(Press-News.org) University of Central Florida researcher Debashis Chanda, a professor at the NanoScience Technology Center, has developed a new technique to detect photons — elementary particles that span from visible light to radio frequencies and are instrumental in carrying cellular communication.
The advancement could lead to more precise and efficient technologies in various fields, from improving medical imaging and communication systems to enhancing scientific research and even potentially bolstering security measures.
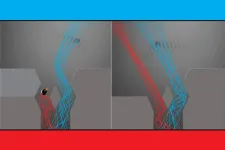
Photon detection has typically relied on change/modulation of voltage or current amplitude. But Chanda has developed a way to detect photons by modulating the frequency of an oscillating circuit, paving the path for ultra-sensitive photon detection.
Chanda’s method uses a special, phase-change material (PCM) that changes its form when light touches it, making an electrical rhythm that stays steady, or a stable electrical circuit oscillation. When a light photon hits the material, it changes how fast the rhythm goes, or shifts the oscillation frequency. How much the rhythm changes depends on how strong the light is, similar to how a person’s voice changes the sound on the radio.
The new development was published recently in Advanced Functional Materials.
Long Wave Infrared (LWIR) detection in the 8 to 12 micrometer wavelength range is extremely important in astronomy, climate science, materials analysis and security. However, LWIR detection at room temperature has been a long-standing challenge due to the low energy of photons.
LWIR detectors that are currently available can be broadly categorized into two types: cooled and uncooled detectors, with both having their own limitations.
While cooled detectors offer excellent detectivity, they require cryogenic cooling — making them expensive and limiting their practical utility. On the other hand, uncooled detectors can operate at room temperature but suffer from low detectivity and slow response due to the higher thermal noise intrinsic to room temperature operation. A low-cost, highly sensitive, fast infrared detector/camera continues to confront scientific and technological challenges.
This is the main reason LWIR cameras are not widely used except in Department of Defense and space-specific applications.
“Unlike all present photon detection schemes where light power changes the amplitude of voltage or current (amplitude modulation — AM), in the proposed scheme hits, or incidents of photons, modulate the frequency of an oscillating circuit and are detected as a frequency shift, offering inherent robustness to noises, which are AM in nature,” Chanda says.
“Our FM-based approach yields an outstanding room temperature noise equivalent power, response time and detectivity,” Chanda says. “This general FM-based photon detection concept can be implemented in any spectral range based on other phase-change materials.”
“Our results introduce this novel FM-based detector as a unique platform for creating low-cost, high-efficiency uncooled infrared detectors and imaging systems for various applications such as remote sensing, thermal imaging and medical diagnostics,” Chanda says. “We strongly believe that the performance can be further enhanced with proper industry-scale packaging.”
This concept developed by the Chanda group provides a paradigm shift to high sensitive, uncooled LWIR detection as noise limits detection sensitivity. This result promises a novel uncooled LWIR detection scheme that is high sensitive, low cost, and can be easily integrated with electronic readout circuitry, without the need for complex hybridization.
The fundamental research is funded under a U.S. National Science Foundation grant #ECCS-2015722. The camera technology is under development with funding from Chanda’s Samsung Global Research Outreach Award 2022.
Licensing Opportunity?
The technology is patented. Find out more information about licensing this technology.
Researcher’s Credentials
Chanda has joint appointments in UCF’s NanoScience Technology Center, Department of Physics and CREOL, The College of Optics and Photonics. He received his doctorate in photonics from the University of Toronto and worked as a postdoctoral fellow at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. He joined UCF in Fall 2012.
END
UCF researcher discovers new technique for photon detection
The discovery could improve communications, medical imaging, security measures and more.
2023-12-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Fat flies live longer on a diet at any age
2023-12-12
Old, obese flies get healthier and live longer if put on a diet, University of Connecticut researchers report on Dec. 8 in PNAS. If the effect holds true for humans, it would mean it’s never too late for obese people to improve their health with diet.
For way too many of us, eating too much goes along with getting old and a tendency to be obese. Different health organizations define obesity differently, but all agree it means having too much body fat, and is associated with a host of diseases related to metabolism including heart disease and diabetes. Many animal studies have shown that eating less—meaning sharply ...
European Policy Lab gathers stakeholders to map forest policy opportunities and barriers
2023-12-12
ForestPaths’ first Policy Lab convened stakeholders in Helsinki, Finland, on 27-29 September 2023. Nineteen carefully selected participants with diverse expertise – including research, policy, governance, civil society, value chain professionals, and forestry practitioners – engaged in discussions on forest-based policymaking and modelling related to climate change and biodiversity.
Tasked with considering policy actions given different timescales, governance paradigms, enablers, and barriers, participants contributed ...
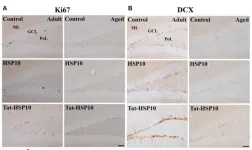
Tat-heat shock protein 10 ameliorates age-related phenotypes in the hippocampus
2023-12-12
“Mitochondrial dysfunction is a major cellular change observed in the hippocampus during aging.”
BUFFALO, NY- December 12, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 22, entitled, “Tat-heat shock protein 10 ameliorates age-related phenotypes by facilitating neuronal plasticity and reducing age-related genes in the hippocampus.”
In this new study, researchers Hyo Young Jung, Hyun Jung Kwon, Kyu ...
MIT researchers observe a hallmark quantum behavior in bouncing droplets
2023-12-12
In our everyday classical world, what you see is what you get. A ball is just a ball, and when lobbed through the air, its trajectory is straightforward and clear. But if that ball were shrunk to the size of an atom or smaller, its behavior would shift into a quantum, fuzzy reality. The ball would exist as not just a physical particle but also a wave of possible particle states. And this wave-particle duality can give rise to some weird and sneaky phenomena.
One of the stranger prospects comes from a thought experiment known as the “quantum bomb tester.” The experiment proposes that a quantum particle, such ...
Smoking causes brain shrinkage
2023-12-12
Smoking shrinks the brain, according to a study by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. The good news is that quitting smoking prevents further loss of brain tissue — but still, stopping smoking doesn’t restore the brain to its original size. Since people’s brains naturally lose volume with age, smoking effectively causes the brain to age prematurely, the researchers said.
The findings, published in Biological Psychiatry: Global Open Science, help explain why smokers are at high risk of age-related cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease.
“Up until recently, scientists have overlooked ...
Mammogram rates increase when patients schedule themselves
2023-12-12
PHILADELPHIA— Having the ability to self-schedule mammograms was associated with a 15 percentage point increase following through with getting the screening, according to research from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. The paper was published today in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine.
“Self-scheduling helps make the path to mammogram completion a little smoother, where you don’t have to find the time to call a scheduling line, wait on hold, or go back and forth trying to find an appointment that works for your schedule,” said the study’s lead author, Kimberly Waddell, ...
Protein study could one day advance Parkinson’s, breast cancer care
2023-12-12
PORTLAND, Oregon -- New research from Oregon Health & Science University could one day lead to therapies that prevent or treat diseases and infections tied to a protein that’s found in all human cells.
A study published today in the journal Molecular Cell describes how the protein ubiquitin is modified during a bacterial infection. The study details the steps taken to create a form of the protein known as lysine 6 polyubiquitin, where a long chain of ubiquitin molecules are linked through ...
Study exposes opportunities for strengthening cancer drugs trials in China
2023-12-12
More than one-eighth of the randomized trials of cancer drugs seeking regulatory approval in China in recent years used inappropriate controls to test the effectiveness and safety of the drugs, according to a new study published December 12th in the open access journal PLOS Medicine by Professor Xiaodong Guan of Peking University, China, and colleagues.
In randomized trials, patients are assigned to either a control arm, in which they receive the current optimal treatment, or an experimental arm, in which they receive the new drug being tested. However, studies have previously ...
Zapping manure with special electrode promises an efficient method to produce fertilizers, other chemicals
2023-12-12
MADISON – An interdisciplinary team led by University of Wisconsin–Madison scientists has developed a new technique that could help farmers extract useful nutrients such as ammonia and potassium from livestock manure to efficiently make fertilizer and other useful chemical products. While the strategy still needs to be scaled up beyond a proof-of-concept stage, the group's preliminary analyses show it could offer considerable benefits by cutting water and air pollution while simultaneously creating products that farmers could use or sell.
Manure stinks in part because it contains ammonia, one of the more ...
Novel early-detection method aims to stem disease spread in animal trade
2023-12-12
DENVER/Dec. 12, 2023 – A new article published in the journal Methods in Ecology and Evolution by Morris Animal Foundation-funded researchers describes a simplified method to detect a deadly fungus killing European salamanders. The ability to rapidly find the fungus is significant as the disease, although not detected in the U.S., could impact the millions of amphibians and salamanders annually imported.
The fungal pathogen Batrachochytrium salamandrivorans, or Bsal, threatens salamander diversity. Initially identified in northern Europe, evidence suggests it was introduced from Southeast Asia via the pet trade.
“The impacts of Bsal ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
Researchers find that landowner trust, experience influence feral hog management
Breaking down the battery problem
ACMG Foundation to present adaptive bikes to Baltimore-area children with genetic conditions at heartwarming “Day of Caring” event on March 13
Racial disparities in food insecurity for high- and low-income households
Incidence of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest on a postholiday weekday
Prior authorization bans for buprenorphine alone may not improve treatment retention
When light boosts protein evolution
New model may predict preeclampsia in late pregnancy
Lifestyle medicine experts call meaning, purpose, and spirituality foundational to evidence-based, whole-person lifestyle change
Significant acceleration of global warming since 2015
FAU awarded $2.4M NIH grant to study immune signaling and social behavior
Deep learning-enabled virtual multiplexed immunostaining of label-free tissue for vascular invasion assessment
New PET imaging study reveals how ketamine relieves treatment-resistant depression
New study reveals differences between anime bamboo muzzle and actual bamboo
The ‘Great Texas Freeze’ killed thousands of purple martins; biologists worry recovery could take decades
Cancer has a unique nuclear metabolic fingerprint
Tiny thermometers offer on-chip temperature monitoring for processors
New compound stops common complications after intestinal surgery
Breaking through water treatment limits with defect-free, high-efficiency next-generation ceramic filters!
Researchers determine structural motifs of water undecamer cluster
Researchers enhance photocatalytic hydrogen evolution performance of covalent organic frameworks by constitutional isomer strategy
Molecular target drives immunogenicity in cancer immunotherapy
Plant cell structure could hold key to cancer therapies and improved crops
Sustainable hydrogen peroxide production: Breakthroughs in electrocatalyst design for on-site synthesis
[Press-News.org] UCF researcher discovers new technique for photon detectionThe discovery could improve communications, medical imaging, security measures and more.