(Press-News.org) The average menstruator will use over 11,000 tampons or sanitary pads in their lifetime. Vaginal and vulvar tissue that touch pads and tampons is highly permeable. Through this permeable tissue chemicals are absorbed without being metabolized, which makes endocrine-disrupting chemicals potentially dangerous when found in menstrual products. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals can interfere with human hormones and cause medical issues, including gynecological conditions such as endometriosis and uterine fibroids.
Joanna Marroquin, a Mason PhD in Public Health student, and Associate Professor Anna Pollack, reviewed studies conducted since 2103 that measured chemicals in menstrual products and that measured human biomarkers of chemical exposure and determined that endocrine-disrupting chemicals were found in menstrual products including tampons, pads, and liners.
“Identifying chemicals in menstrual products that menstruators regularly use is important because exposure through these products can impact menstruators’ reproductive health,” said Marroquin, the paper’s first author.
The study found that menstrual products contain a variety of endocrine-disrupting chemicals including phthalates, volatile organic compounds, parabens, environmental phenols, fragrance chemicals, dioxins and dioxin-like compounds.
This issue is even more relevant thanks to the Robin Danielson Menstrual Product and Intimate Care Product Safety Act of 2023, which was introduced in the U.S. House of Representatives in October 2023. The Act would establish a program of research regarding the risks posed by the presence of dioxins, phthalates, pesticides, chemical fragrances, and other components in menstrual products and intimate care products.
This literature reviewed 15 papers published between 2013 and 2023 that tested menstrual products in the U.S., Japan, and South Korea. The researchers note that there are few publications available that measure chemicals in menstrual products.
Additionally, though forever chemicals (PFAS) have been found in menstrual underwear, there is a lack of peer-reviewed research on menstrual underwear and other newly-popular-in-the-U.S. products such as menstrual cups and discs.
Chemicals in menstrual products: A systematic review was published in BJOG, an international journal of obstetrics and gynecology in September 2023. Additional authors include Marianthi-Anna Kiomourtzoglou from Mailman School of Public Health, Columbia University and Alexandra Scranton from Women's Voices for the Earth.
The research was supported by Pollack's National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences R01ES31079 award.
END
Endocrine-disrupting chemicals found in menstrual products including tampons, pads, and liners
Endocrine-disrupting chemicals can interfere with human hormones and cause medical issues
2023-12-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Five researchers named Argonne Distinguished Fellows for 2023
2023-12-15
The U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory has named five highly accomplished scientists as Argonne Distinguished Fellows in 2023. They are Glenn Decker, Paul Fenter, Robert Fischetti, Sven Leyffer and Valentine Novosad.
The honor recognizes scientists who have not only achieved international esteem but who have also demonstrated exceptional achievements in science or engineering relevant to Argonne’s core missions. They are leaders of major, complex, high-priority projects or programs that have an impact on the future of the Laboratory. Only a small ...
Study shows exposure to household chemicals can lower odds of getting pregnant
2023-12-15
Exposure to phthalates, a group of plasticizing and solvent chemicals found in many household products, was linked to a lower probability of getting pregnant, but not to pregnancy loss, according to research by a University of Massachusetts Amherst environmental and reproductive epidemiologist.
The study, published this week in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives, also noted an association between preconception exposure to phthalates and changes in women’s reproductive hormones, as well as increased inflammation and oxidative stress.
“Phthalates ...
NRL’s Debra Rolison elected 2023 National Academy of Inventors Fellow
2023-12-15
WASHINGTON – Debra Rolison, Ph.D., of the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) has been named Fellow of the National Academy of Inventors (NAI), for having demonstrated a highly prolific spirit of innovation in creating and facilitating outstanding inventions that have made a tangible impact on the quality of life, economic development, and welfare of society.
Rolison has been at the lab for over 43 years and heads the Advanced Electrochemical Materials section. The recognition by the NAI is attributed to the efforts made by her team’s inventions related to a new form factor for zinc anodes in rechargeable ...
North America’s first people may have arrived by sea ice highway
2023-12-15
SAN FRANCISCO — One of the hottest debates in archeology is how and when humans first arrived in North America. Archaeologists have traditionally argued that people walked through an ice-free corridor that briefly opened between ice sheets an estimated 13,000 years ago.
But a growing number of archeological and genetic finds — including human footprints in New Mexico dated to around 23,000 years old — suggests that people made their way onto the continent much earlier. These early Americans likely traveled along the Pacific coastline from Beringia, the land bridge between Asia and North America ...
Xinfeng Gao named 2024 AIAA Associate Fellow
2023-12-15
We are pleased to announce that the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics (AIAA), a preeminent aerospace professional society, has selected professor Xinfeng Gao to be a member of the class of 2024 AIAA associate fellows. Only one member of the Institute for every 150 members is selected as an associate fellow each year by the review committee.
“This recognition illustrates the impact of our outstanding faculty. Aerospace engineering at UVA continues on a great trajectory and professor Gao is a big part of that,” said Richard W. Kent, professor and chair of the Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering.
Pioneering ...
Substance-abuse stigma impedes treatment in various ways, scientists say
2023-12-15
Addiction is one of society’s most misunderstood and rebuked health conditions. That stigma discourages many people from seeking treatment for substance dependence, according to a new report published in Psychological Science in the Public Interest, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
Research on stigma toward people with substance use disorder (SUD) is relatively sparse, the report adds.
“Characterizing the nature and etiology of SUD stigma is critical for developing tailored and effective interventions ...
Ultrafast lasers map electrons 'going ballistic' in graphene, with implications for next-gen electronic devices
2023-12-15
LAWRENCE — Research appearing in ACS Nano, a premier journal on nanoscience and nanotechnology, reveals the ballistic movement of electrons in graphene in real time.
The observations, made at the University of Kansas’ Ultrafast Laser Lab, could lead to breakthroughs in governing electrons in semiconductors, fundamental components in most information and energy technology.
“Generally, electron movement is interrupted by collisions with other particles in solids,” said lead author Ryan Scott, ...
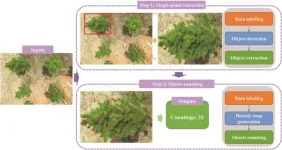
Revolutionizing forestry: 'CountShoots' unveils advanced UAV and AI techniques for precise slash pine shoot counting
2023-12-15
In southern China, the genetically improved slash pine (Pinus elliottii) plays a crucial role in timber and resin production, with new shoot density being a key growth trait. Current manual counting methods are inefficient and inaccurate. Emerging technologies such as UAV-based RGB imaging and deep learning (DL) offer promising solutions. However, DL methods face challenges in global feature capture, necessitating additional mechanisms. Innovations like the Vision Transformer and its derivatives (e.g., TransCrowd, CCTrans) show potential in plant trait counting, offering simplified and more effective approaches for large-scale and accurate ...
UMSOM researchers discover first ever link between hemoglobin-like protein and normal heart development
2023-12-15
BALTIMORE, December 14, 2023– In a landmark study led by the University of Maryland School of Medicine, researchers discovered for the first time that a certain kind of protein similar to hemoglobin, called cytoglobin, plays an important role in the development of the heart. Specifically, it affects the correct left-right pattern of the heart and other asymmetric organs. The findings, published today in the journal Nature Communications, could eventually lead to the development of new therapeutic interventions to alter the processes that lead ...
Facility fees charged by hospitals for colonoscopy procedures are about 55 percent higher than those charged by surgical centers
2023-12-15
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL FRIDAY DECEMBER 15 AT 11 A.M. EST.
U.S. hospitals charge facility fees for colonoscopy procedures covered by private health insurance that are on average approximately 55 percent higher than facility fees billed by smaller clinics known as ambulatory surgical centers, according to a study led by researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
The findings appear in a peer-reviewed research letter to be published online December 15 in JAMA Health Forum.
Colonoscopies ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Chimps’ love for crystals could help us understand our own ancestors’ fascination with these stones
Vaginal estrogen therapy not linked to cancer recurrence in survivors of endometrial cancer
How estrogen helps protect women from high blood pressure
Breaking the efficiency barrier: Researchers propose multi-stage solar system to harness the full spectrum
A new name, a new beginning: Building a green energy future together
From algorithms to atoms: How artificial intelligence is accelerating the discovery of next-generation energy materials
Loneliness linked to fear of embarrassment: teen research
New MOH–NUS Fellowship launched to strengthen everyday ethics in Singapore’s healthcare sector
Sungkyunkwan University researchers develop next-generation transparent electrode without rare metal indium
What's going on inside quantum computers?: New method simplifies process tomography
This ancient plant-eater had a twisted jaw and sideways-facing teeth
Jackdaw chicks listen to adults to learn about predators
Toxic algal bloom has taken a heavy toll on mental health
Beyond silicon: SKKU team presents Indium Selenide roadmap for ultra-low-power AI and quantum computing
Sugar comforts newborn babies during painful procedures
Pollen exposure linked to poorer exam results taken at the end of secondary school
7 hours 18 mins may be optimal sleep length for avoiding type 2 diabetes precursor
Around 6 deaths a year linked to clubbing in the UK
Children’s development set back years by Covid lockdowns, study reveals
Four decades of data give unique insight into the Sun’s inner life
Urban trees can absorb more CO₂ than cars emit during summer
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
New NIH grant advances Lupus protein research
New farm-scale biochar system could cut agricultural emissions by 75 percent while removing carbon from the atmosphere
From herbal waste to high performance clean water material: Turning traditional medicine residues into powerful biochar
New sulfur-iron biochar shows powerful ability to lock up arsenic and cadmium in contaminated soils
AI-driven chart review accurately identifies potential rare disease trial participants in new study
Paleontologist Stephen Chester and colleagues reveal new clues about early primate evolution
UF research finds a gentler way to treat aggressive gum disease
Strong alcohol policy could reduce cancer in Canada
[Press-News.org] Endocrine-disrupting chemicals found in menstrual products including tampons, pads, and linersEndocrine-disrupting chemicals can interfere with human hormones and cause medical issues