(Press-News.org)
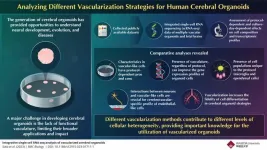
Cerebral organoids are three-dimensional, in vitro cultured brains that mimic the activities of the human brain. They have emerged as invaluable tools to comprehend evolution, disease pathogenesis, and neurodevelopmental processes. However, the development of these organoids is still in nascent stages with several limitations that hinder their broad applications. A major obstacle is the absence of a functional vasculature that can restrict the size of organoids, trigger cell death, and prevent cell differentiation in the organoids.
To address this, diverse strategies aiming to vascularize human cerebral organoids have been developed.
Recently, Assistant Professor Kosuke Kataoka, along with co-authors Yuya Sato and Toru Asahi from the Graduate School of Advanced Science and Engineering, Waseda University, conducted a comprehensive investigation into various strategies for vascularizing cerebral organoids. Their study was published online in BMC Biology on November 9, 2023. Kataoka says, “Several strategies have been proposed to construct functional vascular systems in cerebral organoids, however, no integrated comparative study of these strategies previously existed. Therefore, the characteristics and problems of each vascularization strategy have not been precisely characterized.”
Through an integrated comparison of single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) data, the study evaluated various vascularized human cerebral organoids created using different approaches, followed by an analysis of these datasets in conjunction with fetal brain data. This research outlined the impact of various vascularization techniques on cell type differentiation and the transcriptome profiles of both neuronal and vascular cells in these organoids.
It was observed that all the vascularization protocols improved the correlation value in most cell types. “This finding suggests that regardless of the protocol type, vascularized cerebral organoids exhibited a gene expression profile closer to the fetal human brain than non-vascularized organoids,” explains Kataoka.
They also found that vascular induction had transcriptomic effects on neuronal and vascular-like cell populations. The vascular cells of the fetal brain showed expression of all the marker genes, but the various vascularized and vascular organoids had an insufficient expression profile. Furthermore, this expression profile was found to be dependent on the vascularization strategy.
The study also revealed the importance of interactions between vascular-like cells and neurons for blood vessels to develop their cerebrovascular-specific profile to perform their vasculature functions characteristic of the brain, like the blood-brain barrier.
Expanding on the future applications of these findings, Kataoka says, "Our findings could contribute to providing more realistic human brain models with blood vessels. This will not only help in developing a better understanding of the human brain but also in accelerating the research on various brain diseases and enable more accurate drug screening."
Vascularized cerebral organoids are unlikely to undergo cell death and, thus are thought to become the standard for future brain research.
The present research is crucial for the fabrication of vascularized organoids in the future. Here's hoping for the development of vascularized organoids with higher fidelity.
***
Reference
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12915-023-01711-1
Authors: Yuya Sato1, Toru Asahi1,2,3* and Kosuke Kataoka2*
Affiliations:
1 Graduate School of Advanced Science and Engineering, Waseda University, Tokyo, Japan
2 Comprehensive Research Organization, Waseda University, Tokyo, Japan 3 Research Organization for Nano & Life Innovation, Waseda University, Tokyo, Japan
About Waseda University
Located in the heart of Tokyo, Waseda University is a leading private research university that has long been dedicated to academic excellence, innovative research, and civic engagement at both the local and global levels since 1882. The University has produced many changemakers in its history, including nine prime ministers and many leaders in business, science and technology, literature, sports, and film. Waseda has strong collaborations with overseas research institutions and is committed to advancing cutting-edge research and developing leaders who can contribute to the resolution of complex, global social issues. The University has set a target of achieving a zero-carbon campus by 2032, in line with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) adopted by the United Nations in 2015.
To learn more about Waseda University, visit https://www.waseda.jp/top/en
About Professor Kosuke Kataoka
Professor Kosuke Kataoka holds a Doctor of Science degree from Waseda University and currently serves as an Assistant Professor at Waseda University's Comprehensive Research Organization. With a rich academic background spanning several years, Professor Kataoka has made substantial contributions to various research areas including insect science, genome biology, neuroscience, cell biology, and molecular biology. His authorship encompasses multiple peer-reviewed publications, showcasing his expertise in diverse fields. Notable achievements include winning the Demo Day Best Presentation Award and the Award in JSN oral educational session for young investigators.
END
NEWS RELEASE
EMBARGOED UNTIL FRI, DEC. 15 – 5:00 A.M. Eastern
Contact
Colleen McDonald - Sr. Consultant, Earned Media
414.801.3146 | cmcdonald@mcw.edu
Trip or Treat?
Scientists at the Medical College of Wisconsin make strides in designing non-hallucinogenic psychedelic treatments that may accelerate research on mental health benefits; research findings published in Nature Communications.
Milwaukee, Wis. – Dec. 15, 2023 – There is nothing magic about the recent increase ...
CAMBRIDGE, MA — During a chemical reaction, molecules gain energy until they reach what’s known as the transition state — a point of no return from which the reaction must proceed. This state is so fleeting that it’s nearly impossible to observe it experimentally.
The structures of these transition states can be calculated using techniques based on quantum chemistry, but that process is extremely time-consuming. A team of MIT researchers has now developed an alternative approach, based on machine learning, that can calculate ...
Child psychologists have long known that play is essential for children’s cognitive development because it boosts their social, physical, and emotional skills. But beginning in the 21st century, specialists repeatedly sounded the alarm that ‘play is under siege’ for US children. Kids were playing less, and – it was feared – with a lesser quality.
But are today’s parents sufficiently aware of the importance of letting their children play? Yes, found a team of researchers who tested this through a survey of the opinions of 1,172 US parents. Their results showed that today’s ...
To an everyday consumer, the best gadgets on the market have the highest speed, the largest memory, and the longest battery life. Chasing this demand, the forefront of research often only considers these tangible performance metrics when innovating and designing next-generation electronics. In the wake of this technological stampede, the long-term environmental impacts lie obscured and neglected under the dust.
Researchers at the Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD) hope to be the catalyst for sustainability-driven science. Assistant Professor Ang Yee Sin from the Science, Mathematics ...
Transformer architectures have facilitated the development of large-scale and general-purpose sequence models for prediction tasks in natural language processing and computer vision, e.g., GPT-3 and Swin Transformer. Although originally designed for prediction problems, it is natural to inquire about their suitability in another important field, sequential decision-making and reinforcement learning problems, which are typically beset by long-standing issues involving sample efficiency, credit assignment, and partial observability, etc. In recent years, sequence models, especially the Transformer, have attracted increasing interest in the RL communities, spawning ...
Not all discoveries turn out to be actual new discoveries. This was the case for the extremely red objects (EROs) found in James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) data. Analysis shows that they are very similar to blue-excess dust obscured galaxies (BluDOGs) already reported in Subaru Telescope data.
Quasars, some of the brightest objects in the Universe, are driven by a supermassive black hole with a mass that can reach more than a billion times that of the Sun. These objects are the focus of much research, but how ...
A research team at the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) has outlined the high-resolution structure of a little-known virus, improving our understanding of viral infection, which could pave the way for more accurate predictions of climate change.
With the help of an advanced technique involving cryo-electron microscopy, they managed to capture images of the virus – the cyanophage P-SCSP1u – at near-atomic resolution in its native form and examined it to see how its different parts fit together. This helped show how different proteins work in the virus and how they interact to make the virus ...
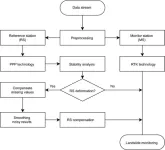
In a new study published on 13 November 2023, in the journal Satellite Navigation, researchers from Chang’an University have developed a novel approach using the Precise Point Positioning (PPP) technique combined with a cumulative sum control chart (CUSUM) method. This method enables the analysis of reference station stability and compensates for deformation at monitoring stations.
In the study conducted at the Tengqing landslide in Liupanshui, Guizhou Province, Southwest China, an innovative method was applied, showcasing a significant leap in landslide monitoring using GNSS PPP technology. ...
The risk of death from COVID-19 decreases significantly after vaccination but this protection diminishes after six months, providing evidence for continued booster doses, a new study has found.
Researchers from the UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA) analysed more than 10 million cases of COVID-19 in adults between May 2020 and February 2022. Their findings are published in the Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine (JRSM).
The Case Fatality Risk (CFR) - the proportion of cases that resulted in death - was cross-referenced with vaccination ...
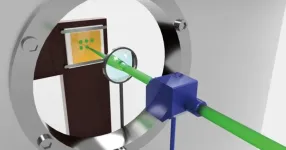
In a significant advancement in optical technology, researchers from Tohoku University and Toyohashi University of Technology have developed a new method for creating transparent magnetic materials using laser heating. This breakthrough, recently published in the journal Optical Materials, presents a novel approach to integrating magneto-optical materials with optical devices, a long-standing challenge in the field.
"The key to this achievement lies in creating 'Cerium-substituted Yttrium Iron Garnet (Ce:YIG)', ...