(Press-News.org) Artificial intelligence (AI) systems are often depicted as sentient agents poised to overshadow the human mind. But AI lacks the crucial human ability of innovation, researchers at the University of California, Berkeley have found.
While children and adults alike can solve problems by finding novel uses for everyday objects, AI systems often lack the ability to view tools in a new way, according to findings published according to findings published in Perspectives on Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
AI language models like ChatGPT are passively trained on data sets containing billions of words and images produced by humans. This allows AI systems to function as a “cultural technology” similar to writing that can summarize existing knowledge, Eunice Yiu, a co-author of the article, explained in an interview. But unlike humans, they struggle when it comes to innovating on these ideas, she said.
“Even young human children can produce intelligent responses to certain questions that [language learning models] cannot,” Yiu said. “Instead of viewing these AI systems as intelligent agents like ourselves, we can think of them as a new form of library or search engine. They effectively summarize and communicate the existing culture and knowledge base to us.”
Yiu and Eliza Kosoy, along with their doctoral advisor and senior author on the paper, developmental psychologist Alison Gopnik, tested how the AI systems’ ability to imitate and innovate differs from that of children and adults. They presented 42 children ages 3 to 7 and 30 adults with text descriptions of everyday objects. In the first part of the experiment, 88% of children and 84% of adults were able to correctly identify which objects would “go best” with another. For example, they paired a compass with a ruler instead of a teapot.
In the next stage of the experiment, 85% of children and 95% of adults were also able to innovate on the expected use of everyday objects to solve problems. In one task, for example, participants were asked how they could draw a circle without using a typical tool such as a compass. Given the choice between a similar tool like a ruler, a dissimilar tool such as a teapot with a round bottom, and an irrelevant tool such as a stove, the majority of participants chose the teapot, a conceptually dissimilar tool that could nonetheless fulfill the same function as the compass by allowing them to trace the shape of a circle.
When Yiu and colleagues provided the same text descriptions to five large language models, the models performed similarly to humans on the imitation task, with scores ranging from 59% for the worst-performing model to 83% for the best-performing model. The AIs' answers to the innovation task were far less accurate, however. Effective tools were selected anywhere from 8% of the time by the worst-performing model to 75% by the best-performing model.
“Children can imagine completely novel uses for objects that they have not witnessed or heard of before, such as using the bottom of a teapot to draw a circle,” Yiu said. “Large models have a much harder time generating such responses.”
In a related experiment, the researchers noted, children were able to discover how a new machine worked just by experimenting and exploring. But when the researchers gave several large language models text descriptions of the evidence that the children produced, they struggled to make the same inferences, likely because the answers were not explicitly included in their training data, Yiu and colleagues wrote.
These experiments demonstrate that AI’s reliance on statistically predicting linguistic patterns is not enough to discover new information about the world, Yiu and colleagues wrote.
“AI can help transmit information that is already known, but it is not an innovator,” Yiu said. “These models can summarize conventional wisdom but they cannot expand, create, change, abandon, evaluate, and improve on conventional wisdom in the way a young human can.” The development of AI is still in its early days, though, and much remains to be learned about how to expand the learning capacity of AI, Yiu said. Taking inspiration from children’s curious, active, and intrinsically motivated approach to learning could help researchers design new AI systems that are better prepared to explore the real world, she said.
The article, “Transmission versus truth, imitation versus innovation: what children can do that large language and language-and-vision models cannot (yet),” is available for free at https://doi.org/10.1177/17456916231201401
END
Artificial intelligence systems excel at imitation, but not innovation
2023-12-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
MSK’s Omar Abdel-Wahab honored for research targeting blood cancers
2023-12-12
Physician-scientist Omar Abdel-Wahab, MD, is being honored at the 2023 American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting with the William Dameshek Prize, which recognizes individuals who have made outstanding contributions to the field of hematology. The award will be presented December 12.
Dr. Abdel-Wahab, who chairs the Molecular Pharmacology Program at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK), was selected for his “trailblazing research” characterizing the genetic mutations that drive blood ...
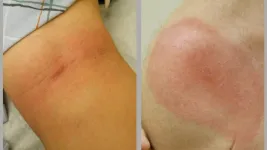
Black individuals more likely to experience inequities in early diagnosis and treatment of Lyme disease, new research shows
2023-12-12
A new study out of the Johns Hopkins Medicine Lyme Disease Research Center has revealed disparities in the diagnosis and treatment of Lyme disease between Black and White patients with the condition. Researchers say the data, which draws on participants’ medical histories, whether from Johns Hopkins Medicine or other institutions, highlights issues in the nation’s medical education on Lyme disease.
In the full article, published December 12 in JAMA Network Open, researchers say that Black patients were more likely to have advanced stages of Lyme disease when clinically diagnosed and also experience a longer time before receiving antibiotic treatment for the condition.
Lyme ...
National Academy of Inventors honors SMU professor J.-C. Chiao as fellow
2023-12-12
DALLAS (SMU) J.-C. Chiao, the Mary and Richard Templeton Centennial Chair and professor in the Electrical and Computer Engineering Department in the SMU Lyle School of Engineering, has been named a fellow of the National Academy of Inventors (NAI).
Election as an NAI fellow is the highest professional distinction awarded to academic inventors. The NAI Fellows Program highlights academic inventors who have demonstrated a spirit of innovation in creating or facilitating outstanding inventions that have made a tangible impact on quality of life, economic development and the welfare of society.
Chiao, one of 162 inventors selected for the ...
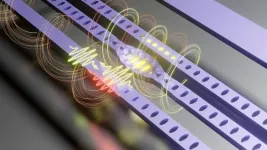
Study paves way for development of advanced quantum networks
2023-12-12
The ability to transmit information coherently in the band of the electromagnetic spectrum from microwave to infrared is vitally important to the development of the advanced quantum networks used in computing and communications.
A study conducted by researchers at the State University of Campinas (UNICAMP) in Brazil, in collaboration with colleagues at ETH Zurich in Switzerland and TU Delft in the Netherlands, focused on the use of nanometric optomechanical cavities for this purpose. These nanoscale resonators promote interaction between high-frequency ...
Sanford Burnham Prebys elects Lori Moore to its Board of Trustees
2023-12-12
Sanford Burnham Prebys today announced that Lori Moore will join the Institute’s Board of Trustees.
“With many years in health care, both as a provider and a leader, Lori brings a welcomed depth and breadth of experience,” says David A. Brenner, president and CEO of Sanford Burnham Prebys. “Her perspectives will be much valued as the Institute advances its message of translating science into health.”
Moore is a registered nurse, a fifth-generation San Diegan and a member of the Cushman family, whose philanthropic endeavors span decades. She serves as vice president of The Cushman Foundation, which supports a wide range of community ...
New study explores ways to reduce inflammation and preserve bone health with prunes
2023-12-12
A new study published in The Journal of Nutrition shows daily consumption of prunes may reduce inflammation markers connected to bone signaling pathways and reduce the effects of bone loss among postmenopausal women.
“Bone loss is a significant issue impacting more than 50% of women over the age of 50, and there is no cure,” said Principal Investigator Mary Jane De Souza, PhD, Professor, Department of Kinesiology, Pennsylvania State University. “While medications and hormone therapies are available, they often require lifelong management and come with risks. It’s ...
Cannabis exposure linked to 1.5 times higher risk of unhealthy pregnancy outcomes
2023-12-12
SALT LAKE CITY - In the past ten years, the percentage of Americans who use medical marijuana has more than doubled as state-level legalization becomes increasingly common. But despite its prevalence as a medication, the full health effects of cannabis remain unknown, especially for specific populations—such as pregnant people—that might be especially at risk of health complications.
Now, in a large study of more than 9,000 pregnant people from across the U.S., researchers at University of Utah Health have found that cannabis ...
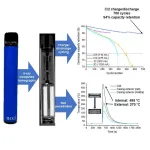
Single-use e-cigarettes contain batteries that last hundreds of cycles despite being discarded
2023-12-12
While the lithium-ion batteries in disposable electronic cigarettes are discarded after a single use, they can continue to perform at high capacity for hundreds of cycles, according to a study published December 12 in the journal Joule. The analysis, conducted by scientists from University College London (UCL) and the University of Oxford and supported by The Faraday Institution, highlights a growing environmental threat from these increasingly popular vape pens, which are not designed to be recharged.
“The surprise for us were the results that pointed toward just how long these batteries could potentially cycle,” says ...
Cannabis exposure and adverse pregnancy outcomes related to placental function
2023-12-12
About The Study: In a multicenter observational cohort, a composite adverse pregnancy outcome (small-for-gestational-age birth, medically indicated preterm birth, stillbirth, or hypertensive disorders of pregnancy) was more frequent in pregnant individuals with cannabis exposure ascertained by a urine drug assay compared with unexposed individuals. The risk for an adverse outcome was higher among those who continued to use cannabis beyond the first trimester.
Authors: Torri Metz, M.D., M.S., of University of Utah ...
Metformin plus insulin for preexisting diabetes or gestational diabetes in early pregnancy
2023-12-12
About The Study: Using metformin plus insulin to treat preexisting type 2 or gestational diabetes diagnosed early in pregnancy did not reduce a composite neonatal adverse outcome in a randomized clinical trial of 794 pregnant adults. The effect of reduction in odds of a large-for-gestational-age infant observed after adding metformin to insulin warrants further investigation.
Authors: Kim A. Boggess, M.D., of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed ...