(Press-News.org) ForestPaths’ first Policy Lab convened stakeholders in Helsinki, Finland, on 27-29 September 2023. Nineteen carefully selected participants with diverse expertise – including research, policy, governance, civil society, value chain professionals, and forestry practitioners – engaged in discussions on forest-based policymaking and modelling related to climate change and biodiversity.
Tasked with considering policy actions given different timescales, governance paradigms, enablers, and barriers, participants contributed observations essential for ForestPaths' modelling and data objectives, as well as for the project’s forest-based policy pathways for climate change mitigation. They deliberated on the effects of climate change on forest ecosystems, potential outlooks, associated risks and scenarios, policy trajectories, and the utilisation of forest modelling as an analytical tool.
The project’s Policy Lab embodied an innovative approach for fostering strategic and forward-thinking insights, making use of cross-disciplinary perspectives to strengthen policymaking. The most noteworthy take-home messages included a desire for more sustainable and circular forestry products, a call for the inclusion of long-term forest considerations in policies, and the significance of providing practical guidance to forest managers through advisors to ensure regulatory compliance.
After the Policy Lab, upon being asked for his opinion on the event, Michael Salka (Institute for Advanced Architecture of Catalonia) stated:
“It is no easy feat to convene a dialogue broadly representing forest value chains when every forest is unique and the demand side sectors range from paper products to large wood buildings. The first ForestPaths Policy Lab excelled in distilling specific, synergetic policy priorities for a circular bioeconomy from such complex, multi-dimensional conversations. I look forward to discovering how these priorities become actions through the next events."
The feedback and lessons learnt from this first event will be built upon in the remaining Policy Labs, which aim to:
Second Policy Lab (September 2024): Elicit medium and long-term visions of European forests and the forest-based sector and policy actions to achieve them;
Third Policy Lab (September 2025): Co-examine initial pathways results;
Fourth Policy Lab (October 2026): Provide policy recommendations derived from the pathway analysis and evaluation.
Following the successful completion of the first Policy Lab, ForestPaths’ co-creation process continues with the project’s online Policy Engagement Forum, enabling a wider array of stakeholders to join the conversation.
******************************************************
ForestPaths (Co-designing Holistic Forest-based Policy Pathways for Climate Change Mitigation) receives funding from the European Union’s Horizon Europe Research and Innovation Programme (ID No 101056755), as well as from the United Kingdom Research and Innovation Council (UKRI). Views and opinions expressed are however those of the author(s) only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or the European Commission. Neither the European Union nor the granting authority can be held responsible for them.
END
European Policy Lab gathers stakeholders to map forest policy opportunities and barriers
The Horizon Europe project ForestPaths held its first Policy Lab collecting stakeholders’ main priorities regarding the opportunities and barriers for forest-based policymaking.
2023-12-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
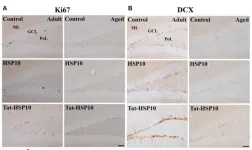
Tat-heat shock protein 10 ameliorates age-related phenotypes in the hippocampus
2023-12-12
“Mitochondrial dysfunction is a major cellular change observed in the hippocampus during aging.”
BUFFALO, NY- December 12, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 22, entitled, “Tat-heat shock protein 10 ameliorates age-related phenotypes by facilitating neuronal plasticity and reducing age-related genes in the hippocampus.”
In this new study, researchers Hyo Young Jung, Hyun Jung Kwon, Kyu ...
MIT researchers observe a hallmark quantum behavior in bouncing droplets
2023-12-12
In our everyday classical world, what you see is what you get. A ball is just a ball, and when lobbed through the air, its trajectory is straightforward and clear. But if that ball were shrunk to the size of an atom or smaller, its behavior would shift into a quantum, fuzzy reality. The ball would exist as not just a physical particle but also a wave of possible particle states. And this wave-particle duality can give rise to some weird and sneaky phenomena.
One of the stranger prospects comes from a thought experiment known as the “quantum bomb tester.” The experiment proposes that a quantum particle, such ...
Smoking causes brain shrinkage
2023-12-12
Smoking shrinks the brain, according to a study by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. The good news is that quitting smoking prevents further loss of brain tissue — but still, stopping smoking doesn’t restore the brain to its original size. Since people’s brains naturally lose volume with age, smoking effectively causes the brain to age prematurely, the researchers said.
The findings, published in Biological Psychiatry: Global Open Science, help explain why smokers are at high risk of age-related cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease.
“Up until recently, scientists have overlooked ...
Mammogram rates increase when patients schedule themselves
2023-12-12
PHILADELPHIA— Having the ability to self-schedule mammograms was associated with a 15 percentage point increase following through with getting the screening, according to research from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. The paper was published today in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine.
“Self-scheduling helps make the path to mammogram completion a little smoother, where you don’t have to find the time to call a scheduling line, wait on hold, or go back and forth trying to find an appointment that works for your schedule,” said the study’s lead author, Kimberly Waddell, ...
Protein study could one day advance Parkinson’s, breast cancer care
2023-12-12
PORTLAND, Oregon -- New research from Oregon Health & Science University could one day lead to therapies that prevent or treat diseases and infections tied to a protein that’s found in all human cells.
A study published today in the journal Molecular Cell describes how the protein ubiquitin is modified during a bacterial infection. The study details the steps taken to create a form of the protein known as lysine 6 polyubiquitin, where a long chain of ubiquitin molecules are linked through ...
Study exposes opportunities for strengthening cancer drugs trials in China
2023-12-12
More than one-eighth of the randomized trials of cancer drugs seeking regulatory approval in China in recent years used inappropriate controls to test the effectiveness and safety of the drugs, according to a new study published December 12th in the open access journal PLOS Medicine by Professor Xiaodong Guan of Peking University, China, and colleagues.
In randomized trials, patients are assigned to either a control arm, in which they receive the current optimal treatment, or an experimental arm, in which they receive the new drug being tested. However, studies have previously ...
Zapping manure with special electrode promises an efficient method to produce fertilizers, other chemicals
2023-12-12
MADISON – An interdisciplinary team led by University of Wisconsin–Madison scientists has developed a new technique that could help farmers extract useful nutrients such as ammonia and potassium from livestock manure to efficiently make fertilizer and other useful chemical products. While the strategy still needs to be scaled up beyond a proof-of-concept stage, the group's preliminary analyses show it could offer considerable benefits by cutting water and air pollution while simultaneously creating products that farmers could use or sell.
Manure stinks in part because it contains ammonia, one of the more ...
Novel early-detection method aims to stem disease spread in animal trade
2023-12-12
DENVER/Dec. 12, 2023 – A new article published in the journal Methods in Ecology and Evolution by Morris Animal Foundation-funded researchers describes a simplified method to detect a deadly fungus killing European salamanders. The ability to rapidly find the fungus is significant as the disease, although not detected in the U.S., could impact the millions of amphibians and salamanders annually imported.
The fungal pathogen Batrachochytrium salamandrivorans, or Bsal, threatens salamander diversity. Initially identified in northern Europe, evidence suggests it was introduced from Southeast Asia via the pet trade.
“The impacts of Bsal ...
EMBO launches new award for sustainability in the lab
2023-12-12
EMBO launches a new award for laboratory sustainability: The EMBO Lab Sustainability Award will recognize new and significant contributions to the development of sustainable wet and dry labs with a focus on their environmental impact. The award will be presented to an individual representing the initiative or project. Applications can be submitted between 15 January and 15 March 2024.
The award winner will have the opportunity to present their initiative or project at scientific events and publish a commentary in EMBO Reports. In addition, the winning project will be supported with a grant of 10,000 euros. The award is one of ...
Clinical trial finds cell therapy improves quality of life in advanced heart failure
2023-12-12
ROCHESTER, Minn. — Stem cell-based therapy improved quality of life for patients with advanced heart failure, Mayo Clinic researchers and international collaborators discovered in a late-stage multinational clinical trial. In one of the largest studies of cell intervention after a heart attack, patients reported their daily hardship lessened when stem cells optimized for heart repair supplemented standard of care. This clinical study further documented lower death and hospitalization rates among those treated with cell therapy. This research ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
[Press-News.org] European Policy Lab gathers stakeholders to map forest policy opportunities and barriersThe Horizon Europe project ForestPaths held its first Policy Lab collecting stakeholders’ main priorities regarding the opportunities and barriers for forest-based policymaking.