Study analyzes what babies hear, say on six continents
Talk from adults stood out as key contributor to early childhood speech; no effects found related to socioeconomics
2023-12-13
(Press-News.org)
Elika Bergelson, associate professor of psychology at Harvard University, studies how infants and toddlers learn language from the world around them. The developmental psychologist specifically strives to parse the various theories that account for the onset and eventual mastery of language comprehension and production. Bergelson’s latest paper, published this month in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, represents a more global approach to developing and testing such theories.
Written with Alejandrina Cristia at the École normale supérieure, PSL University and 11 others, the paper is based on an extremely large sample of two- to 48-month olds. Day-long audio recordings captured the babbling and baby talk of 1,001 children representing 12 countries and 43 languages. Analysis was completed with the help of machine learning.
Results show that the main predictors of language development are age, clinical factors such as prematurity or dyslexia, and how much speech children receive from the world around them. In contrast to previous research, no effects were found related to gender, multilingualism, or socioeconomics.
The study was able to simultaneously consider many variables that are usually looked at separately while also considering how big their effects were. "Notably, it wasn't just child factors like age or risk for language delay that mattered, but a key environmental factor too: how much speech children heard from adults,” Bergelson said. “For every 100 adult vocalizations children heard per hour, they produced 27 more vocalizations themselves, and this effect grew with age."
The work also touches on well-worn critiques of low-income parents and caregivers. “There's been much debate and discussion in the literature in recent years about how socioeconomic status does or doesn't link to language input and language output,” noted Bergelson. “We looked in many, many, many different ways … In no form did we ever find evidence that moms with more education had kids who produced more speech in these tens of thousands of hours of recordings from daily life.”
Financial support for the study was provided by the National Science Foundation, National Institutes of Health, and the National Endowment for the Humanities, among others.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-12-13
DALLAS, Dec. 13, 2023 — The winter holidays can turn deadly as research shows that more people die from heart attacks during the last week of December than at any other time of the year. While being aware of the signs of a heart attack and taking steps to reduce your risk are important all year long, the American Heart Association, the world’s leading voluntary organization focused on heart and brain health for all, says that’s especially critical during the next few weeks.
A number of scientific studies confirm ...
2023-12-13
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center’s Research Highlights showcases the latest breakthroughs in cancer care, research and prevention. These advances are made possible through seamless collaboration between MD Anderson’s world-leading clinicians and scientists, bringing discoveries from the lab to the clinic and back.
Recent developments at MD Anderson include a novel blood-based test to predict lung cancer relapses, improved detection of genes associated with complex traits, insights into how B cell activity influences immunodeficiency, novel targets that drive treatment ...
2023-12-13
The most comprehensive analysis of Indigenous Australians’ genomes collected to date has revealed an “abundance” of DNA variations – some of which have never been reported anywhere else in the world – paving the way for new, personalised treatments that address health inequities for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples.
A team of Australian researchers, led by scientists from The Australian National University (ANU), found DNA differences between Indigenous Australians living in the Tiwi Islands and Indigenous peoples living in the Australian ...
2023-12-13
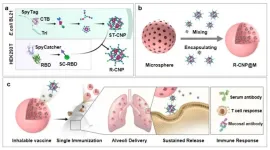
Researchers from the Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have proposed a new “nano-micro composite” delivery concept for vaccines. Based on this idea, they have developed a single-dose, dry-powder, inhalable vaccine platform using nano-micro composite multilevel structures, which has been successfully prepared in the laboratory, and the vaccine has been shown to be effective in blocking respiratory viral infection and transmission in animal models. This platform holds great promise for combating future emerging and epidemic infectious diseases.
This ...
2023-12-13
Cannabis use for medicinal or recreational purposes is now permitted is most states in the U.S. Many of the products sold in dispensaries contain delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (better known as “THC”), and are thus classified as Schedule I drugs, making them illegal under federal law.
However, there is a parallel market for products derived from hemp—defined as cannabis containing less that 0.3 percent THC—spurred in part by the passage of the 2018 Farm Bill, which removed hemp-derived cannabinoids from the federal Controlled Substances Act.
A new U-M study published in JAMA Network Open examines past-year use of some of these hemp-derived ...
2023-12-13
PHILADELPHIA— New research reveals that neurons in the preoptic hypothalamus—the region of the brain that regulates sleep and body temperature—are rhythmically activated during non-rapid eye movement sleep (NREM). Stress activates these brain cells out of turn, causing “microarousals,” that interrupt sleep cycles and decrease the duration of sleep episodes, according to research from Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, published today in Current Biology.
While our bodies are at rest when we are asleep, ...
2023-12-13
By Jake Siegel
Imagine you’re teaching a dog to play fetch. You throw a ball, and your dog sprints after it, picks it up, and runs back. You then reward your panting pup with a treat. But now comes the real trick for your dog: figuring out which part of that sequence earned the treat. Scientists call this the 'credit assignment problem' in the brain. It's a fundamental question about understanding which actions are responsible for the positive outcomes we experience.
Dopamine, a key chemical ...
2023-12-13
LA JOLLA (December 14, 2023)—Salk Institute researchers, as part of a worldwide initiative to revolutionize scientists’ understanding of the brain, analyzed more than 2 million brain cells from mice to assemble the most complete atlas ever of the mouse brain. Their work, published December 14, 2023 in a special issue of Nature, not only details the thousands of cell types present in the brain but also how those cells connect and the genes and regulatory programs that are active in each cell.
The efforts were coordinated by the National Institutes of Health’s Brain Research Through Advancing Innovative Neurotechnologies® Initiative, or the BRAIN Initiative®, ...
2023-12-13
By Jake Siegel
Six years and 32 million cells later, scientists have created the first full cellular map of a mammalian brain. In a set of 10 papers in Nature today, a network of researchers unveiled an atlas cataloging the location and type of every cell in the adult mouse brain. Using advanced technologies that profile individual cells, the teams identified over 5,300 cell types – far more than known before – and pinpointed their locations within the brain’s intricate geography. ...
2023-12-13
SAN FRANCISCO—December 13, 2023—In a study of historic scale, scientists at Gladstone Institutes have created an intricate map of how the immune system functions, examining the detailed molecular structures governing human T cells using the next-generation CRISPR tool known as base editing.
Their findings, published in Nature, uncover detailed information that could help overcome the limitations of today’s immunotherapies and identify new drug targets for a wide range of diseases, including autoimmune diseases and cancer.
Led by Gladstone Senior Investigator Alex Marson, MD, PhD, the team dove deep into the DNA of T cells, pinpointing ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Study analyzes what babies hear, say on six continents
Talk from adults stood out as key contributor to early childhood speech; no effects found related to socioeconomics