A bacterial toolkit for colonizing plants
2023-12-19
(Press-News.org)
Using a novel experimental approach, Max Planck researchers have discovered a core set of genes required by commensal bacteria to colonize their plant hosts. The findings may have broad relevance for understanding how bacteria establish successful host–commensal relationships.
Plants are colonized by an enormous variety of microorganisms, including bacteria, archaea and fungi, that form complex communities, or microbiomes, on their roots and organs. Although invisible to the naked eye, the importance of these tiny inhabitants should not be underestimated. They play a crucial role in plant nutrition, influence the health of plants, strengthen their tolerance to stress factors such as drought and help defend against pathogens. Thus, harnessing the power of these microbial assemblages could contribute to more sustainable agriculture that is less reliant on fertilizers and pesticides.
Understanding how microorganisms colonize their hosts is a prerequisite for designing and applying microbiomes with beneficial functions, and, to this end, scientists often study how individual microorganisms interact with plants. However, researchers still don’t have a good understanding of how multiple microbes concomitantly colonize and interact with plants for successful establishment of more complex host-commensal relationships. This is frustrating, as information on how one microbe interact with its host plant may not be representative of the complex reality observed in a microbial community context. The challenge has been essentially a technical one – how to precisely characterize the behavior of individual strains in a haystack of microbes and the plant itself.
To address the problem, first author Nathan Vannier and Stéphane Hacquard explored the establishment of individual microbes on plant roots in complex communities starting with microbe-free thale cress plants. Subsequently, they re-introduced a defined community of microbes, representing the diversity observed in the roots of plants in the wild, to investigate how these microbes colonize their host. Knowing the identity of these bacteria and armed with reference sequences for their genetic material then allowed them to characterize what microbial genes were activated or repressed during plant colonization. This analysis allowed them to identify numerous genes that were highly expressed in many different bacteria in roots and to select candidate genes potentially involved in host colonization. One regulates bacterial virulence and stress responses; another one is involved in transmembrane polymers transport and a set of genes that functions together act a phosphate sensor. Mutating any three of these genes in bacteria hampered their ability to colonize roots, without affecting their growth in media. Thus, the authors’ approach allowed them to identify a core set of genes required by many bacteria to persist on the roots of plants.
The strategy used by Hacquard and his team allowed them to understand both structural and functional organization of complex microbial communities that colonize plant roots. The genes identified may be broadly utilized by very diverse bacteria to colonize and persist on their hosts.
“Our results could potentially pave the way for engineering beneficial bacteria that can efficiently colonize host niches and promote host health. This has implications not only for sustainable agriculture but also for advancements in medical science.”, Stéphane Hacquard emphasizes.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-12-19
A new study provides the latest data on the low rates for screening and documenting Social Determinants of Health (SDOH) in healthcare settings.
SDOHs are a person's social, environmental and economic conditions highly correlated with their health outcomes. This includes unemployment, homelessness and illiteracy, among many other factors. Although SDOHs can contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of a patient's health and inform important policy changes, clinical offices fall short of tracking this information.
To better understand ...
2023-12-19
On December 9, 2023, the 5th International Conference on Flexible Electronics (ICFE 2023) was held in Hangzhou, China. The international academic journal, FlexTech, was officially inaugurated at this conference.
FlexTech is an initiative led by Tsinghua University, with academic support from the Laboratory of Flexible Electronics Technology Laboratory, Tsinghua University. This journal is co-published by Tsinghua University Press and John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
The editorial board of FlexTech is under the distinguished leadership of Professor Xue ...
2023-12-19
CLEVELAND—Throughout our lives, changes in our DNA, called genetic mutations, occur in every healthy cell of the human body—mutations which have long been thought to be an important reason why our bodies age.
But it’s not known whether some people accumulate mutations at a faster or slower rate with age, and whether those differences might predict how long we live and the risk for aging-related diseases like cancer.
With a $3.5 million research project grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), Jonathan Shoag, a surgeon-scientist at the Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine and urologic oncologist at ...
2023-12-19
(LOS ANGELES) – December 18, 2023 - The National Academy of Inventors (NAI) has named Ali Khademhosseini, Ph.D., Director and CEO of the Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI), as a 2023 National Academy of Inventors Fellow. This distinctive honor is the highest professional award that is exclusively bestowed upon inventors. The Academy has chosen to honor him for his achievements and contributions to the innovation ecosystem, which vastly influences science, society, and the global economy. Dr. Khademhosseini will be formally recognized at the NAI thirteenth annual meeting on June 18, 2024, where he will be presented with a medal by a senior official from the United States ...
2023-12-19
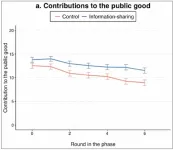
How is cooperation affected when people can receive secondhand information about what others are contributing? Ashley Harrell and Tom Wolff investigated this question through an online cooperation game. Participants were recruited from a large subject pool of university students and other adults, maintained by the Interdisciplinary Behavioral Research Center at Duke University. Over 200 participants were placed in groups of 6–10; however, each participant was only linked to some of the other participants. In the control condition, players could only see the contributions ...
2023-12-19
COLUMBUS, Ohio – New technology has allowed scientists to see how a major sporting event can disrupt public transportation in an entire city for hours before and after the event.
Researchers conducted a case study in Columbus on days that The Ohio State University had home football games, attracting more than 100,000 fans to Ohio Stadium on the university’s campus.
Findings showed that bus service across the entire city was significantly less reliable for more than 7 hours on game days compared to other days, meaning that even bus riders who were not traveling near the university ...
2023-12-19
In a perspective, Athanassios S. Fokas considers a timely question: whether artificial intelligence (AI) can reach and then surpass the level of human thought. Typically, researchers have sought to measure the ability of computer models to accomplish complex goals, such as winning the game of Go or carrying on a conversation that seems human enough to fool an interlocutor. According to Fokas, this approach has a key methodological limitation. Any AI would have to be tested on every single conceivable human goal before anyone could claim that the program was thinking as well as a human. Alternative methodologies are therefore needed. In addition, the “complex goal” focus does not ...
2023-12-19
In an editorial, Monica M. Bertagnolli assesses the promise of artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML) to study and improve health. The editorial was written by Dr. Bertagnolli in her capacity as director of the National Cancer Institute. AI/ML offer powerful new tools to analyze highly complex datasets, and researchers across biomedicine are taking advantage. However, Dr. Bertagnolli argues that human judgment is still required. Humans must select and develop the right computational models and ensure that the data used to train ...
2023-12-19
Bethesda, MD (Dec. 19, 2023) — The American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) has released the first comprehensive evidence-based guideline on the management of pouchitis, the most common complication people with ulcerative colitis experience following surgery to remove their colon.
Between 150,000 and 300,000 people with ulcerative colitis in the U.S. live with a surgically created internal reservoir or “pouch” created from their small intestine as an alternate way to store and pass ...
2023-12-19
Scientists have so far identified around 800 different neuromuscular diseases. These conditions are caused by problems in the way muscle cells, motor neurons and peripheral cells interact. These disorders, including amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and spinal muscular atrophy, lead to muscle weakness, paralysis, and in some cases death.
“These diseases are highly complex, and the causes of the dysfunction can vary widely,” says Dr. Mina Gouti, head of the Stem Cell Modeling of Development and Disease Lab at the Max Delbrück Center. The problem might lie with the neurons, the muscle cells or the connections between the two. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A bacterial toolkit for colonizing plants