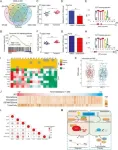
(Press-News.org) In a rapid communication published in the journal Genes & Diseases, has shed light on the role of the Wnt signaling pathway in influencing the immune response of colorectal cancer (CRC) patients. Researchers from Nankai University discovered that abnormalities in this pathway can affect a patient's response to immunotherapy, paving the way for more tailored treatment strategies. They integrated transcriptome data from 425 CRC patients, aiming to explore the underlying mechanism of MSI. They identified that the Wnt signaling pathway, essential for various cellular processes, showed signs of inhibition in MSI patients. The team also noted a significant down-regulation in mismatch repair enzyme gene MLH1 in these patients. Intriguingly, the expression of the MLH1 gene, crucial for DNA repair, was influenced by the activity of the Wnt signaling pathway. In MSI patients, the canonical Wnt signaling pathway was notably suppressed, resulting in the diminished expression of the mismatch repair enzyme, MLH1. This decrease in MLH1 expression underpins defects in the mismatch repair system, a defining characteristic of MSI. Concurrently, the study identified a down-regulation of SET, another pivotal gene, in these patients. The reduced SET expression correlated with a surge in immune infiltration and activation, hinting at an intensified immune response. Intriguingly, this research posits that MSI patients with such decreased SET expression may exhibit an enhanced responsiveness to immunotherapy, particularly immune checkpoint blockade (ICB).
The communication indicates that dysfunction in the Wnt signaling pathway could be a driving force behind MSI in CRC. Reduced activity of specific transcription factors led to decreased MLH1 expression, impairing DNA repair mechanisms. Additionally, the role of the SET gene in modulating immune responses provides valuable insights into why MSI patients might respond better to immunotherapy.
###
References
DOI
10.1016/j.gendis.2023.03.026
Original Source URL
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gendis.2023.03.026
Funding information
The National Nature Science Foundation of China (81973356, 81902826 and 82273963),
The Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin (21JCZDJC00060 and 21JCYBJC00180),
The Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of Nankai University (ZB22010404, 3206054, 91923101, 63213082, and 92122017).
About Genes & Diseases
Genes & Diseases is a journal for molecular and translational medicine. The journal primarily focuses on publishing investigations on the molecular bases and experimental therapeutics of human diseases. Publication formats include full length research article, review article, short communication, correspondence, perspectives, commentary, views on news, and research watch.
END
Wnt pathway dysfunction influences colorectal cancer response to immunotherapy
2023-12-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Molecular trap and zap
2023-12-15
Patients struggling with some chronic diseases often must wait years for a proper diagnosis. For example, symptoms such as shortness of breath can be attributed to many pulmonary as well as cardiovascular disorders, so patients may be treated for a misdiagnosed disease that is far from accurate diagnosis and treatment. Therefore, one of the most promising methods to deal with this problem is to track the levels of specific compounds in the body during the development of a specific disease. Moving in this direction, scientists at the Institute of Physical Chemistry of the Polish Academy of Sciences (Warsaw, Poland) and the National ...
New method paves the way for new antibiotics
2023-12-15
“Antimicrobial resistance is a major problem, and being able to help solve it is really great,” says Amanda Holstad Singleton, a PhD candidate at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU).
Singleton is the lead author of a study that shows how a combination of two new substances effectively kills methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
These substances have been developed at NTNU and may become a completely new antibiotic that is effective against a wide group of bacteria.
“It's ...
Frontiers for Young Minds and CERN ‘SPARK’ big questions in health technology
2023-12-15
Frontiers for Young Minds, the award-winning, open-access scientific journal for kids, has published the first articles in a new collection in collaboration with CERN, one of the world’s largest centers for scientific research. The collection, entitled SPARK-ing big questions: what is the future of health technology?, addresses key questions on how ground-breaking health technologies and science can improve human health for future generations.
The articles are written by researchers who attended the SPARKS! Serendipity Forum at CERN in 2022, an event for scientific and ...
Role of cleaning fishes in conserving biodiversity distinguished with FLAD Science Award Atlantic 2023
2023-12-15
José Ricardo Paula, researcher at the Marine and Environmental Sciences Centre, Faculty of Sciences of the University of Lisbon (Portugal), will receive 300.000 euros in funding in three years to develop a project that aims to improve the understanding of the role of cleaning mutualisms in the conservation of Atlantic biodiversity, using emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence.
In the global ocean, there are several fish species, known as cleaners, that specialize in providing ...
GYA and 30 Young Academies and Associations release statement suggesting actionable steps to connect fundamental science with sustainable development
2023-12-15
GYA and 30 Young Academies and Associations release statement suggesting actionable steps to connect fundamental science with sustainable development during Closing Ceremony of IYBSSD meeting
In a collective statement endorsed by 30 Young Academies and Associations, the Global Young Academy (GYA) underscored the pivotal role of fundamental science in achieving the United Nation Sustainable Development Goals (UN SDGs). The statement (link here) was delivered during the closing ceremony of the International Year of Basic Sciences for Sustainable Development (IYBSSD) at CERN in Switzerland on 15 December 2023.
The joint statement acknowledges the historical ...
Brief teacher training better prepares medical students for patient education & communication
2023-12-15
(Boston)—Teaching is an integral communication skill central to the practice of medicine. The art of teaching extends beyond disseminating information. The skill directly translates to health provider-patient communication, the success of which is positively correlated with improved patient outcomes.
“Teaching is a large part of medicine - patient education is critical to providing high quality patient centered care. Education helps patients understand the 'why' and 'what' of their treatments and allows them to be better participants in their ...
Local Philadelphia area business owner recognized as national champion for health equity
2023-12-15
DALLAS, December 15, 2023 — Devon Mitchell, an American Heart Association local volunteer and franchise owner at Anytime Fitness in Delaware, is the 2023 National Leaders of Impact™ Winner. Mitchell, one of the 295 leaders in cities across the country, worked to improve heart health in his community while raising funds to fuel the mission of the Association. The Leaders of Impact campaign pairs community leaders in a head-to-head competition to support the health equity work of the American ...
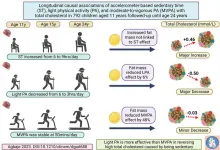
Childhood sedentariness causes elevated cholesterol but light physical activity may neutralize it
2023-12-15
Increased sedentary time from childhood through young adulthood significantly increased cholesterol levels in a new follow-up study. However, the results also showed that light physical activity (LPA) may completely reverse the adverse process. Moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (MVPA) may also reduce cholesterol levels, but its effect is diminished by body fat. The study was conducted in collaboration between the University of Bristol in the UK, the University of Exeter in the UK, and the University of Eastern ...
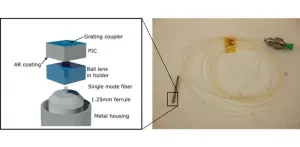
From PIC to probe
2023-12-15
Similarly as for electronics, photonic circuits can be miniaturized onto a chip, leading to a so-called photonic integrated circuit (PIC). Although these developments are more recent than for electronics, this field is rapidly evolving. One of the main issues, however, is to turn such a PIC into a functional device. This requires optical packaging and coupling strategies to bring light into and to get light out of the PIC. For example, for optical communication a connection needs to be made with optical fibers, which then transport the light ...
Prone to abandoning New Year’s resolutions? Bayes’ research suggests blaming money worries rather than being time-poor
2023-12-15
People who abandon New Year’s resolutions or other commitments can maintain the respect of their peers by blaming external factors such as lack of money, new research suggests.
Studies have found that people were more likely to be seen as having good self-control despite abandoning a commitment to live a healthier life if they claimed they did not have the money for a gym membership or expensive new cooking equipment. People who instead claimed they didn’t have the time to exercise or to replace a takeaway ...