(Press-News.org) Humans have wiped out around 1,400 bird species – twice as many as previously thought – with major implications for the ongoing biodiversity crisis, a new study has found.
Many of the world’s islands were previously untouched paradises, but the arrival of people to places like Hawaii, Tonga and the Azores led, over time, to far-reaching impacts including deforestation, overhunting and the introduction of invasive species. Consequently, bird species were wiped out.
While the demise of many birds since the 1500s has been recorded, our knowledge of the fate of species before this relies on fossils, and these records are limited because birds’ lightweight bones disintegrate over time. This conceals the true extent of global extinctions.
Researchers now believe 1,430 bird species – almost 12 per cent – have died out over modern human history, since the Late Pleistocene around 130,000 years ago, with the vast majority of them becoming extinct directly or indirectly due to human activity.
The study, led by the UK Centre for Ecology & Hydrology (UKCEH) and published in Nature Communications, used statistical modelling to estimate the undiscovered bird extinctions.
Lead author Dr Rob Cooke, an ecological modeller at UKCEH, says: “Our study demonstrates there has been a far higher human impact on avian diversity than previously recognised. Humans have rapidly devastated bird populations via habitat loss, overexploitation and the introduction of rats, pigs and dogs that raided nests of birds and competed with them for food. We show that many species became extinct before written records and left no trace, lost from history.”
Dr Søren Faurby of the University of Gothenburg, a co-author of the study, adds: “These historic extinctions have major implications for the current biodiversity crisis.
“The world may not only have lost many fascinating birds but also their varied ecological roles, which are likely to have included key functions such as seed dispersal and pollination. This will have had cascading harmful effects on ecosystems so, in addition to bird extinctions, we will have lost a lot of plants and animals that depended on these species for survival.”
Observations and fossils show 640 bird species have been driven extinct since the Late Pleistocene period – 90 per cent of these on islands inhabited by people. These range from the iconic Dodo of Mauritius to the Great Auk of the North Atlantic to the lesser-known Saint Helena Giant Hoopoe. But the researchers estimated there have been further 790 unknown extinctions, meaning a total of 1,430 lost species – leaving just under 11,000 today.
The scientists say their study has uncovered the largest human-driven vertebrate extinction event in history, during the 14th century, estimating that 570 bird species were lost after people first arrived in the Eastern Pacific, including Hawaii and the Cook Islands – nearly 100 times the natural extinction rate.
They believe there was also a major extinction event in the ninth century BC, primarily driven by the arrival of people to the Western Pacific, including Fiji and the Mariana Islands, as well as the Canary Islands, and highlight the ongoing extinction event, which started in the mid-18th century. Since then, in addition to an increase in deforestation and spread of invasive species, birds have faced the additional human-driven threats of climate change, intensive agriculture and pollution.
Previous research by the authors suggests we are at risk of losing up to 700 additional bird species in the next few hundred years, which would be an unprecedented human-driven decimation of species. But Dr Cooke points out: “Whether or not further bird species will go extinct is up to us. Recent conservation has saved some species and we must now increase efforts to protect birds, with habitat restoration led by local communities.”
The study team based their modelled estimates on known extinctions and the extent of relevant research effort in regions compared to New Zealand. The country is the only place in the world where the pre-human bird fauna is believed to be completely known, with well-preserved remains of all birds there. The fewer studies in a region, the more incomplete the fossil record is expected to be, and the greater the number of estimated undiscovered extinctions.
Ends
Media enquiries
The paper plus illustrations of known extinct birds and AI-generated images of what the other extinct species may have looked like are available on request. For interviews and further information, please contact Simon Williams, Media Relations Officer at UKCEH, via simwil@ceh.ac.uk or +44 (0)7920 295384.
Paper information
Cooke et al. 2023. Undiscovered bird extinctions obscure the true magnitude of human-driven extinction waves. Nature Communications. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-43445-2
The study involved scientists at UKCEH, the University of Gothenburg, Gothenburg Global Biodiversity Centre, the Centre for Ecological Research and Forestry Applications (CREAF), Uppsala University in Sweden, University College London, the Zoological Society of London (ZSL), the University of Bayreuth in Germany, the Royal Botanic Gardens Kew and the University of Oxford.
About the UK Centre for Ecology & Hydrology (UKCEH)
The UK Centre for Ecology & Hydrology is a world-leading centre for excellence in environmental sciences across water, land and air. We have a long history of monitoring and modelling environmental change. We identify key drivers of biodiversity change, develop tools and technologies for monitoring biodiversity, and provide robust socio-economic and environmental solutions for restoring biodiversity.
The UK Centre for Ecology & Hydrology is a strategic delivery partner for the Natural Environment Research Council, part of UK Research and Innovation.
www.ceh.ac.uk / @UK_CEH / LinkedIn: UK Centre for Ecology & Hydrology
END
Study uncovers major hidden human-driven bird extinctions
Scientists say 1 in 9 species have been lost – double the current estimate
2023-12-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Promising new treatment for a common hereditary nerve disease
2023-12-19
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) develop a genome-editing technique that reduces disease-causing proteins and related issues in cells from a patient with Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease type 1A
Tokyo, Japan – Scientific advances in the last century have changed our world significantly. For example, the world of genetics has opened doors to a myriad of possibilities: augmented human capabilities, cures for diseases, and even changes to the course of evolution.
In a study published last month in Communications Medicine, researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) have unveiled a groundbreaking genome-editing technique. This ...
Moderation surpasses excess
2023-12-19
Kyoto, Japan -- Down syndrome, a congenital disorder stemming from abnormal cell division and differentiation, is most common in newborns fated to neurodevelopmental delays and other health complications.
The genetic defect causes the dysfunction of the protein kinase DYRK1A, which is encoded on chromosome 21 and is deeply associated with both Down syndrome and autism spectrum disorder. DYRK1A has attracted attention as a target molecule for treating various diseases, but specific cellular mechanisms regulating ...
Linking genes and brain circuitry in anxiety disorders
2023-12-19
Kyoto, Japan – December 2023
Anxiety disorders (ADs) affect more than 280 million people worldwide, making them one of the most common mental health conditions. ADs have a genetic basis as seen from inheritance in families, and people with one subtype of AD tend to have another subtype, suggesting a shared genetic basis. Although the brain circuitry involved in ADs has been identified, its link with gene expression remains unclear. Two researchers at Kyoto University in Japan set out to uncover this link and found two gene clusters expressed in ...
A bacterial toolkit for colonizing plants
2023-12-19
Using a novel experimental approach, Max Planck researchers have discovered a core set of genes required by commensal bacteria to colonize their plant hosts. The findings may have broad relevance for understanding how bacteria establish successful host–commensal relationships.
Plants are colonized by an enormous variety of microorganisms, including bacteria, archaea and fungi, that form complex communities, or microbiomes, on their roots and organs. Although invisible to the naked eye, the importance of these tiny inhabitants should not be underestimated. They play a crucial role in plant nutrition, influence the health of plants, strengthen their tolerance to stress factors such as ...
Study provides new insight into low social determinants of health screening rates
2023-12-19
A new study provides the latest data on the low rates for screening and documenting Social Determinants of Health (SDOH) in healthcare settings.
SDOHs are a person's social, environmental and economic conditions highly correlated with their health outcomes. This includes unemployment, homelessness and illiteracy, among many other factors. Although SDOHs can contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of a patient's health and inform important policy changes, clinical offices fall short of tracking this information.
To better understand ...
FlexTech: A new era in flexible electronics research
2023-12-19
On December 9, 2023, the 5th International Conference on Flexible Electronics (ICFE 2023) was held in Hangzhou, China. The international academic journal, FlexTech, was officially inaugurated at this conference.
FlexTech is an initiative led by Tsinghua University, with academic support from the Laboratory of Flexible Electronics Technology Laboratory, Tsinghua University. This journal is co-published by Tsinghua University Press and John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
The editorial board of FlexTech is under the distinguished leadership of Professor Xue ...
Why do people age differently?
2023-12-19
CLEVELAND—Throughout our lives, changes in our DNA, called genetic mutations, occur in every healthy cell of the human body—mutations which have long been thought to be an important reason why our bodies age.
But it’s not known whether some people accumulate mutations at a faster or slower rate with age, and whether those differences might predict how long we live and the risk for aging-related diseases like cancer.
With a $3.5 million research project grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), Jonathan Shoag, a surgeon-scientist at the Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine and urologic oncologist at ...
Ali Khademhosseini named as 2023 National Academy of Inventors Fellow
2023-12-19
(LOS ANGELES) – December 18, 2023 - The National Academy of Inventors (NAI) has named Ali Khademhosseini, Ph.D., Director and CEO of the Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI), as a 2023 National Academy of Inventors Fellow. This distinctive honor is the highest professional award that is exclusively bestowed upon inventors. The Academy has chosen to honor him for his achievements and contributions to the innovation ecosystem, which vastly influences science, society, and the global economy. Dr. Khademhosseini will be formally recognized at the NAI thirteenth annual meeting on June 18, 2024, where he will be presented with a medal by a senior official from the United States ...
Information sharing and cooperation
2023-12-19
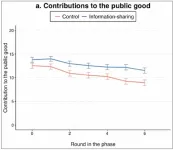
How is cooperation affected when people can receive secondhand information about what others are contributing? Ashley Harrell and Tom Wolff investigated this question through an online cooperation game. Participants were recruited from a large subject pool of university students and other adults, maintained by the Interdisciplinary Behavioral Research Center at Duke University. Over 200 participants were placed in groups of 6–10; however, each participant was only linked to some of the other participants. In the control condition, players could only see the contributions ...
How big events can disrupt public transit over an entire city
2023-12-19
COLUMBUS, Ohio – New technology has allowed scientists to see how a major sporting event can disrupt public transportation in an entire city for hours before and after the event.
Researchers conducted a case study in Columbus on days that The Ohio State University had home football games, attracting more than 100,000 fans to Ohio Stadium on the university’s campus.
Findings showed that bus service across the entire city was significantly less reliable for more than 7 hours on game days compared to other days, meaning that even bus riders who were not traveling near the university ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
Researchers develop a biomimetic platform to enhance CAR T cell therapy against leukemia
Heart and metabolic risk factors more strongly linked to liver fibrosis in women than men, study finds
Governing with AI: a new AI implementation blueprint for policymakers
Recent pandemic viruses jumped to humans without prior adaptation, UC San Diego study finds
Exercise triggers memory-related brain 'ripples' in humans, researchers report
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
[Press-News.org] Study uncovers major hidden human-driven bird extinctionsScientists say 1 in 9 species have been lost – double the current estimate