(Press-News.org) UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Self-propelled nanoparticles could potentially advance drug delivery and lab-on-a-chip systems — but they are prone to go rogue with random, directionless movements. Now, an international team of researchers has developed an approach to rein in the synthetic particles.
Led by Igor Aronson, the Dorothy Foehr Huck and J. Lloyd Huck Chair Professor of Biomedical Engineering, Chemistry and Mathematics at Penn State, the team redesigned the nanoparticles into a propeller shape to better control their movements and increase their functionality. They published their results in the journal Small.
Due to fabrication challenges, the shape of nanoparticles has previously been limited to rods and donuts, according to Ashlee McGovern, doctoral student in chemistry at Penn State and first author on the paper. With a nanoscribe machine that can 3D print at the nanoscale in Penn State’s Materials Research Institute, McGovern experimented to optimize the nanoparticle shape. She redesigned the shape of the particles to a propeller, which can spin efficiently when triggered by a chemical reaction or magnetic field.
The propeller shape employs chirality, akin to a screw or spiral staircase, where the top face is mirrored by the bottom face.
“Shape predetermines how a particle is going to move,” McGovern said. “Chirality, or handedness, as a design feature has not been utilized enough in nanoparticle research and is a way to make the particles move in more and more complex ways.”
The chiral shape allows the particles to move in a prescribed direction, and, depending on the tilt of the blades, spin clockwise or counterclockwise in place, fueled by a chemical reaction between the metals in the nanoparticles and hydrogen peroxide.
After experimenting with different numbers and angles of fins, as well as different thicknesses, researchers found that using four or more fins at a 20-degree tilt and 3.3-micron thickness allowed for the greatest amount of stability. With three or fewer fins, the propellers exhibit uncontrolled movement.
The increased control allowed researchers to manipulate the particles to capture and transport polymer cargo particles.
“Using a magnetic field, we can steer the micropropellers to hunt down and collect cargo particles,” McGovern said. “Our lab’s rod- and donut-shaped nanoparticles would accidentally pick up cargo, but not in any controlled fashion.”
To further control the movements of the particles, researchers manipulated the rotational direction of the micropropellers.
“With the built-in flows that the particles create, we can control the particle-to-particle interactions between the two propellers,” McGovern said. “Switching the rotational direction from counterclockwise to clockwise and vice versa allows two propellers to attract or repel each other.”
Aronson, who heads the Active Biomaterials Lab in which McGovern works, emphasized the future reach of this research.
“Using tailored mechanical, magnetic and chemical responses, we can exert more control than ever before on these nanoparticles,” Aronson said. “In the future, we can leverage this control to apply this technology to design concepts for microscale devices or microrobotics.”
In addition to McGovern and Aronson, the co-authors include Mu-Jie Huang and Raymond Kapral from the University of Toronto and Jiyuan Wang from the Heilongjiang University of Science and Technology, who contributed simulation work to support the experimental research. The U.S. Department of Energy and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada partially funded this work.
Video URL: https://vimeo.com/892258599
END
Spinning up control: Propeller shape helps direct nanoparticles, researchers say
2023-12-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Karandeep Singh, MD, named inaugural Chief Health AI Officer at UC San Diego Health
2023-12-12
Karandeep Singh, MD, has been recruited as the Joan and Irwin Jacobs Endowed Chair in Digital Health Innovation at University of California School of Medicine and named as the inaugural chief health artificial intelligence (AI) officer at UC San Diego Health, a newly developed position for the region’s only academic medical center.
This new role will be effective December 29, 2023.
In this position, Singh will focus on implementing change that advances safety and health outcomes in acute and ambulatory settings. His contributions will be pivotal in bringing innovation to ...
Genetic safeguard protects some considered high risk for kidney disease
2023-12-12
NEW YORK, NY--Many Black Americans who are thought to have a high risk of developing kidney disease possess a protective genetic variant that nullifies the extra risk, a new study from Columbia researchers has found.
The study found that high-risk people who carry this variant have a risk of developing kidney disease much closer to that of the general population.
The findings will have an immediate impact on clinical practice, says study leader Simone Sanna-Cherchi, MD, associate professor of medicine at Columbia’s Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons.
“Physicians ...
Liquid biopsy predicts immunotherapy response and toxicity in patients with advanced lung cancer
2023-12-12
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Using a “liquid biopsy” to study genetic material from tumors shed into the bloodstream together with immune cells could help clinicians predict which patients with advanced lung cancers are responding to immunotherapies and which patients may develop immune-related side effects several months later, according to research directed by investigators at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center, the Bloomberg~Kimmel Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy and Allegheny Health Network Cancer Institute in Pittsburgh.
By monitoring changes in circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) among 30 patients treated with immunotherapies for metastatic non-small cell lung cancers, ...
Heavy metals in our food are most dangerous for kids
2023-12-12
WASHINGTON, DC, 2023, December 12, 2023 – The problem of foodborne metal contamination has taken on new urgency, thanks in part to a 2021 US Congressional Report detailing high levels of metals found in infant food pulled off grocery shelves. (More recently, high levels of lead were discovered in children’s fruit puree pouches.) Now, two new studies provide information on the correlation between exposure to heavy metals in food and the risk of cancers and other serious health risks. The findings will be presented ...
Artificial intelligence systems excel at imitation, but not innovation
2023-12-12
Artificial intelligence (AI) systems are often depicted as sentient agents poised to overshadow the human mind. But AI lacks the crucial human ability of innovation, researchers at the University of California, Berkeley have found.
While children and adults alike can solve problems by finding novel uses for everyday objects, AI systems often lack the ability to view tools in a new way, according to findings published according to findings published in Perspectives on Psychological Science, a journal of ...
MSK’s Omar Abdel-Wahab honored for research targeting blood cancers
2023-12-12
Physician-scientist Omar Abdel-Wahab, MD, is being honored at the 2023 American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting with the William Dameshek Prize, which recognizes individuals who have made outstanding contributions to the field of hematology. The award will be presented December 12.
Dr. Abdel-Wahab, who chairs the Molecular Pharmacology Program at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK), was selected for his “trailblazing research” characterizing the genetic mutations that drive blood ...
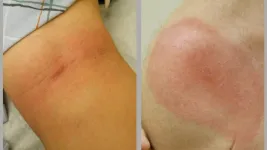
Black individuals more likely to experience inequities in early diagnosis and treatment of Lyme disease, new research shows
2023-12-12
A new study out of the Johns Hopkins Medicine Lyme Disease Research Center has revealed disparities in the diagnosis and treatment of Lyme disease between Black and White patients with the condition. Researchers say the data, which draws on participants’ medical histories, whether from Johns Hopkins Medicine or other institutions, highlights issues in the nation’s medical education on Lyme disease.
In the full article, published December 12 in JAMA Network Open, researchers say that Black patients were more likely to have advanced stages of Lyme disease when clinically diagnosed and also experience a longer time before receiving antibiotic treatment for the condition.
Lyme ...
National Academy of Inventors honors SMU professor J.-C. Chiao as fellow
2023-12-12
DALLAS (SMU) J.-C. Chiao, the Mary and Richard Templeton Centennial Chair and professor in the Electrical and Computer Engineering Department in the SMU Lyle School of Engineering, has been named a fellow of the National Academy of Inventors (NAI).
Election as an NAI fellow is the highest professional distinction awarded to academic inventors. The NAI Fellows Program highlights academic inventors who have demonstrated a spirit of innovation in creating or facilitating outstanding inventions that have made a tangible impact on quality of life, economic development and the welfare of society.
Chiao, one of 162 inventors selected for the ...
Study paves way for development of advanced quantum networks
2023-12-12
The ability to transmit information coherently in the band of the electromagnetic spectrum from microwave to infrared is vitally important to the development of the advanced quantum networks used in computing and communications.
A study conducted by researchers at the State University of Campinas (UNICAMP) in Brazil, in collaboration with colleagues at ETH Zurich in Switzerland and TU Delft in the Netherlands, focused on the use of nanometric optomechanical cavities for this purpose. These nanoscale resonators promote interaction between high-frequency ...
Sanford Burnham Prebys elects Lori Moore to its Board of Trustees
2023-12-12
Sanford Burnham Prebys today announced that Lori Moore will join the Institute’s Board of Trustees.
“With many years in health care, both as a provider and a leader, Lori brings a welcomed depth and breadth of experience,” says David A. Brenner, president and CEO of Sanford Burnham Prebys. “Her perspectives will be much valued as the Institute advances its message of translating science into health.”
Moore is a registered nurse, a fifth-generation San Diegan and a member of the Cushman family, whose philanthropic endeavors span decades. She serves as vice president of The Cushman Foundation, which supports a wide range of community ...