(Press-News.org) DALLAS, Dec. 13, 2023 — The winter holidays can turn deadly as research shows that more people die from heart attacks during the last week of December than at any other time of the year. While being aware of the signs of a heart attack and taking steps to reduce your risk are important all year long, the American Heart Association, the world’s leading voluntary organization focused on heart and brain health for all, says that’s especially critical during the next few weeks.
A number of scientific studies confirm this deadly phenomenon.
A study published in Circulation, the flagship journal of the American Heart Association, reported that more cardiac deaths occur in the U.S. on December 25 than on any other day of the year, followed by December 26 and January 1.
In a British Medical Journal study reviewing more than 16 years of data on heart attacks among people in Sweden, there was a 15% overall increase in heart attacks during the winter holidays. Of particular note, heart attacks increased 37% on Dec. 24 (Christmas Eve), peaking at 10 p.m. and more often in people over 75 and those with diabetes or previous cardiovascular disease.
A study presented at the British Cardiovascular Society meeting in June supported previous research finding more serious heart attacks occur on Mondays than any other day of the week. This year, Dec. 25 (Christmas Day) falls on a Monday.
"No one wants to think of tragedy during this joyous time of year as we gather with family and friends. However, these startling facts are very sobering. We don’t know exactly what triggers this increase in heart attacks during the holidays, it’s likely a combination of factors,” said Johanna Contreras, M.D., M.Sc., FAHA, clinical volunteer for the American Heart Association and a cardiologist at Mt. Sinai Hospital System in New York City. “Winter weather has been noted to increase heart attack risk due to restricted blood flow when arteries may be constricted in cold temperatures. We also know the holidays bring a lot of added stress to many people. There are lots of parties and family gatherings where many tend to overindulge in rich foods and drink.”
According to Contreras, one of the most critical factors might be that people ignore important warning signs of a heart attack or stroke.
“While you may not want to spend the holidays in a doctor’s office or hospital, getting checked out and receiving prompt treatment if there is a problem is one of the best gifts you can give yourself and your loved ones for all the celebrations to come,” she said.
Giving the gift of life may also come into play if you see someone experiencing heart attack or stroke symptoms. You could be out shopping at the mall, enjoying the sights and sounds of the holiday season or spending time at a family gathering and witness someone having a heart attack and going into cardiac arrest. Starting CPR immediately and calling 9-1-1 could be the difference in life or death in those situations.
“Hands-Only CPR is something nearly everyone can learn and do. We encourage at least one person in every family to learn CPR because statistics show that most cardiac arrests occur outside the hospital and often in the home,” Contreras said. “The American Heart Association has a short instructional video at Heart.org/HandsOnlyCPR. Watching the video and learning Hands-Only CPR could be a lifesaving and lifechanging activity for the family to do together as you’re gathered for the holidays.”
Contreras notes that family gatherings are also a good time to talk about family health history.
“Many of the health factors that impact heart disease and stroke are heredity,” she said. “If any of your parents, siblings or grandparents have had a heart attack or stroke, you are likely at higher risk, too. But the good news is, you can lower your risk with preventive measures. Knowing that history is an important first step.”
Following are several heart-healthy tips for the upcoming holidays:
Know symptoms and take action: Heart attack signs and stroke symptoms vary in men and women and it’s important to recognize them early and call 9-1-1 for help. The sooner medical treatment begins, the better the chances of survival and preventing heart damage.
Celebrate in moderation Eating healthfully during the holidays doesn’t have to mean depriving yourself, there are still ways to eat smart. Look for small, healthy changes and swaps you can make so you continue to feel your best while eating and drinking in moderation, and don’t forget to watch your salt intake.
Plan for peace on earth and goodwill toward yourself: Make time to take care of yourself during the busy holiday. Reduce stress from family interactions, strained finances, hectic schedules and other stressors prevalent this time of year, including traveling.
Keep moving: The American Heart Association recommends at least 150 minutes of physical activity per week and this number usually drops during the hustle and bustle of the holidays. Get creative with ways to stay active, even if it’s going for a family walk or another fun activity you can do with your loved ones.
Stick to your meds: Busy holidays can cause you to skip medications, forgetting them when away from home or not getting refills in a timely manner. The American Heart Association has a medication chart to help stay on top of it, and be sure to keep tabs on your blood pressure numbers.
“We do know there are ways to mitigate your risk for a deadly heart attack. So, we encourage everyone to pause during the holiday hustle and bustle and make note of these important steps that could be lifesaving,” Contreras said.
The American Heart Association has more on ways to live heart-healthy during the holidays and all year long at heart.org.
Additional Resources:
Multimedia is available in the right column of the release link.
Spanish news release
AHA health resources: Heart attack warning-signs infographic
AHA health resources: Stress Management infographic
AHA health resources: Season's Healing: 5 Tips to Reduce Holiday Stress | American Heart Association
AHA health resources: Holiday Stress? Try Our Top 5 Tips for a Healthy Holiday Season
AHA health resources: 5 Tips to Host a Heart-Healthy Holiday Party | American Heart Association
AHA news release: Make a list, check it twice with these heart-healthy holiday travel hacks.
AHA health resources: Join the Nation of Lifesavers
Studies published in the American Heart Association’s scientific journals are peer-reviewed. The statements and conclusions in each manuscript are solely those of the study authors and do not necessarily reflect the Association’s policy or position. The Association makes no representation or guarantee as to their accuracy or reliability. The Association receives funding primarily from individuals; foundations and corporations (including pharmaceutical, device manufacturers and other companies) also make donations and fund specific Association programs and events. The Association has strict policies to prevent these relationships from influencing the science content. Revenues from pharmaceutical and biotech companies, device manufacturers and health insurance providers and the Association’s overall financial information are available here.
###
About the American Heart Association
The American Heart Association is a relentless force for a world of longer, healthier lives. We are dedicated to ensuring equitable health in all communities. Through collaboration with numerous organizations, and powered by millions of volunteers, we fund innovative research, advocate for the public’s health and share lifesaving resources. The Dallas-based organization has been a leading source of health information for nearly a century. Connect with us on heart.org, Facebook, X or by calling 1-800-AHA-USA1.
END
Heart attack deaths spike during the winter holidays
The American Heart Association urges people to be aware of and reduce risks for deadly ‘holiday heart attacks’
2023-12-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
MD Anderson Research Highlights for December 13, 2023
2023-12-13
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center’s Research Highlights showcases the latest breakthroughs in cancer care, research and prevention. These advances are made possible through seamless collaboration between MD Anderson’s world-leading clinicians and scientists, bringing discoveries from the lab to the clinic and back.
Recent developments at MD Anderson include a novel blood-based test to predict lung cancer relapses, improved detection of genes associated with complex traits, insights into how B cell activity influences immunodeficiency, novel targets that drive treatment ...
DNA discovery opens door to personalised medicine for Indigenous Australians
2023-12-13
The most comprehensive analysis of Indigenous Australians’ genomes collected to date has revealed an “abundance” of DNA variations – some of which have never been reported anywhere else in the world – paving the way for new, personalised treatments that address health inequities for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples.
A team of Australian researchers, led by scientists from The Australian National University (ANU), found DNA differences between Indigenous Australians living in the Tiwi Islands and Indigenous peoples living in the Australian ...
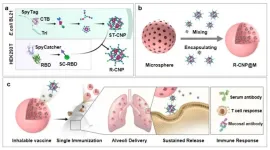
Researchers develop a novel dry-powder inhaled vaccine platform
2023-12-13
Researchers from the Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have proposed a new “nano-micro composite” delivery concept for vaccines. Based on this idea, they have developed a single-dose, dry-powder, inhalable vaccine platform using nano-micro composite multilevel structures, which has been successfully prepared in the laboratory, and the vaccine has been shown to be effective in blocking respiratory viral infection and transmission in animal models. This platform holds great promise for combating future emerging and epidemic infectious diseases.
This ...
Growing use of hemp-derived alternative cannabis products containing CBD, Delta-8-THC, CBG, CBN
2023-12-13
Cannabis use for medicinal or recreational purposes is now permitted is most states in the U.S. Many of the products sold in dispensaries contain delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (better known as “THC”), and are thus classified as Schedule I drugs, making them illegal under federal law.
However, there is a parallel market for products derived from hemp—defined as cannabis containing less that 0.3 percent THC—spurred in part by the passage of the 2018 Farm Bill, which removed hemp-derived cannabinoids from the federal Controlled Substances Act.
A new U-M study published in JAMA Network Open examines past-year use of some of these hemp-derived ...
Penn Medicine research shows how stress activates neurons that disrupt sleep
2023-12-13
PHILADELPHIA— New research reveals that neurons in the preoptic hypothalamus—the region of the brain that regulates sleep and body temperature—are rhythmically activated during non-rapid eye movement sleep (NREM). Stress activates these brain cells out of turn, causing “microarousals,” that interrupt sleep cycles and decrease the duration of sleep episodes, according to research from Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, published today in Current Biology.
While our bodies are at rest when we are asleep, ...
New study sheds light on how the brain learns to seek reward
2023-12-13
By Jake Siegel
Imagine you’re teaching a dog to play fetch. You throw a ball, and your dog sprints after it, picks it up, and runs back. You then reward your panting pup with a treat. But now comes the real trick for your dog: figuring out which part of that sequence earned the treat. Scientists call this the 'credit assignment problem' in the brain. It's a fundamental question about understanding which actions are responsible for the positive outcomes we experience.
Dopamine, a key chemical ...
Salk teams assemble first full epigenomic cell atlas of the mouse brain
2023-12-13
LA JOLLA (December 14, 2023)—Salk Institute researchers, as part of a worldwide initiative to revolutionize scientists’ understanding of the brain, analyzed more than 2 million brain cells from mice to assemble the most complete atlas ever of the mouse brain. Their work, published December 14, 2023 in a special issue of Nature, not only details the thousands of cell types present in the brain but also how those cells connect and the genes and regulatory programs that are active in each cell.
The efforts were coordinated by the National Institutes of Health’s Brain Research Through Advancing Innovative Neurotechnologies® Initiative, or the BRAIN Initiative®, ...
Scientists unveil first complete cellular map of adult mouse brain
2023-12-13
By Jake Siegel
Six years and 32 million cells later, scientists have created the first full cellular map of a mammalian brain. In a set of 10 papers in Nature today, a network of researchers unveiled an atlas cataloging the location and type of every cell in the adult mouse brain. Using advanced technologies that profile individual cells, the teams identified over 5,300 cell types – far more than known before – and pinpointed their locations within the brain’s intricate geography. ...
Using next-gen CRISPR tool, Gladstone scientists create unprecedented molecular map of human immune response
2023-12-13
SAN FRANCISCO—December 13, 2023—In a study of historic scale, scientists at Gladstone Institutes have created an intricate map of how the immune system functions, examining the detailed molecular structures governing human T cells using the next-generation CRISPR tool known as base editing.
Their findings, published in Nature, uncover detailed information that could help overcome the limitations of today’s immunotherapies and identify new drug targets for a wide range of diseases, including autoimmune diseases and cancer.
Led by Gladstone Senior Investigator Alex Marson, MD, PhD, the team dove deep into the DNA of T cells, pinpointing ...
Discovery of magnetic liquid crystal
2023-12-13
Liquid crystal is a state of matter that exhibits properties of both liquid and solid. It can flow like a liquid, while its constituent molecules are aligned as in a solid. The liquid crystal is widely used nowadays, for example, as a core element of LCD devices. The magnetic analog of this kind of material is dubbed the “spin-nematic phase”, where spin moments play the role of the molecules. However, it has not yet been directly observed despite its prediction a half-century ago. The main challenge stems ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
[Press-News.org] Heart attack deaths spike during the winter holidaysThe American Heart Association urges people to be aware of and reduce risks for deadly ‘holiday heart attacks’