First observation of how water molecules move near a metal electrode
Movements of water molecules change depending on the applied voltage
2023-12-18
(Press-News.org)
A collaborative team of experimental and computational physical chemists from South Korea and the United States have made an important discovery in the field of electrochemistry, shedding light on the movement of water molecules near metal electrodes. This research holds profound implications for the advancement of next-generation batteries utilizing aqueous electrolytes.
In the nanoscale realm, chemists typically utilize laser light to illuminate molecules and measure spectroscopic properties to visualize molecules. However, studying the behavior of water molecules near metal electrodes proved challenging due to the overwhelming interference from metal atoms in the electrode itself. Additionally, water molecules distant from the electrode surface also contribute to the response of the applied light, complicating the selective observation of molecules at the liquid-metal electrode interface.
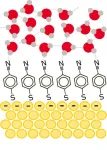
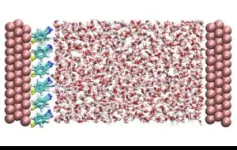
Led by Professor Martin Zanni from the University of Wisconsin at Madison and Director CHO Minhaeng from the Center for Molecular Spectroscopy and Dynamics within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) addressed this challenge with newly developed spectroscopic techniques coupled with computer simulations. In order to minimize the interference from the metals, the authors coated the surface of the electrode with specially designed organic molecules. Then, surface-enhanced femtosecond (10-15 second) two-dimensional vibrational spectroscopy was employed to observe the changes in the movement of water molecules near the metal electrode.
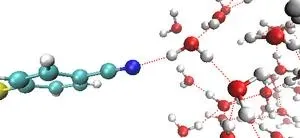
Depending on the magnitude and polarity of the applied voltage on the metal electrode, the researchers observed, for the first time, either a deceleration or acceleration of the motion of water molecules near the electrode. “When a positive voltage is applied to the electrode, the movement of nearby water molecules slows down. Conversely, when a negative voltage is applied, the opposite is observed both in femtosecond vibrational spectroscopy and in computer simulations,” explains Dr. Kwac.
“The results of this study provide crucial information for understanding electrochemical reactions, offering essential physical insights necessary for the research and development of aqueous electrolyte batteries in the future,” comments Director CHO Minhaeng of the IBS Center for Molecular Spectroscopy and Dynamics, a corresponding author of the study.
This outcome implies a close relationship between electrochemical reactions involving water on the surface of electrodes and the dynamics of interfacial water molecules. It is expected to not only advance our understanding of fundamental electrochemical processes but also pave the way for the design of more efficient and sustainable battery technologies.
This research was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) on December 18, 2023.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-12-18
A study conducted by pre-PhD researcher Pablo S. Valera and recently published in PNAS demonstrates the potential of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) to explore metabolites secreted by cancer cells in cancer research. The study, which has been led by Ikerbasque Research Professors Luis Liz-Marzán (from CIC biomaGUNE) and Arkaitz Carracedo (of CIC bioGUNE) and in which other researchers from both centers, also members of the Networking Biomedical Research Centre (CIBER), have participated as well, provides valuable information to guide more specific experiments to reveal ...
2023-12-18
Myosteatosis, or aging-related fat accumulation in skeletal muscles, is a leading cause of declines in muscle strength and quality of life in elderly adults.
Older adults who are sedentary and develop accumulated fat in the skeletal muscle are often prescribed exercise by their doctors to combat the condition. If scientists were to develop a new therapy, such as medications, to combat myosteatosis, they would need to replicate the mechanism by which exercise might reduce fat accumulation in muscles.
Fibro-adipogenic ...
2023-12-18
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope recently trained its sights on unusual and enigmatic Uranus, an ice giant that spins on its side. Webb captured this dynamic world with rings, moons, storms, and other atmospheric features – including a seasonal polar cap. The image expands upon a two-color version released earlier this year, adding additional wavelength coverage for a more detailed look.
With its exquisite sensitivity, Webb captured Uranus’ dim inner and outer rings, including the ...
2023-12-18
How are memories consolidated during sleep? In 2021, researchers led by Dr. Thomas Schreiner, leader of the Emmy Noether junior research group at LMU’s Department of Psychology, had already shown there was a direct relationship between the emergence of certain sleep-related brain activity patterns and the reactivation of memory contents during sleep. However, it was still unclear whether these rhythms are orchestrated by a central pacemaker. So the researchers joined up with scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Human Development in Berlin and the University of Oxford to reanalyze the data. Their results have identified ...
2023-12-18
Zholents was honored for his work on the theory of optical stochastic cooling.
Alexander Zholents, a senior physicist at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory and distinguished fellow in the Accelerator Systems division is one of the recipients of this year’s Dieter Möhl Award.
The award is presented by CERN, the European laboratory for particle physics. It is in tribute to the late Dieter Möhl, a pioneer in the realm of particle beam cooling. The awards celebrate both early career and lifetime achievements in the field of beam cooling and its applications.
“I am deeply honored to receive this award,” said Zholents. “The ...
2023-12-18
(Memphis, Tenn.—December 18, 2023) Children with bilateral Wilms tumor have a tumor in each of their kidneys — a condition that strongly suggests an underlying genetic or epigenetic predisposition driving the disease. Scientists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital gathered a large cohort of bilateral Wilms tumor samples and conducted analyses to assess which factors contribute to predisposition comprehensively. The work has implications for counseling patient families, guiding treatment decisions and informing the design of future clinical trials. The study was published today in Nature Communications.
Having tumors in ...
2023-12-18
A new study answers a timely question: What is the hardest part of waiting? Consumers do plenty of it—online, in line, in traffic, or for deliveries. And now we know it’s the final phase that’s most problematic for them.
In this season of joyful—and not-so-joyful—anticipation, the research has deep implications for marketers and psychological insights for us all, says Annabelle Roberts, coauthor and assistant professor of marketing at the University of Texas McCombs School of Business. The paper shows:
It’s better for companies to communicate possible delays early in the wait;
It’s better for ...
2023-12-18
ITHACA, N.Y. - A tiny, hard-working bacterium – which weighs one-trillionth of a gram – may soon have a large influence on processing rare earth elements in an eco-friendly way.
In a new study, Cornell University scientists show that genetically engineering this bacterium could improve the efficiency for the purification of elements found in smartphones, computers, electric cars and wind turbines, and could even boost global economic supply chains.
Vibrio natriegens, the bacterium, offers a sustainable ...
2023-12-18
A new study Dec. 18 in Nature reports an AI-driven advance in biotechnology with implications for drug development, disease detection, and environmental monitoring. Scientists at the Institute for Protein Design at the University of Washington School of Medicine used software to create protein molecules that bind with exceptionally high affinity and specificity to a variety of challenging biomarkers, including human hormones. Notably, the scientists achieved the highest interaction strength ever reported between a computer-generated biomolecule and its target.
Senior author David Baker, professor of biochemistry at UW Medicine, ...
2023-12-18
Artificial intelligence developed to model written language can be utilized to predict events in people's lives. A research project from DTU, University of Copenhagen, ITU, and Northeastern University in the US shows that if you use large amounts of data about people's lives and train so-called 'transformer models', which (like ChatGPT) are used to process language, they can systematically organize the data and predict what will happen in a person's life and even estimate the time of death.
In a new scientific article, 'Using Sequences of Life-events to Predict Human Lives', published ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] First observation of how water molecules move near a metal electrode
Movements of water molecules change depending on the applied voltage