(Press-News.org) American Geophysical Union
Press Release 23-47
21 December 2023
For Immediate Release
This press release is also available online at: https://news.agu.org/press-release/fleeing-drought-vulnerable-populations-face-flood-risk-in-most-african-countries
AGU press contact:
Liza Lester, +1 (202) 777-7494, news@agu.org (UTC-5 hours)
Contact information for the researchers:
Serena Ceola, University of Bologna, serena.ceola@unibo.it (GMT+1 hours)
WASHINGTON — In 80% of African countries, moved toward rivers and into cities during or following drought, increasing the number of people living in flood-risk areas in recent decades, according to a new study. This resettlement pattern will likely intensify in coming decades as climate change is expected to make droughts more frequent and severe.
"It's a cycle that exacerbates how many people are negatively impacted by drought, and not only in the ways we might normally expect," said Serena Ceola, a hydrologist at the University of Bologna in Italy who led the study. "As regional climates change and both droughts and floods become bigger problems, more people will struggle to find a safe place to settle. People may move from one drought-affected place to another or move somewhere that just poses different climate risks."
In Somalia, for example more than 3.8 million people have been displaced in part by drought over the last three years. Many of those climate refugees sought shelter near rivers, where farming could resume, but heavy rains and flash floods then displaced more than half a million people.
The study was published in Earth’s Future, which publishes interdisciplinary research on the past, present and future of our planet and its inhabitants. Prior to this study, research on drought-driven migrations in Africa focused on single countries or specific drought events, limiting scientists’ understanding of how drought influences patterns of human settlements at large scales. The new study is the first to examine changes in human settlement patterns associated with droughts on a continental scale.
“We want the whole society to be aware of just how many people are moving from one climate threat to another,” Ceola said.
Untangling drought
Droughts may push people closer to rivers to continue agricultural activities, and others may adapt by moving to cities, which offer diverse economic opportunities when drought limits agriculture. Scientists have hypothesized that drought can be a main driver of human displacement, but many factors — often inextricably linked to drought itself — can contribute to displacement. Drought can exacerbate conflict, political violence and food and job insecurity, each of which can prompt mass migrations on their own.
The researchers chose to focus on drought alone due to its potential impact on many different factors. They used two indices, EM-DAT and SPEI-12, which respectively reflect socioeconomic and evapotranspiration impacts of drought, to look for droughts in 50 African countries from 1992 to 2013. They included in their analyses the years preceding and following the drought to test for strength of the drought signal and lingering effects of drought on human movement.
To determine whether people moved to rivers, the researchers used satellite-based nighttime light detection to check for either changes in existing settlements’ luminosities or the development of new settlements. They used annual, country-based World Bank census data to track populations in urban centers.
Where does drought drive people?
The study found people moved toward rivers or urban centers in up to 80% of African countries experiencing droughts as indicated by at least one of the two indices used. During drought years identified by at least one of the indices, about half to three-quarters of all studied countries had settlements move closer to rivers, and one-third to half of countries had urban populations grow. The urban-growth signal could have been weaker than river-based migration because people may move to cities for many reasons, Ceola said.
Seventeen countries experienced droughts according to both drought indices during the study period. Up to 65% of those countries saw increased human movement toward rivers during drought years when the pre-drought year was included in the analysis.
Notably, all countries in southern Africa saw drought-related migration toward rivers based on at least one drought index over the study period. Ceola pointed to Burundi, Guinea Bissau and Namibia as particularly interesting.
The methods have some limitations. Nighttime lights are used as a proxy for human settlements and activities, meaning that the amount of observed light may not reflect the number of people. Smaller concentrations of lights may not show up, and it might leave out the poorest groups that lack enough lights to appear. Limited data for many regions and populations on the continent mean scientists have to get creative with the sources of information available to prepare people and governments for current and future hazards, Ceola said.
“Policy makers need data and detailed information in order to implement strategic planning, support sustainable development and increase the resilience of people living in vulnerable areas. Likewise, people living in those areas need to be aware of the risks and should have the opportunity to freely move to safer locations,” Ceola said.
#
Notes for journalists:
Neither this paper nor this press release are under embargo. The study is published in Earth’s Future, an open-access journal. View and download a pdf of the study here.
Paper title:
“Drought and human mobility in Africa”
Authors:
S. Ceola (corresponding author), Department of Civil, Chemical, Environmental, and Materials Engineering, Alma Mater Studiorum Universita di Bologna, Bologna, Italy
J. Mård and G. Di Baldassarre, Centre of Natural Hazards and Disaster Science, Uppsala, Sweden, and Department of Earth Sciences, Air, Water and Landscape science, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden
#
AGU (www.agu.org) is a global community supporting more than half a million advocates and professionals in Earth and space sciences. Through broad and inclusive partnerships, AGU aims to advance discovery and solution science that accelerate knowledge and create solutions that are ethical, unbiased and respectful of communities and their values. Our programs include serving as a scholarly publisher, convening virtual and in-person events and providing career support. We live our values in everything we do, such as our net zero energy renovated building in Washington, D.C. and our Ethics and Equity Center, which fosters a diverse and inclusive geoscience community to ensure responsible conduct.
END
Fleeing drought, vulnerable populations face flood risk in most African countries
The Horn of Africa and southern Africa saw the most people move during droughts, according to a new continent-scale assessment of settlement locations in Africa
2023-12-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The future of canine stem cell therapy: unprecedented, painless, and feeder-free
2023-12-21
Osaka, Japan – Dog owners may need to learn to appreciate their best friend’s urine. Scientists at Osaka Metropolitan University have devised an efficient, non-invasive, and pain-free method to reprogram canine stem cells from urine samples, bringing furry companions one step closer to veterinary regenerative treatment.
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) have been widely employed in studies on human generative medicine. With the growing importance of advanced medical care for dogs and cats, there is an expectation that new therapies utilizing iPSCs will ...
New insights revealed on tissue-dependent roles of JAK signaling in inflammation
2023-12-21
Researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have gained a deeper understanding of the nuanced roles of JAK inhibitors, or modulators, in inflammation across various cell types and tissues. Their findings suggest a more precise approach is required to potentially expand JAK inhibitor use to a wider range of allergy and inflammatory disorders. Details on the findings were published in the December 21, 2023, issue of the journal Cell.
JAK1 is a key protein in the body that supports cell communication and controls the immune system. It is part of ...
Researchers discover key to epithelial cell growth
2023-12-21
RESEARCHERS DISCOVER KEY TO EPITHELIAL CELL GROWTH
Australian researchers have discovered a new way that epithelial cells, which form layers in organs like the skin and stomach, attach to one another, and how they perceive growth signals at these attachments, helping them form tissues of the right size and shape.
Epithelial cells cover the surfaces of most organs in the body and must adhere to each other to form both a protective and permeable barrier. They are exquisitely designed to both be tightly sealed against pathogens like bacteria, and to also allow the transport of salts, fluids, and nutrients.
Researchers, led by Professor Kieran Harvey and Dr Benjamin Kroeger, at the ...
Race and ethnicity of infants enrolled in neonatal clinical trials
2023-12-21
About The Study: This systematic review of 120 studies with 14,000 participants found that Asian, Black, Hispanic, and Indigenous (e.g., Alaska Native, American Indian, and Native Hawaiian) participants were underrepresented in neonatal clinical trials, while white participants were overrepresented. There was wide variation in the terms used to report race and ethnicity data, and geographic representation was unevenly distributed, with some central and western U.S. regions underrepresented.
Authors: Elliott M. Weiss, M.D., M.S.M.E., of the University of Washington School of Medicine in Seattle, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For ...
Wearable biosensing to predict imminent aggressive behavior in psychiatric inpatient youths with autism
2023-12-21
About The Study: The results of this study involving 70 youths with autism across four psychiatric inpatient hospitals suggest that wearable biosensing and machine learning may hold promise for identifying objective indicators of impending aggressive behaviors in youths with autism who are psychiatric inpatients. The findings may lay the groundwork for developing just-in-time adaptive intervention mobile health systems that may enable new opportunities for preemptive intervention.
Authors: Matthew S. Goodwin, Ph.D., of Northeastern University in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: ...
Back to the future: Weizmann Institute scientists develop the first method to measure cellular changes in the body over time
2023-12-21
While physicists continue to argue about whether time is indeed an illusion, as Albert Einstein claimed, biologists have no doubt about its significance for understanding life as a dynamic system. In recent years, they have been gaining an increasingly deeper understanding of complex biological systems using tools enabling the simultaneous analysis of vast amounts of cellular and molecular data and the probing of cellular circuitry that drives disease. However, these in-depth investigations of how cells behave and interact have provided only separate snapshots of what happens inside complex organisms, without accounting ...
The key mechanism to cell growth has been elucidated
2023-12-21
Osaka, Japan – Amino acids are the building blocks of life. We obtain them from the food we eat, and the body uses them to make proteins, which in turn are used for growth, development, and a multitude of other functions. However, before the body can build with these blocks, it must first be able to sense their presence.
When amino acids are available, a master regulator protein called TORC1 is switched on, causing proteins to be manufactured and cells to grow. If no amino acids are available, TORC1 is switched off, and cells start to recycle themselves in a process known as autophagy. Until now, it was unclear exactly how amino acids triggered the TORC1 switch in yeast.
Now, in a study ...
One of the keys to healthy sleep and blood sugar has been found
2023-12-21
Osaka, Japan – Only recently was it discovered that amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, exist in two different forms: L- and D-forms. While all natural proteins consist exclusively of L-amino acids, the function of D-amino acids remained poorly understood, despite being present in the food we eat every day.
Now, a multi-institutional research team led by Osaka University has revealed a function of one D-form amino acid: D-alanine. So, what does it do, and how did they uncover its function? To understand, we need a little background information.
The circadian clock, a natural ...
Artery calcification more common in night owls
2023-12-21
Artery calcification is almost twice as common in night owls compared to early birds, according to a study from the University of Gothenburg, Sweden. Circadian function appears to be particularly important during the early stages of cardiovascular disease.
Atherosclerosis involves fatty deposits accumulating on the inside of the arteries, making it harder for blood to pass through. The disease develops over a very long period of time and is not noticed until it leads to blood clots causing angina, heart attack, or stroke. Previous research has shown that people with late-night habits have an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, but this is the first study to show how circadian rhythms ...
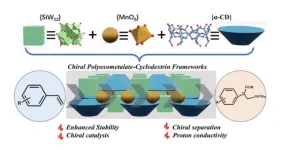
Scientists create chiral POM-based frameworks with enhanced stability and catalytic activity
2023-12-21
A team of scientists has created a chiral assembly by blending inorganic polyoxometalates and organic cyclodextrin molecules. Polyoxometalates are a class of nanomaterials with many useful applications. But the use of polyoxometalates as building blocks to construct chiral POM-based frameworks has been a long-stranding challenge for researchers. In this research, the team produced a 3D framework, constructed by coordination assembly. The resulting framework features an interlaced organic-inorganic hybrid layer.
The team has published their work in the journal, Polyoxometalates, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
Psilocybin trends in states that decriminalized use
New data signals high demand in aesthetic surgery in southern, rural U.S. despite access issues
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
[Press-News.org] Fleeing drought, vulnerable populations face flood risk in most African countriesThe Horn of Africa and southern Africa saw the most people move during droughts, according to a new continent-scale assessment of settlement locations in Africa