(Press-News.org) BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- The rapidly evolving nature of digital media presents a challenge for those who study digital addiction – social networks like TikTok and video games like Fortnite might be popular now, but they could be irrelevant in a matter of years. A new tool developed by researchers from Binghamton University, State University of New York will make it easier for clinicians and researchers to measure digital media addiction as new technologies emerge.
“We wanted to create a tool that was immediately useful in the clinic and lab, that reflects current understandings about how digital addiction works, that wouldn't go obsolete once the next big tech change hits,” said Daniel Hipp, who co-led the study. Hipp graduated with his PhD from Binghamton University’s Infant and Child Studies lab in 2015, and has continued collaborating with his former PhD advisor and Professor of Psychology, Peter Gerhardstein, ever since.
Current tools for measuring the relationship between psychology and technology are not only outdated in the way they speak about tech; they are also often written with specific antiquated technology questions in mind. To address this shortcoming, Hipp and Gerhardstein, together with the Digital Media Treatment and Education Center in Boulder, Colo., developed the Digital Media Overuse Scale, or dMOS. Clinicians and researchers who use the tool can be free to make their investigations as broad (i.e. social media) or as granular (i.e. Instagram) as they want for their particular use.
“Rather than focusing on the tech, we built into the scale a set of ‘skeletal’ questions that focus on psychology,” said Hipp, now a research consultant at the Digital Media Treatment and Education Center. “For example, one question type is ‘I have trouble stopping myself from using X even when I know I should.’ Replacing X with a tech domain, such as social media or gaming, we can ask the same question about several different tech domains. And we can replace X in future studies with new technology domains (i.e. TikTok-style ‘shorts’) as they emerge.”
To test the Digital Media Overuse Scale, the researchers conducted an anonymous survey with over 1,000 college students to investigate clinically relevant behaviors and attitudes as they relate to five digital media domains: general smartphone use, internet video consumption, social media use, gaming, and pornography use.
They found the following:
A majority of students demonstrate few indicators of addiction or overuse
Use patterns were highly targeted to specific domains for specific users.
A select set of students’ responses indicated attitudes and behaviors around digital media use that, if they were derived from drug use or sex, would be deemed clinically problematic.
“Overall, the outcome reveals that overuse is not a general thing; respondents typically reported overuse in one or a few domains only, such as social media,” said Gerhardstein. “More broadly, the data paint a picture of a population using digital media substantially, and social media in particular, to a level that increases concern regarding overuse issues.”
Initial indications are that the Digital Media Overuse Scale is a reliable, valid, and extendible clinical instrument capable of providing clinically relevant scores within and across digital media domains, wrote the researchers.
The team is currently extending the scale to two new tech domains in a follow-up study Gerhardstein's lab is conducting in continued collaboration with the Digital Media Treatment and Education Center. They are also initiating collaborations with other researchers with an eye to improving our collective understanding of how human psychology relates to the rapidly changing landscape of digital media.
The paper, “The Digital Media Overuse Scale (dMOS): A Modular and Extendible Questionnaire for Indexing Digital Media Overuse,” was published in a special edition of Technology, Mind, and Behavior.
END
Addicted to your phone? New tool identifies overuse of digital media
Digital Media Overuse Scale adapts to changing technology
2023-12-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
International consensus report on gaps and opportunities for the clinical translation of precision diabetes medicine
2023-12-05
Boston, MA - A new international consensus report on precision medicine in diabetes prevention and care highlights the significant advancements in precision medicine in diabetes prevention, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis while also shedding light on numerous knowledge gaps.
The report, Second international consensus report on gaps and opportunities for the clinical translation of precision diabetes medicine, was published in Nature Medicine on October 5, 2023.
Supported by the American Diabetes Association (ADA), the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD), and the Novo Nordisk Foundation, the consensus report was made possible through a huge collaborative ...
Depression, constipation, and urinary tract infections may precede MS diagnosis
2023-12-05
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, TUESDAY, DECEMBER 5, 2023
MINNEAPOLIS – In some diseases, the underlying processes can start years before a diagnosis is made. A new study finds that people who later develop multiple sclerosis (MS) are more likely to have conditions like depression, constipation and urinary tract infections five years before their MS diagnosis than people who do not develop MS. The study, which is published in the December 5, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology, also found that sexual problems and bladder infections, or cystitis, ...
Chemists create organic molecules in a rainbow of colors
2023-12-05
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Chains of fused carbon-containing rings have unique optoelectronic properties that make them useful as semiconductors. These chains, known as acenes, can also be tuned to emit different colors of light, which makes them good candidates for use in organic light-emitting diodes.
The color of light emitted by an acene is determined by its length, but as the molecules become longer, they also become less stable, which has hindered their widespread use in light-emitting applications.
MIT chemists have now come up with a way to make these molecules more stable, allowing them to synthesize acenes of varying lengths. Using their new approach, ...
NCCN summit navigates solutions for financial and other cancer-related hardships
2023-12-05
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [December 5, 2023] — Today, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®)—an alliance of leading cancer centers—hosted a Patient Advocacy Summit to explore the role of navigation throughout the cancer process. A diverse group of subject matter experts addressed the impact patient navigation has on care and how to utilize navigators to reduce economic burdens and disparities in care. The speakers included patients and advocates, policymakers, health care providers, and health data analysts.
The summit featured a series of best practice presentations highlighting some of the tools available to assist in various ...
Incarcerated women punished at higher rates for minor infractions than men, UTEP study shows
2023-12-05
EL PASO, Texas (Dec. 5, 2023) – A new study from The University of Texas at El Paso reveals a gender disparity in prison infractions that disproportionately affects women.
The study, led by Melinda Tasca, Ph.D., an associate professor in the Department of Criminal Justice and Security Studies at UTEP, and published in Justice Quarterly, analyzed the disciplinary infraction records of more than 20,000 males and females in a large western state prison, who were released between 2010 and 2013.
The researchers set out to answer three questions: ...
Conference on microplastics in water: characterization, cure and prevention
2023-12-05
Plastics are ubiquitous in all aspects of modern life, including food packaging, health care and household products. There has been a massive increase in plastics production over the past several decades and there has been serious attention paid to managing plastic wastes, particularly focused on recycling/reuse. However, as of the present time it has not been feasible, either technically or economically, to achieve a fully circular system. Those plastic materials that are not processed for reuse, known as end-of-life pastics, end up in landfillsor in other waste processing systems (e.g., incineration) or advanced recycling (eg., pyrolysis) or directly disposed in the ...
Dorothee Dormann receives an ERC Consolidator Grant to support her research into neurodegenerative diseases
2023-12-05
The protein TDP-43 is present in all cells of our body and important for their biochemical processes. However, this protein can aggregate into large clumps in the brain, which can cause degenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and other dementias. How exactly this happens and how these protein clumps are linked to disease is a subject of intense research. Professor Dorothee Dormann of Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) suspects that these proteins may also assemble in healthy cells – and that this assembly on a much smaller scale is important for the normal function of the TDP-43 protein. Her research group investigates the reason for these assemblies in ...
Reducing the energy consumption of software: Sebastian Erdweg receives ERC Consolidator Grant
2023-12-05
The energy consumption of data centers and information and communication technology (ICT) devices is growing at an alarming rate, projected to constitute up to 20 percent of global energy consumption by 2030. To support the digital transformation effectively, we need to enhance software efficiency. A promising avenue in this endeavor is incremental computing, where computations react to input changes rather than recomputing results from scratch. However, existing approaches to incrementality have limited applicability: They either demand expert knowledge, support only specialized domains (e.g., ...
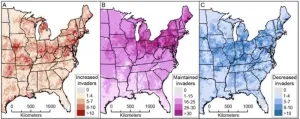
Study finds plant nurseries are exacerbating the climate-driven spread of 80% of invasive species
2023-12-05
AMHERST, Mass. – Researchers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst recently published a pair of papers that, together, provide the most detailed maps to date of how 144 common invasive plants species will react to 2° Celsius of climate change in the eastern U.S., as well as the role that garden centers currently play in seeding future invasions. Together, the papers, published in Diversity and Distributions and BioScience, and the publicly available maps, which track species at the county level, promise to give invasive species managers in the U.S. the tools they need ...
Jefferson Lab site grows with addition of Applied Research Center
2023-12-05
NEWPORT NEWS, VA – The Applied Research Center (ARC) is tying the knot with the U.S. Department of Energy’s Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility. Today, the City of Newport News announced the transfer of the Applied Research Center to Jefferson Lab and the DOE. The announcement was made in a ribbon-tying ceremony for the facility.
“Newport News is a hub of innovation and research, thanks in large part to Jefferson Lab’s robust educational and scientific offerings,” said Newport News Mayor Phillip Jones. “Since 1985, the city has invested more than $64 ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] Addicted to your phone? New tool identifies overuse of digital mediaDigital Media Overuse Scale adapts to changing technology