano Institute have invented a compact silicon semiconductor chip that integrates electronics with photonic, or light, components. The new technology significantly expands radio-frequency (RF) bandwidth and the ability to accurately control information flowing through the unit.
Expanded bandwidth means more information can flow through the chip and the inclusion of photonics allows for advanced filter controls, creating a versatile new semiconductor device.
Researchers expect the chip will have application in advanced radar, ...
Meteorites likely source of nitrogen for early Earth
2023-12-01
Micrometeorites originating from icy celestial bodies in the outer Solar System may be responsible for transporting nitrogen to the near-Earth region in the early days of our solar system. That discovery was published today in Nature Astronomy by an international team of researchers, including University of Hawai'i at Mānoa scientists, led by Kyoto University.
Nitrogen compounds, such as ammonium salts, are abundant in material born in regions far from the sun, but evidence of their transport to Earth's orbital region had been poorly understood.
"Our recent findings suggests the possibility that a greater amount of nitrogen compounds than previously ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Clinical smart watch finds success at identifying atrial fibrillationThe device would be the first clinical-grade, diagnostic wrist-worn device for long term Afib monitoring