(Press-News.org) Sage has launched a tool to empower researchers to discover the real-world impact of their work on policy. Sage Policy Profiles lets researchers easily see specific citations of their work in policy documents and then illustrate and share that work’s impact graphically. The tool is powered by Overton, which hosts an extensive repository of global policy documents, guidelines, think-tank publications, and working papers.
The free-of-charge, browser-based tool shows researchers where their work appears in evidence-based policies, offering insights into how policymakers make use of their research. Sage Policy Profiles presents these results in a personalized dashboard from which researchers can export citations and present their policy impact visually.
"Here at Sage, we've long focused on making sure everyone outside of the social and behavioral science community can see—and make use of—the clear benefits this research brings to tackle wicked problems,” said Ziyad Marar, president of Global Publishing at Sage. “The launch of Sage Policy Profiles is really the other side of that coin, allowing researchers themselves to both see how important their work is and then be able to alert a wider audience to that very real impact,” he continued. “We believe it will help widen the research impact conversation so that it centers not just on scholarly progress but on societal good."
Additional functionalities include:
Identifying second-order citations where policies citing their work have continued to influence subsequent discussions and decisions.
Personalized alerts that inform users when cited or mentioned in new policy documents.
Exporting results into PowerPoint for presenting.
Creating a shareable link to personalized dashboards.
“The current system we have for assessing research impact and researchers has real flaws, but we don’t need to overhaul the whole thing to make meaningful improvements for researchers who want their work to be useful,” said Euan Adie, founder and managing director of Overton. “We share with Sage the belief that there are incremental improvements we can make, and Sage Policy Profiles is an important next step.”
Sage is committed to broadening how research impact is defined, shifting the focus from purely scholarly dimensions to encompass its contributions to policy, practice, and the public. Recognizing that such a transformation will require time and dedication, Sage, as an independent company, is committed to this goal for the long term.
While researchers in all disciplines can benefit from the tool, given social and behavioral sciences (SBS) outsized impact in the policy world, Sage has housed it on Social Science Space to bring attention to the unique, real-world value of SBS.
# # #
About Sage
Sage is a global academic publisher of books, journals, and library resources with a growing range of technologies to enable discovery, access, and engagement. Believing that research and education are critical in shaping society, 24-year-old Sara Miller McCune founded Sage in 1965. Today, we are controlled by a group of trustees charged with maintaining our independence and mission indefinitely.
Our guaranteed independence means we’re free to:
Do more – supporting an equitable academic future, furthering disciplines that drive social change, and helping social and behavioral science make an impact
Work together – building lasting relationships, championing diverse perspectives, and co-creating resources to transform teaching and learning
Think long-term – experimenting, taking risks, and investing in new ideas
About Overton
Overton is the world’s largest collection of policy documents, parliamentary transcripts, government guidance, and think tank research. We make this data available through the Overton.io web application, reports, and an API. Our users include funders, universities, academic journals, and journalists.
END
ITHACA, N.Y. – Cornell University researchers have released a new, open-source platform called Cascade that can run artificial intelligence models in a way that slashes expenses and energy costs while dramatically improving performance.
Cascade is designed for settings like smart traffic intersections, medical diagnostics, equipment servicing using augmented reality, digital agriculture, smart power grids and automatic product inspection during manufacturing – situations where AI models must react within a fraction of a second.
With the rise of AI, many companies are eager to leverage new capabilities but worried about the associated computing ...
Maternal inflammation risk factors may be associated with dysregulation in children, according to a study funded by the Environmental influences on Child Health Outcomes (ECHO) Program at the National Institutes of Health. “Dysregulation” in this context refers to children’s attention, anxiety and depression, and aggression being measurably different from what is typically expected at their age.
While inflammation is a normal bodily response to injury or infection, ECHO investigators wanted to learn whether factors linked ...
Around 320,000 new cases of leukaemia, a type of blood cancer that can affect all population groups, are diagnosed every year in Europe. In children, cases of leukaemia make up a third of diagnosed cancers. Chemotherapy is the main treatment for leukaemia. Often, the exact cause cannot be identified and the molecular and cellular mechanisms responsible for leukaemia remain shrouded in mystery. Discovering new detection methods and new treatments to eradicate leukaemia is therefore a major challenge in oncology.
Messenger RNA has been in the news in recent months, in connection with COVID-19 vaccinations. In an article published in Molecular Cell, researchers ...
ITHACA, N.Y. – A new study of paper wasps suggests social interactions may make animals smarter. The research offers behavioral evidence of an evolutionary link between the ability to recognize individuals and social cooperation.
Furthermore, genomic sequencing revealed that populations of wasps that recognized each other – and cooperated more – showed recent adaptations (positive selection) in areas of the brain associated with cognitive abilities such as learning, memory and vision.
The study focused on two distinct populations of paper wasps (Polistes fuscatus): A southern ...
Key to fatty liver disease and its consequences for billions of people
The global rise in obesity and diabetes is leading to an epidemic in fatty liver disease affecting 20-30 per cent of the world’s population. Almost a third of people with fatty liver disease go on to develop an advanced form of the disease, known as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) that can progress to cirrhosis and end-stage liver disease, or even liver cancer, and is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease.
Why some people remain relatively healthy with fatty liver disease and some go onto potentially life-threatening illness has been a mystery. Until now.
A study ...
From the 1950s to the 1970s, a Colombian priest named Padre Gustavo Huertas collected rocks and fossils near a town called Villa de Levya. Two of the specimens he found were small, round rocks patterned with lines that looked like leaves; he classified them as a type of fossil plant. But in a new study, published in the journal Palaeontologia Electronica, researchers re-examined these “plant” fossils and found that they weren’t plants at all: they were the fossilized remains of baby turtles.
“It was truly surprising to find these fossils,” says Héctor Palma-Castro, a paleobotany student at the Universidad Nacional de Colombia.
The plants in question ...
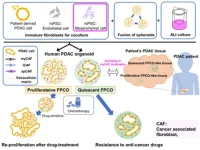
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), that arises from pancreatic epithelial cells, is the most common form of pancreatic cancer, with a very high mortality rate. This elevated mortality is associated with the unique tumor microenvironment (TME), known for increased resistance to chemotherapy and high metastatic potential. TME is characterized by the presence of a complex stromal structure comprising cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), tumor endothelial cells (TECs), and a variety of immune cells.
CAFs are specific cells, primarily involved in the overall aggressiveness and spread of cancer cells. These cells can further be categorized into several types based on their ...
DALLAS, December 7, 2023 — The Tobacco Endgame — the path to ending tobacco use and nicotine addiction in the U.S. — is within sight, but there has been a sharp increase in electronic cigarette use among high school students, from 1.5% in 2011 to about 27.4% in 2019.[1]
The American Heart Association, the world’s leading nonprofit organization focused on heart and brain health for all, is collaborating with the Association for the Treatment of Tobacco Use and Dependence (ATTUD) to change that. New individual certification as a Certified Professional by the American Heart Association – Tobacco Treatment is ...
A multidisciplinary study led by the Institute of Evolutionary Biology in Spain (a joint center of the Spanish National Research Council and Pompeu Fabra University), the University of Belgrade in Serbia, the University of Western Ontario in Canada, and Harvard University in the USA, reconstructs the genomic history of the Balkan Peninsula during the first millennium of the common era, a time and place of profound demographic, cultural and linguistic change. The team has recovered and analyzed whole genome data from 146 ancient people excavated primarily from Serbia and Croatia—more than a third of which came from the ...
Despite the Roman Empire’s extensive military and cultural influence on the nearby Balkan peninsula, a DNA analysis of individuals who lived in the region between 1 and 1000 CE found no genetic evidence of Iron Age Italian ancestry. Instead, a study published December 7 in the journal Cell revealed successive waves of migrations from Western Anatolia, central and northern Europe, and the Pontic-Kazakh Steppe during the Empire’s reign.
From the 7th century CE onwards (coincident with the fall of the Western Roman Empire), large numbers of people emigrated from Eastern Europe, likely related to the arrival of Slavic-speaking populations, which ...