(Press-News.org) Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), that arises from pancreatic epithelial cells, is the most common form of pancreatic cancer, with a very high mortality rate. This elevated mortality is associated with the unique tumor microenvironment (TME), known for increased resistance to chemotherapy and high metastatic potential. TME is characterized by the presence of a complex stromal structure comprising cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), tumor endothelial cells (TECs), and a variety of immune cells.
CAFs are specific cells, primarily involved in the overall aggressiveness and spread of cancer cells. These cells can further be categorized into several types based on their cellular characteristics and roles, such as inflammatory, myo-fibroblastic, and antigen-presenting CAFs. Therefore, the development of a cell culture system for PDAC that mimics the unique TME involving different types of CAFs, is the need of the hour.
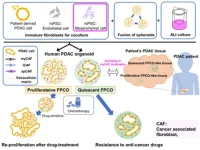
To this end, a research team from Japan attempted to create cancer cell organoid systems that can effectively resemble PDAC and act as a screening tool in anticancer research. Dr. Takeuchi Kenta, a research assistant at the Institute of Medical Science, including Associate Professor Tanimizu Naoki, and Professor Taniguchi Hideki, both from the Institute of Medical Science, The University of Tokyo, were involved in this novel research. Their research findings were published in volume 42, issue 11 of the Cell Reports journal on November 28, 2023.
Dr. Takeuchi Kenta briefly discusses his motivation behind the research. He says, “To reproduce the complexity of PDAC-TME in cell culture models is challenging. Therefore, we used human-induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC)-derived mesenchymal cells that can differentiate to multiple types of CAFs and established a novel PDAC organoid.”
The research team used patient-derived PDAC cells with hiPSC-derived endothelial and mesenchymal cells to create fused pancreatic cancer organoid (FPCO). This innovative approach yielded two distinct FPCOs, a proliferative FPCO (pFPCO), and a quiescent FPCO (qFPCO), which resemble a typical patient’s PDAC tissue. Notably, qFPCOs exhibited strong chemo-resistance capabilities, whereas pFPCOs could reproliferate after initial drug treatment. Using advanced techniques such as stem cell technology along with analyses like single cell RNA sequencing, and in-vitro cancer assays, the functional properties of the PDAC organoid system were studied and characterized.
Dr. Tanimizu Naoki concludes, “PDAC is a disease that often requires surgical resection and has no other viable treatment options. Also, anti-PDAC drugs have generally failed at different stages of clinical trials. Hence, PDAC organoids with unique TME profiles should be used for anticancer drug screening. Our PDAC model can help future research in cancer biology and in personalized healthcare.”
Thanks to the research team for the creation of a novel PDAC organoid system that can alter the landscape of cancer biology as an effective screening tool!
END
Novel and promising pancreatic cancer organoids for effective screening of anticancer drugs
2023-12-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New certification applies proven science to tobacco cessation treatment
2023-12-07
DALLAS, December 7, 2023 — The Tobacco Endgame — the path to ending tobacco use and nicotine addiction in the U.S. — is within sight, but there has been a sharp increase in electronic cigarette use among high school students, from 1.5% in 2011 to about 27.4% in 2019.[1]
The American Heart Association, the world’s leading nonprofit organization focused on heart and brain health for all, is collaborating with the Association for the Treatment of Tobacco Use and Dependence (ATTUD) to change that. New individual certification as a Certified Professional by the American Heart Association – Tobacco Treatment is ...
Ancient Balkan genomes trace the rise and fall of Roman Empire’s frontier, reveal Slavic migrations to southeastern Europe
2023-12-07
A multidisciplinary study led by the Institute of Evolutionary Biology in Spain (a joint center of the Spanish National Research Council and Pompeu Fabra University), the University of Belgrade in Serbia, the University of Western Ontario in Canada, and Harvard University in the USA, reconstructs the genomic history of the Balkan Peninsula during the first millennium of the common era, a time and place of profound demographic, cultural and linguistic change. The team has recovered and analyzed whole genome data from 146 ancient people excavated primarily from Serbia and Croatia—more than a third of which came from the ...
Ancient DNA analysis reveals how the rise and fall of the Roman Empire shifted populations in the Balkans
2023-12-07
Despite the Roman Empire’s extensive military and cultural influence on the nearby Balkan peninsula, a DNA analysis of individuals who lived in the region between 1 and 1000 CE found no genetic evidence of Iron Age Italian ancestry. Instead, a study published December 7 in the journal Cell revealed successive waves of migrations from Western Anatolia, central and northern Europe, and the Pontic-Kazakh Steppe during the Empire’s reign.
From the 7th century CE onwards (coincident with the fall of the Western Roman Empire), large numbers of people emigrated from Eastern Europe, likely related to the arrival of Slavic-speaking populations, which ...
Why presence of healthy cells enables cancer to resist treatment
2023-12-07
Chemotherapy becomes less effective because healthy cells push cancer cells to grow more slowly, according to two studies from researchers at UCL and Yale.
In the two studies, supported by Cancer Research UK and published in Cell, researchers used ‘mini-tumours’ and the latest single-cell analysis technologies to begin to solve the puzzle of why healthy cells in a patient’s bowel cancer tumour might lead to poor outcomes.
Bowel cancer kills over 900,000 people a year and is the second highest cause of cancer mortality worldwide. In the UK, it accounts for 10% of all cancer deaths.
In the first study, UCL researchers used the latest single-cell analysis ...
Cocoa extract supplement found to have benefits for cognition among older adults with lower diet quality
2023-12-07
WHO: Mass General Brigham researchers, Dr. Chirag Vyas and Dr. Olivia I. Okereke at Massachusetts General Hospital, and Dr. Howard Sesso and Dr. JoAnn Manson at Brigham and Women’s Hospital
WHAT: Cocoa extract has shown a potential protective effect on cognition but randomized clinical trials in older adults have had inconsistent results. A new study of cognition in a randomized trial, known as the Cocoa Supplement and Multivitamin Outcomes Study (COSMOS), suggests that taking cocoa extract supplements containing 500 mg per day of cocoa flavanols had cognitive benefits for older adults who had lower habitual ...
New Case Western Reserve University study finds diabetes drug may reduce risk for colorectal cancer
2023-12-07
CLEVELAND—A groundbreaking study by researchers at Case Western Reserve University suggests a class of medications used to treat type 2 diabetes may also reduce the risk of colorectal cancer (CRC).
The findings, published today (Dec. 7) in the journal JAMA Oncology, support the need for clinical trials to determine whether these medications could prevent one of the deadliest types of cancers. Eventually, the medications may also show promise in warding off other types of cancer associated with obesity and diabetes.
“Our results clearly demonstrate ...
Ecology: Mediterranean green turtles nesting range expands under warming climate
2023-12-07
Rising global temperatures could lead to an increase in the nesting range of green turtles in the Mediterranean Sea, according to a modelling study published in Scientific Reports. Under the worst-case climate scenario, the nesting range could increase by over 60 percentage points, spreading west from the current area to include much of the North African, Italian, and Greek coastlines.
Human-caused climate change has caused sea surface temperatures to increase globally, with severe impacts on some marine life. Sea turtles are potentially particularly susceptible, as the sex of their offspring is dependent on incubation temperature. Although previous research ...
Racial and ethnic disparities in clinical trial enrollment among women with gynecologic cancer
2023-12-07
About The Study: Clinical trial enrollment was lower among certain minoritized racial and ethnic groups in this study of 562,000 women with endometrial, ovarian, or cervical cancer. Continued efforts are needed to address disparate clinical trial enrollment among underrepresented groups.
Authors: Ashley S. Felix, Ph.D., of Ohio State University in Columbus, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.46494)
Editor’s ...
Opioid prescribing by surgeons
2023-12-07
About The Study: This study found that during 2016 to 2022, the rate and size of opioid prescriptions from U.S. surgeons declined, but these declines were slower after mid-2020 compared with before 2020. During the initial months of the COVID-19 pandemic, the opioid dispensing rate declined, potentially owing to decreased surgical volume, while opioid prescription size increased, potentially because surgeons wrote larger discharge prescriptions owing to barriers to obtaining refills. However, these changes were transient.
Authors: Kao-Ping ...
Improving prediction of advanced breast cancer among women of different races and ethnicities
2023-12-07
While regular screenings may decrease the chance of diagnosis of advanced breast cancer in some women and lead to a 20% reduction in breast cancer mortality, other women will be diagnosed with advanced breast cancer despite screening at regular intervals. The chances of being diagnosed with advanced breast cancer are higher among women who are Black or Hispanic/Latinx as well as women who are overweight and obese.
In a study publishing December 7, 2023 in JAMA Oncology, UC San Francisco researchers found that regular screening is not always sufficient to prevent an advanced breast cancer diagnosis. To reduce the number of advanced cancer diagnoses, ...