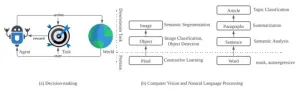
(Press-News.org) Transformer architectures have facilitated the development of large-scale and general-purpose sequence models for prediction tasks in natural language processing and computer vision, e.g., GPT-3 and Swin Transformer. Although originally designed for prediction problems, it is natural to inquire about their suitability in another important field, sequential decision-making and reinforcement learning problems, which are typically beset by long-standing issues involving sample efficiency, credit assignment, and partial observability, etc. In recent years, sequence models, especially the Transformer, have attracted increasing interest in the RL communities, spawning numerous approaches with notable effectiveness and generalizability. To inspire more investigation into this trending topic and empower more real-world applications, e.g., robotics, automatic vehicles, and the automated industry, a research team led by Muning WEN published their survey on 15 Dec 2023 in Frontiers of Computer Science co-published by Higher Education Press and Springer Nature.
This survey presents a comprehensive overview of recent works aimed at solving sequential decision-making tasks with sequence models such as the Transformer, by discussing the connection between sequential decision-making and sequence modeling, and categorizing them based on the way they utilize the Transformer. These works suggest the potential for constructing a large decision model for general purposes, that is, a large sequence model that can harness a vast number of parameters to perform hundreds or more sequential decision-making tasks, analogous to the way in which large sequence models have been leveraged for NLP and CV.
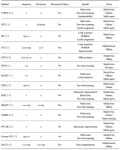
To examine the development of the Transformer in the field of sequential decision-making, the authors summarized recent works that converting the reinforcement learning problem into sequential form to leverage sequence models for specific reinforcement learning settings, as shown below:
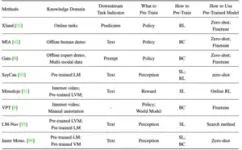
Beside, the authors summary methods leveraging diverse data to pre-train a large-scale sequence model for various downstream sequential decision-making tasks, inspired by the tremendous success of NLP and CV, as shown below:
At the end, the team puts forth various potential avenues for future research intending to improve the effectiveness of large sequence models for sequential decision-making, encompassing theoretical foundations, network architectures, algorithms, and efficient training systems, hoping this survey could inspire more investigation into this trending topic.
DOI: 10.1007/s11704-023-2689-5
END
Large sequence models for sequential decision-making
2023-12-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New red galaxies turn out to be already known blue galaxies
2023-12-15
Not all discoveries turn out to be actual new discoveries. This was the case for the extremely red objects (EROs) found in James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) data. Analysis shows that they are very similar to blue-excess dust obscured galaxies (BluDOGs) already reported in Subaru Telescope data.
Quasars, some of the brightest objects in the Universe, are driven by a supermassive black hole with a mass that can reach more than a billion times that of the Sun. These objects are the focus of much research, but how ...
HKUST researchers report the high-res structure of a cyanobacterial virus
2023-12-15
A research team at the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) has outlined the high-resolution structure of a little-known virus, improving our understanding of viral infection, which could pave the way for more accurate predictions of climate change.
With the help of an advanced technique involving cryo-electron microscopy, they managed to capture images of the virus – the cyanophage P-SCSP1u – at near-atomic resolution in its native form and examined it to see how its different parts fit together. This helped show how different proteins work in the virus and how they interact to make the virus ...
Advanced GNSS technique enhances accuracy in landslide monitoring
2023-12-15
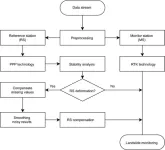
In a new study published on 13 November 2023, in the journal Satellite Navigation, researchers from Chang’an University have developed a novel approach using the Precise Point Positioning (PPP) technique combined with a cumulative sum control chart (CUSUM) method. This method enables the analysis of reference station stability and compensates for deformation at monitoring stations.
In the study conducted at the Tengqing landslide in Liupanshui, Guizhou Province, Southwest China, an innovative method was applied, showcasing a significant leap in landslide monitoring using GNSS PPP technology. ...
Risk of death reduces after COVID-19 vaccine but protection wanes after six months – study
2023-12-15
The risk of death from COVID-19 decreases significantly after vaccination but this protection diminishes after six months, providing evidence for continued booster doses, a new study has found.
Researchers from the UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA) analysed more than 10 million cases of COVID-19 in adults between May 2020 and February 2022. Their findings are published in the Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine (JRSM).
The Case Fatality Risk (CFR) - the proportion of cases that resulted in death - was cross-referenced with vaccination ...
The breakthrough is a step towards the development of next-generation magnetic devices that control light
2023-12-15
In a significant advancement in optical technology, researchers from Tohoku University and Toyohashi University of Technology have developed a new method for creating transparent magnetic materials using laser heating. This breakthrough, recently published in the journal Optical Materials, presents a novel approach to integrating magneto-optical materials with optical devices, a long-standing challenge in the field.
"The key to this achievement lies in creating 'Cerium-substituted Yttrium Iron Garnet (Ce:YIG)', ...
How an overlooked study over a century ago helped fuel the Colorado River crisis
2023-12-15
When it comes to the Colorado River, history often repeats itself—but it doesn’t have to.
That’s the take-home message from CU Boulder hydrologist Shemin Ge, who will present a little-known piece of history from the river this Thursday at the American Geophysical Union (AGU) meeting in San Francisco.
The story of hydrologist Eugene Clyde La Rue, Ge said, may help to explain the current water crisis facing many states in the American West.
Ge’s presentation centers around a decision ...
Basic monthly income trial at USC shows promise with significant reduction in homelessness
2023-12-15
Researchers at the Center for Homelessness, Housing, and Health Equity Research at the University of Southern California released an interim report on the first six months of a randomized controlled trial to study the impact of a basic income and social support intervention for 103 individuals experiencing homelessness in Los Angeles County and the San Francisco Bay Area.
Two key findings so far are that participants in the Miracle Money study who received $750 per month were less likely to remain unsheltered and closer ...
New gene therapy could significantly reduce seizures in severe childhood epilepsy
2023-12-15
UCL researchers have developed a new gene therapy to cure a devastating form of childhood epilepsy, which a new study shows can significantly reduce seizures in mice.
The study, published in Brain, sought to find an alternative to surgery for children with focal cortical dysplasia.
Focal cortical dysplasia is caused by areas of the brain that have developed abnormally and is among the most common causes of drug-resistant epilepsy in children. It frequently occurs in the frontal lobes, which are important for planning and decision-making. Epilepsy in focal cortical dysplasia is associated with comorbidities, including learning disabilities.
Although surgery to remove the affected brain malformation ...
Mount Sinai receives $1.3 million from the National Institutes of Health to support program that introduces high school students to virus surveillance
2023-12-15
The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai has received more than $1.3 million from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to expand the New York City Virus Hunters program. The program engages high school students from communities historically underrepresented in science in the first large-scale citizen science effort to catalog and map circulating avian influenza and avian paramyxoviruses in New York City’s wild birds. The goal is to track emerging viruses and to prevent future outbreaks.
Wild birds can disseminate infectious ...
UM School of Medicine awarded up to $7.3M from DARPA to drive innovation in trauma triage technology, improve mass casualty response efforts
2023-12-15
In an effort to better optimize the triage of patients during mass casualty events, University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) researchers are receiving up to $7.3 million in funding from the Defense Advanced Research Project Agency (DARPA) for vital new research. The funding will be used to support a study that will collect data over the next 3.5 years on trauma patients with the aim of identifying and implementing lifesaving advancements in medical triage for large-scale mass casualty incidents.
“The importance of early interventions in trauma is described as the concept of the ‘golden ...