(Press-News.org) Auburn University's Department of Physics is hosting a special meeting targeting college students passionate about pursuing a PhD in Physics. This engaging event is set for December 8 at 2 PM Central Time. Interested individuals can join the session virtually via Zoom at https://aub.ie/faKH5W.
Studying Physics at Auburn University is an immersive journey into the universe's fundamental principles. Our PhD program offers a robust foundation in physics and promotes groundbreaking research and discovery. Known for small class sizes and personalized attention, the program ensures each of our approximately 75 students receive dedicated support, leading to a more enriching learning experience. This approach is key to our educational philosophy and essential for student success. A PhD in Physics from Auburn prepares students to be skilled scientists and problem-solvers, offering opportunities to develop critical thinking skills and gain insights from our expert faculty.
The Department of Physics boasts the state-of-the-art Leach Science Center, a $24 million, 62,000 square-foot expansion featuring the latest technology and inviting study areas. We host diverse research groups in six areas: Atomic Physics, Biophysics, Condensed Matter Physics, Plasma Physics, Space Physics, and Discipline-based Education Research (DBER). Each group provides unique specializations and research opportunities.
A program highlight is the hands-on research experience. Students participate in internationally recognized projects, contributing to high-impact journal publications. These opportunities enhance practical skills and deepen understanding of physics.
Furthermore, Auburn University is a rapidly growing R1 institution, ranked among the top 50 public schools in the US by USNews 2024, highlighting its commitment to academic excellence and research leadership.
The upcoming information session is a valuable opportunity for anyone pursuing a PhD in Physics. It's informative for both domestic and international students, offering insights into Auburn's offerings and a chance to interact with our faculty. We invite aspiring physicists to explore the exciting opportunities at Auburn University's Department of Physics.
END
Auburn University invites aspiring physicists to PhD program information meeting
2023-12-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Social media influencers may affect more than voter opinions
2023-12-01
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — If Thanksgiving dinner conversations have turned into heated political arguments over the past two decades, social media may be to blame. Popular social media figures — or influencers — who create or share distorted political messages may cause political parties to moderate their policies to win over independent voters in general elections but tend to polarize the rest of society, according to researchers who created a model to study how social media may affect election ...
1 in 8 older adults use cannabis products, suggesting need to screen for risks
2023-12-01
More older Americans use cannabis now than before the pandemic, with 12% saying they’ve consumed a THC-containing substance in the past year and 4% saying they do so multiple times a week, according to a new study of people aged 50 to 80. Those who drink alcohol at risky levels have a much higher rate of cannabis use.
The new findings, published in the journal Cannabis and Cannabinoids Research by a team from the University of Michigan’s Institute for Healthcare Policy and Innovation, suggest a need for more education and screening of older adults for cannabis-related ...
Study identifies peptide as key mediator in heavy alcohol drinking
2023-12-01
(Boston)—Alcohol is the most common addictive substance in the world. Every year in the U.S. excessive alcohol use costs $249 billion and causes approximately 88,000 deaths, as well as various chronic diseases and social issues. Alcohol use disorder, a highly prevalent, chronic, relapsing disorder, affects more than 14 million people in the U.S. alone, in addition to being severely under-treated, with only three modestly effective pharmacological therapies available.
Chronic exposure to alcohol has been shown to produce profound neuroadaptations in specific brain regions, including the recruitment of key stress neurotransmitters, ultimately ...
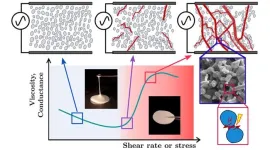
New understanding of oobleck-like fluids contributes to smart material design
2023-12-01
If you mix cornstarch and water in the right proportions, you get something that seems not-quite-liquid but also not-quite-solid. Oobleck flows and settles like a liquid when untouched, but stiffens when you try to pick it up or stir it with a spoon. The properties of oobleck and other non-Newtonian fluids — including Silly Putty, quicksand, paint, and yogurt — change under stress or pressure and scientists have long struggled to prove exactly why.
Now, researchers at the University of Chicago’s Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering (PME) have used piezoelectric nanoparticles, which themselves change in response to pressure, to investigate the fundamental physics of non-Newtonian ...
Brainstorming with a bot
2023-12-01
A researcher has just finished writing a scientific paper. She knows her work could benefit from another perspective. Did she overlook something? Or perhaps there's an application of her research she hadn't thought of. A second set of eyes would be great, but even the friendliest of collaborators might not be able to spare the time to read all the required background publications to catch up.
Kevin Yager—leader of the electronic nanomaterials group at the Center for Functional Nanomaterials (CFN), a U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science User Facility ...
Hip hop dancing promotes awareness of disability rights and performance equality, study shows
2023-12-01
Hip hop dancing can be used to spread awareness of disability rights and help those with sight problems to participate in performance equally, a new study says.
Breakin’ – which is commonly referred to as breakdancing - is good for mobility and helps promote balance and stability as well as wellbeing.
It also offers an important opportunity for people to slow down and to connect with their inner selves, their feelings, their bodies, and their peers, according to researchers. It has been used to treat symptoms of depression, anxiety and PTSD.
Nathan Geering, ...
Urgent work needed to tackle “substantial” digital health inequality, study recommends
2023-12-01
Millions of people are suffering from digital health inequality because of poverty, experts have warned.
A new study says urgent work is needed to ensure those from deprived areas can access healthcare as the NHS increasingly turns to the use of apps and online health portals for the provision of healthcare.
A team of doctors and academics found a “significant association” between increased poverty and reduced use of digital services. Their modelling estimates that this association accounts for 4.27million patients across England who have not downloaded the NHS app. In October 2022 it was estimated more than 37million patients had activated ...
Unlocking the secret strength of marine mussels
2023-12-01
How do you create strong, yet quick-release connections between living and non-living tissues? This is a question that continues to puzzle bioengineers who aim to create materials that bond together for advanced biomedical applications.
Looking to nature for inspiration, the McGill-led research zeroed in on the marine mussel byssus, a fibrous holdfast, which these bivalve mollusks use to anchor themselves in seashore habitats. The byssus attaches to rocky surfaces using an underwater glue, but the other end (the byssus stem root) is firmly anchored within the mussel’s soft living tissue. This area of contact between the living ...
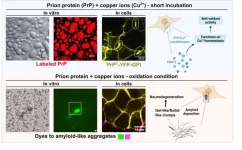
When physics meets biology: prion protein orchestrates liquid-liquid phase separation with copper
2023-12-01
In a groundbreaking study published in Science Advances, researchers from the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro (UFRJ) and the German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases (DZNE-Berlin) shed light on the intricate dance between the prion protein and copper ions in the physiopathology of live cells. The research paves the way for potential treatments addressing copper-bound prion protein clusters to prevent abnormal solid formation and mitigate neurodegenerative outcomes.
Like oil droplets in water, cells harbor membrane-bound organelles that ...
Eminent scientists say a child-centric approach is the blueprint to improve communities
2023-12-01
Communities can prosper by providing attentive education and social services to their youngest residents — but the challenge is for leaders to work together.
That is the message of Craig Ramey and Sharon Ramey, Virginia Tech distinguished research professors of the Fralin Biomedical Research Institute at VTC, who today (Dec. 1, 2023) presented details of a decades-long study that focuses on early childhood education and development.
In a research article in the journal Medical Research Archives, the official journal of the European Society of Medicine, the scientists discuss lessons ...