(Press-News.org) The energy consumption of data centers and information and communication technology (ICT) devices is growing at an alarming rate, projected to constitute up to 20 percent of global energy consumption by 2030. To support the digital transformation effectively, we need to enhance software efficiency. A promising avenue in this endeavor is incremental computing, where computations react to input changes rather than recomputing results from scratch. However, existing approaches to incrementality have limited applicability: They either demand expert knowledge, support only specialized domains (e.g., database queries), or yield only modest speedups. At Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU), Professor Sebastian Erdweg and his team aim to develop a methodology for automatically incrementalizing computations and significantly improving their time and energy efficiency. The European Research Council (ERC) is sponsoring the new project "AutoInc" to the extent of EUR 2 million. Sebastian Erdweg was appointed professor at JGU's Institute of Computer Science in 2019, where he leads the Programming Languages group. The ERC Consolidator Grant is one of the EU's most prestigious and valuable research awards for outstanding researchers.
Increased use of incremental computing for reactive applications
The digital transformation demands substantial energy resources. While servers and ICT devices must contribute to the necessary reductions in energy consumption, hardware improvements alone will not be sufficient. "To sustain the ongoing digital transformation, we must find ways to run software much more efficiently," said Professor Sebastian Erdweg. "Incremental computing has the potential for enormous improvements in energy efficiency, provided we can solve its fundamental limitations." Incremental computing is used, for example, in vehicle navigation systems for calculating detours to avoid traffic jams or in spell checkers integrated into text programs. "Incremental computing lies at the core of reactive applications like these, which involve the input of data and an immediate system response," added Erdweg. Instead of recalculating results from scratch, incremental computations react only to these changes in input. This saves both time and energy.
Incremental computing is demanding in terms of both technology and conception
"Incremental computing is highly rewarding, but its creation requires much effort and is very demanding both on a technical and conceptional level." According to Erdweg, this is why incremental computing is used rarely or only in simple applications, such as spell checking. The development of incremental computing techniques requires considerable expertise. In their new project, "AutoInc – Asymptotic Speedups for Free through Automatic Incremental Computing," Erdweg and his team aim to overcome this challenge and facilitate a breakthrough in incremental computing: The idea is to convert non-incremental computations automatically into incremental computations. In preliminary experiments, the team has achieved calculations up to 10,000 times faster. The researchers expect that the results of the project will not only improve the efficiency of software programs but also provide fundamental insights into the nature and limitations of automatic incremental computing.
Together with his team, Sebastian Erdweg focuses on programming abstractions, programming languages, and programming tools designed to simplify the development and maintenance of complex software systems. He earned his doctorate at Philipps-Universität Marburg in 2013. He then held a postdoc position at TU Darmstadt until 2016, after which he was appointed as an assistant professor at TU Delft in the Netherlands. In 2019, Sebastian Erdweg was appointed as a Professor of Programming Languages at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz.
The ERC Consolidator Grant
The ERC Consolidator Grant is one of the most valuable EU funding schemes awarded to individual researchers. Through these grants, the European Research Council (ERC) supports outstanding scientists within seven to twelve years after completing their doctorate. Successful applicants must not only demonstrate excellence in research but also provide evidence of the groundbreaking nature and feasibility of their project. The funding period spans five years.
The European Research Council has also approved two other ERC Consolidator Grants at JGU: Professor Dorothee Dormann's project on neurodegenerative diseases and Professor Shuqing Xu's project on the evolution of ecosystems in climate change. Furthermore, JGU-based palaeogeneticist Professor Joachim Burger is involved in an ERC Consolidator Grant project researching the adaptation of historical populations to urban life, which is coordinated by Professor Christina Papageorgopoulou from Democritus University of Thrace.
END
Reducing the energy consumption of software: Sebastian Erdweg receives ERC Consolidator Grant
Incremental computations can react to changes in data instantly / Large potential for energy savings
2023-12-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
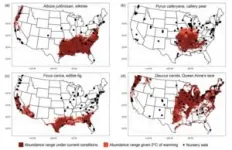
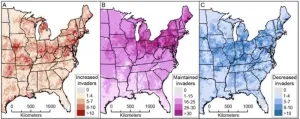
Study finds plant nurseries are exacerbating the climate-driven spread of 80% of invasive species
2023-12-05
AMHERST, Mass. – Researchers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst recently published a pair of papers that, together, provide the most detailed maps to date of how 144 common invasive plants species will react to 2° Celsius of climate change in the eastern U.S., as well as the role that garden centers currently play in seeding future invasions. Together, the papers, published in Diversity and Distributions and BioScience, and the publicly available maps, which track species at the county level, promise to give invasive species managers in the U.S. the tools they need ...
Jefferson Lab site grows with addition of Applied Research Center
2023-12-05
NEWPORT NEWS, VA – The Applied Research Center (ARC) is tying the knot with the U.S. Department of Energy’s Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility. Today, the City of Newport News announced the transfer of the Applied Research Center to Jefferson Lab and the DOE. The announcement was made in a ribbon-tying ceremony for the facility.
“Newport News is a hub of innovation and research, thanks in large part to Jefferson Lab’s robust educational and scientific offerings,” said Newport News Mayor Phillip Jones. “Since 1985, the city has invested more than $64 ...
Texas A&M receives $1.8 million NIH grant to support bone health in people with down syndrome
2023-12-05
By Courtney Price, Texas A&M University School of Veterinary Medicine & Biomedical Sciences
Texas A&M University researchers have been awarded a $1.8 million grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to study bone regeneration throughout the lifespan to ultimately benefit individuals with Down syndrome.
The new INvestigation of Co-occurring conditions across the Lifespan to Understand Down syndromE (INCLUDE) Project grant will help scientists understand whether bone regeneration holds the key to helping people ...
Membrane raft redox signaling contributes to visfatin-induced inflammation and kidney damage
2023-12-05
“[...] the exact mechanism of how obesity increases the advancement of chronic kidney disease is still uncertain.”
BUFFALO, NY- December 5, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 22, entitled, “Contribution of membrane raft redox signalling to visfatin-induced inflammasome activation and podocyte injury.”
The number of obese patients with end-stage renal disease has ...
New study highlights COVID-19’s adaptive strategy for infection
2023-12-05
MINNEAPOLIS/ST. PAUL (12/05/2023) – Researchers have discovered a novel mechanism whereby the SARS-CoV-2 virus, which causes COVID-19, can vary its mode of infection in human cells. Published in the journal eLife, a team from the University of Minnesota and the Midwest Antiviral Drug Discovery (AViDD) Center found the virus can alternate between being highly infectious and avoiding detection by the immune system. This understanding is vital for grasping the virus' impact during the pandemic and for predicting its potential evolutionary developments.
The spike protein of the virus, which is crucial for attaching ...
Type 1 diabetes: B cell-derived natural antibodies suppress autoimmune pathogenesis
2023-12-05
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – Researchers have discovered the novel mechanism that underlies a previously reported observation that infection by group A Streptococcus bacteria reduces the risk of later developing Type 1 diabetes.
The Journal of Immunology reports that vaccination of neonatal mice with group A Streptococcus promoted a clonal expansion of innate-like B cells that produce antibody against N-acetyl-D-glucosamine, or GlcNAc. GlcNAc is a derivative of glucose sugar that is found as part of the cell wall of group ...
Cable-Dunlap, Chi, Smith and Thornton named ORNL Corporate Fellows
2023-12-05
Four researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory have been named ORNL Corporate Fellows in recognition of significant career accomplishments and continued leadership in their scientific fields.
Corporate Fellow is the highest recognition for members of the ORNL research staff. Paula Cable-Dunlap, Miaofang Chi, Scott Smith and Peter Thornton have been recognized by the laboratory for their standing in the international scientific community as exceptional and influential researchers and as role models and mentors among peers and early career researchers.
“Paula, Miaofang, Scott and Peter represent ...
UofL secures $6.5 million to enhance training for nursing professionals
2023-12-05
The University of Louisville has received $6.5 million through two federal grants to help increase Kentuckians’ access to health care, particularly in underserved rural and urban areas. The UofL School of Nursing will use the funds from the Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) to develop and implement an accelerated Licensed Practical Nurse-to-Bachelor of Science in Nursing (LPN-to-BSN) pathway in medically underserved areas of Kentucky. The second HRSA-funded project aims ...
Reverse metabolomics: new method finds biomarker for inflammatory bowel disease
2023-12-05
In recent years, microbiome research has started to shift its focus from the microbes themselves to the molecules they produce. After all, it’s these molecules that directly interact with human cells to influence a person’s health. But trying to identify which molecules are being made by a person’s microbiome is quite challenging. A typical metabolomics study can only characterize about 10% of the molecular data from a human microbiome sample.
In a new study published on December 5, 2023 in Nature, microbiome experts at University of California San Diego ...
Older organs accelerate aging in transplant recipients
2023-12-05
Most organ transplantations involve supply from older donors to younger recipients. Aging cells can become senescent, a condition in which they stop multiplying and secrete chemicals that negatively affect neighboring cells. Senescent cells accumulate in older donor organs, and have the potential to compromise transplant outcomes.
A study led by researchers from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, found that in preclinical models, transplanting older organs can trigger ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Nutrient uptake gets to the root of roots
Aspirin not a quick fix for preventing bowel cancer
HPV vaccination provides “sustained protection” against cervical cancer
Many post-authorization studies fail to comply with public disclosure rules
GLP-1 drugs combined with healthy lifestyle habits linked with reduced cardiovascular risk among diabetes patients
Solved: New analysis of Apollo Moon samples finally settles debate about lunar magnetic field
University of Birmingham to host national computing center
Play nicely: Children who are not friends connect better through play when given a goal
Surviving the extreme temperatures of the climate crisis calls for a revolution in home and building design
The wild can be ‘death trap’ for rescued animals
New research: Nighttime road traffic noise stresses the heart and blood vessels
Meningococcal B vaccination does not reduce gonorrhoea, trial results show
AAO-HNSF awarded grant to advance age-friendly care in otolaryngology through national initiative
Eight years running: Newsweek names Mayo Clinic ‘World’s Best Hospital’
Coffee waste turned into clean air solution: researchers develop sustainable catalyst to remove toxic hydrogen sulfide
Scientists uncover how engineered biochar and microbes work together to boost plant-based cleanup of cadmium-polluted soils
Engineered biochar could unlock more effective and scalable solutions for soil and water pollution
Differing immune responses in infants may explain increased severity of RSV over SARS-CoV-2
The invisible hand of climate change: How extreme heat dictates who is born
Surprising culprit leads to chronic rejection of transplanted lungs, hearts
Study explains how ketogenic diets prevent seizures
New approach to qualifying nuclear reactor components rolling out this year
U.S. medical care is improving, but cost and health differ depending on disease
AI challenges lithography and provides solutions
Can AI make society less selfish?
UC Irvine researchers expose critical security vulnerability in autonomous drones
Changes in smoking status and their associations with risk of Parkinson’s, death
In football players with repeated head impacts, inflammation related to brain changes
Being an early bird, getting more physical activity linked to lower risk of ALS
The Lancet: Single daily pill shows promise as replacement for complex, multi-tablet HIV treatment regimens
[Press-News.org] Reducing the energy consumption of software: Sebastian Erdweg receives ERC Consolidator GrantIncremental computations can react to changes in data instantly / Large potential for energy savings