(Press-News.org) The ability to transmit information coherently in the band of the electromagnetic spectrum from microwave to infrared is vitally important to the development of the advanced quantum networks used in computing and communications.
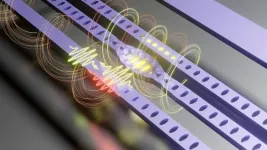
A study conducted by researchers at the State University of Campinas (UNICAMP) in Brazil, in collaboration with colleagues at ETH Zurich in Switzerland and TU Delft in the Netherlands, focused on the use of nanometric optomechanical cavities for this purpose. These nanoscale resonators promote interaction between high-frequency mechanical vibrations and infrared light at wavelengths used by the telecommunications industry.
An article on the study is published in the journal Nature Communications.
“Nanomechanical resonators act as bridges between superconducting circuits and optical fibers. Superconducting circuits are currently among the most promising technologies for quantum computing, while optical fibers are routinely used as long-distance transmitters of information with little noise and no signal loss,” said Thiago Alegre, a professor at the Gleb Wataghin Institute of Physics (IFGW-UNICAMP) and last author of the article.
According to Alegre, one of the key innovations in the study was the introduction of dissipative optomechanics. Traditional optomechanical devices rely on purely dispersive interaction, where only photons confined in the cavity are efficiently dispersed. In dissipative optomechanics, photons can be scattered directly from waveguide to resonator. “Optoacoustic interaction can be controlled more tightly as a result,” he said.
Prior to this study, dissipative optomechanical interaction had been demonstrated only at low mechanical frequencies, precluding important applications such as quantum state transfer between the photonic (optical) and phononic (mechanical) domains. The study demonstrated the first dissipative optomechanical system operating in a regime where the mechanical frequency exceeded the optical linewidth. “We succeeded in raising mechanical frequency by two orders of magnitude and achieved a tenfold rise in the optomechanical coupling rate. This offers highly promising prospects for the development of even more effective devices,” Alegre said.
Quantum networks
Fabricated in collaboration with TU Delft, the devices were designed to use technologies that are well-established in the semiconductor industry. Nanometric silicon beams were suspended and free to vibrate, so that infrared light and mechanical vibrations were confined simultaneously. A laterally placed waveguide positioned to permit the coupling of the optical fiber to the cavity gave rise to dissipative coupling, the key ingredient of the results presented by the researchers.
The study offers novel possibilities for the construction of quantum networks. In addition to this immediate application, it lays a basis for future fundamental research. “We expect to be able to manipulate mechanical modes individually and mitigate optical non-linearities in optomechanical devices,” Alegre said.
The other co-authors are André Garcia Primo, Pedro Vinícius Pinho and Gustavo Silva Wiederhecker, all of whom are also affiliated with UNICAMP; Rodrigo da Silva Benevides at ETH Zürich; and Simon Gröblacher at TU Delft. The study received funding from FAPESP via seven projects (19/09738-9, 20/15786-3, 19/01402-1, 18/15577-5, 18/15580-6, 18/25339-4 and 22/07719-0).
About São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP)
The São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) is a public institution with the mission of supporting scientific research in all fields of knowledge by awarding scholarships, fellowships and grants to investigators linked with higher education and research institutions in the State of São Paulo, Brazil. FAPESP is aware that the very best research can only be done by working with the best researchers internationally. Therefore, it has established partnerships with funding agencies, higher education, private companies, and research organizations in other countries known for the quality of their research and has been encouraging scientists funded by its grants to further develop their international collaboration. You can learn more about FAPESP at www.fapesp.br/en and visit FAPESP news agency at www.agencia.fapesp.br/en to keep updated with the latest scientific breakthroughs FAPESP helps achieve through its many programs, awards and research centers. You may also subscribe to FAPESP news agency at http://agencia.fapesp.br/subscribe.
END
Study paves way for development of advanced quantum networks
This research carried out at the State University of Campinas focused on the use of nanometric optomechanical cavities as bridges between superconducting circuits and optical fibers, with applications in computing and quantum communications
2023-12-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Sanford Burnham Prebys elects Lori Moore to its Board of Trustees
2023-12-12
Sanford Burnham Prebys today announced that Lori Moore will join the Institute’s Board of Trustees.
“With many years in health care, both as a provider and a leader, Lori brings a welcomed depth and breadth of experience,” says David A. Brenner, president and CEO of Sanford Burnham Prebys. “Her perspectives will be much valued as the Institute advances its message of translating science into health.”
Moore is a registered nurse, a fifth-generation San Diegan and a member of the Cushman family, whose philanthropic endeavors span decades. She serves as vice president of The Cushman Foundation, which supports a wide range of community ...
New study explores ways to reduce inflammation and preserve bone health with prunes
2023-12-12
A new study published in The Journal of Nutrition shows daily consumption of prunes may reduce inflammation markers connected to bone signaling pathways and reduce the effects of bone loss among postmenopausal women.
“Bone loss is a significant issue impacting more than 50% of women over the age of 50, and there is no cure,” said Principal Investigator Mary Jane De Souza, PhD, Professor, Department of Kinesiology, Pennsylvania State University. “While medications and hormone therapies are available, they often require lifelong management and come with risks. It’s ...
Cannabis exposure linked to 1.5 times higher risk of unhealthy pregnancy outcomes
2023-12-12
SALT LAKE CITY - In the past ten years, the percentage of Americans who use medical marijuana has more than doubled as state-level legalization becomes increasingly common. But despite its prevalence as a medication, the full health effects of cannabis remain unknown, especially for specific populations—such as pregnant people—that might be especially at risk of health complications.
Now, in a large study of more than 9,000 pregnant people from across the U.S., researchers at University of Utah Health have found that cannabis ...
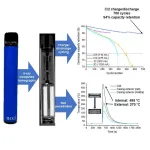
Single-use e-cigarettes contain batteries that last hundreds of cycles despite being discarded
2023-12-12
While the lithium-ion batteries in disposable electronic cigarettes are discarded after a single use, they can continue to perform at high capacity for hundreds of cycles, according to a study published December 12 in the journal Joule. The analysis, conducted by scientists from University College London (UCL) and the University of Oxford and supported by The Faraday Institution, highlights a growing environmental threat from these increasingly popular vape pens, which are not designed to be recharged.
“The surprise for us were the results that pointed toward just how long these batteries could potentially cycle,” says ...
Cannabis exposure and adverse pregnancy outcomes related to placental function
2023-12-12
About The Study: In a multicenter observational cohort, a composite adverse pregnancy outcome (small-for-gestational-age birth, medically indicated preterm birth, stillbirth, or hypertensive disorders of pregnancy) was more frequent in pregnant individuals with cannabis exposure ascertained by a urine drug assay compared with unexposed individuals. The risk for an adverse outcome was higher among those who continued to use cannabis beyond the first trimester.
Authors: Torri Metz, M.D., M.S., of University of Utah ...
Metformin plus insulin for preexisting diabetes or gestational diabetes in early pregnancy
2023-12-12
About The Study: Using metformin plus insulin to treat preexisting type 2 or gestational diabetes diagnosed early in pregnancy did not reduce a composite neonatal adverse outcome in a randomized clinical trial of 794 pregnant adults. The effect of reduction in odds of a large-for-gestational-age infant observed after adding metformin to insulin warrants further investigation.
Authors: Kim A. Boggess, M.D., of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed ...
COVID-19 symptoms and economic hardship among US families
2023-12-12
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that persistent COVID-19 symptoms and, to a lesser extent, previous severe COVID-19 were associated with increased odds of pandemic-related economic hardship in a cohort of U.S. families. The economic consequences of COVID-19 varied according to socioeconomic status; families with lower income before the pandemic were more vulnerable to employment disruptions and earnings losses associated with an adult family member’s COVID-19 illness.
Authors: Nicole L. Hair, Ph.D., of the University of South Carolina Arnold School of Public Health in Columbia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed ...
Percutaneous coronary intervention–capable facility openings and heart attack outcomes by patient race and community segregation
2023-12-12
About The Study: This study found differential benefits associated with a percutaneous coronary intervention–capable facility (PCI-CF) opening based on patient race and community segregation. Black patients in integrated communities demonstrated the greatest benefits across all outcomes, including a five times greater likelihood of receiving same-day PCI after a PCI-CF opening compared with white patients in segregated communities.
Authors: Renee Y. Hsia, M.D., M.Sc., of the University of California, San Francisco, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.47311)
Editor’s ...
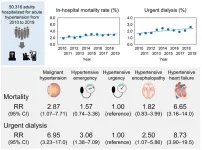
The silent killer gets louder as high blood pressure risks trend upward
2023-12-12
Research from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TDMU) warns that rates of urgent dialysis and death are on the rise over the last decade in people hospitalized for acute high blood pressure.
Tokyo, Japan – High blood pressure is called the silent killer because symptoms can remain hidden until a medical crisis strikes. You might think hypertension is no longer serious because blood pressure medication is widely available, but newly reported trends in people with dangerously high blood pressure ...
Research paves the way for predicting disease progression for incurable cancer
2023-12-12
Researchers have come one step closer to answering why, in some patients, a type of lymphoma changes from indolent to aggressive, and in particular they are closer to identifying which patients are at high risk of this change happening.
Part of the answer lies in the protein expression in the tumour, explains Associate Professor Maja Ludvigsen from the Department of Clinical Medicine at Aarhus University. Maja is one of the authors of a new study on the subject, which has just been published in the scientific journal Blood Advances.
Follicular ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
A clinical reveals that aniridia causes a progressive loss of corneal sensitivity
Fossil amber reveals the secret lives of Cretaceous ants
Predicting extreme rainfall through novel spatial modeling
The Lancet: First-ever in-utero stem cell therapy for fetal spina bifida repair is safe, study finds
Nanoplastics can interact with Salmonella to affect food safety, study shows
Eric Moore, M.D., elected to Mayo Clinic Board of Trustees
NYU named “research powerhouse” in new analysis
New polymer materials may offer breakthrough solution for hard-to-remove PFAS in water
Biochar can either curb or boost greenhouse gas emissions depending on soil conditions, new study finds
Nanobiochar emerges as a next generation solution for cleaner water, healthier soils, and resilient ecosystems
Study finds more parents saying ‘No’ to vitamin K, putting babies’ brains at risk
Scientists develop new gut health measure that tracks disease
Rice gene discovery could cut fertiliser use while protecting yields
Jumping ‘DNA parasites’ linked to early stages of tumour formation
Ultra-sensitive CAR T cells provide potential strategy to treat solid tumors
Early Neanderthal-Human interbreeding was strongly sex biased
North American bird declines are widespread and accelerating in agricultural hotspots
Researchers recommend strategies for improved genetic privacy legislation
How birds achieve sweet success
More sensitive cell therapy may be a HIT against solid cancers
Scientists map how aging reshapes cells across the entire mammalian body
[Press-News.org] Study paves way for development of advanced quantum networksThis research carried out at the State University of Campinas focused on the use of nanometric optomechanical cavities as bridges between superconducting circuits and optical fibers, with applications in computing and quantum communications