(Press-News.org) A pancake stack of radioactivity-sensitive films carried through the sky by a balloon was able to take the world's most accurate picture of a neutron star's gamma ray beam. To achieve this, Kobe University researchers combined the oldest method of capturing radioactive radiation with the newest data capturing techniques and a clever time-recording device.
The stars shine their light on us in the full range of the spectrum of light, from infra-red to gamma rays. For each of these bands, different sensing equipment is needed. The most challenging one is gamma rays, famous for being a high-energy product of nuclear fission, because their very short wavelength means that they don't interact with matter in the same way as other forms of light and thus can't be deflected with lenses or detected by standard sensors. Thus, there is a gap in our ability to detect the light coming from fascinating stellar objects such as supernovae and their remnants.
To resolve this issue, Kobe University astrophysicist AOKI Shigeki and his team turned to the very first material that was used to detect radioactivity, photographic films. "Our group has been focusing on the excellent capability of emulsion film to trace gamma rays with high precision and proposed that it could become an excellent gamma-ray telescope by introducing several modern data capture and analysis features," explains Aoki. Based on the high sensitivity of these films and a novel, automated, high-speed process of extracting data from them, the physicists' idea was to stack up a few of them to accurately capture the trajectory of the particles that the gamma ray produces on impact, just like a single pancake may capture where you poke a straw into it, but it takes a whole stack to record the straw's direction.
To reduce atmospheric interference, they then mounted the stack of films onto a scientific observation balloon to lift it to a height between 35 and 40 kilometers. However, since a balloon is swaying and twisting in the wind, the direction of the "telescope" is not stable, so they added a set of cameras to record the gondola's orientation relative to the stars at any time. But this created another issue, because as anybody who has ever taken a photograph with long exposure knows, photographic film does not record the passage of time and so it is not directly possible to know at what time any given gamma ray impact occurred. To overcome this problem, they made the bottom three layers of film move back and forth at regular but different speeds, just like the hands of a clock. From the relative dislocation of the traces in those lower plates they could then calculate the precise time of the impact and thus correlate it with the cameras' footage.
They have now published the first image resulting from this setup in the journal The Astrophysical Journal. It is the most accurate image ever produced of the Vela pulsar, a fast-spinning neutron star that projects a beam of gamma rays into the sky like a lighthouse at night. "We captured a total of several trillion tracks with an accuracy of 1/10,000 millimeters. By adding time information and combining it with attitude monitoring information, we were able to determine ‘when’ and ‘where’ the events originated with such precision that the resulting resolution was more than 40 times higher than that of conventional gamma-ray telescopes," Aoki summarizes his group's achievements.
While these results are impressive already, the new technique opens the possibility of capturing more details in this frequency band of light than ever before. The Kobe University researcher explains, "By means of scientific balloon-borne experiments, we can attempt to contribute to many areas of astrophysics, and in particular to open up gamma-ray telescopy to 'multi-messenger astronomy' where simultaneous measurements of the same event captured through different techniques are required. Based on the success of the 2018 balloon experiment these data were generated with, we will expand the observation area and time in upcoming balloon flights and are looking forward to scientific breakthroughs in the field of gamma-ray astronomy."
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI grants 17H06132, 18H01228 and 18K13562. It was conducted in collaboration with researchers from Okayama University of Science, Aichi University of Education, Nagoya University and Gifu University.
Kobe University is a national university with roots dating back to the Kobe Commercial School founded in 1902. It is now one of Japan's leading comprehensive research universities with nearly 16,000 students and nearly 1,700 faculty in 10 faculties and schools and 15 graduate schools. Combining the social and natural sciences to cultivate leaders with an interdisciplinary perspective, Kobe University creates knowledge and fosters innovation to address society’s challenges.
END
Pancake stack of films on a balloon most accurate gamma-ray telescope
2023-12-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Wireless tracking system could help improve the XR experience
2023-12-21
A new technology developed by engineers at the University of California San Diego has the potential to make the extended reality (XR) experience smoother and more seamless. The technology consists of an asset localization system that uses wireless signals to track physical objects with centimeter-level accuracy in real time, and then generates a virtual representation of these objects. Applications of this technology range from enhancing virtual gaming experiences to improving workplace safety.
The team, led by Dinesh Bharadia, a professor in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at the UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering, ...
Fleeing drought, vulnerable populations face flood risk in most African countries
2023-12-21
American Geophysical Union
Press Release 23-47
21 December 2023
For Immediate Release
This press release is also available online at: https://news.agu.org/press-release/fleeing-drought-vulnerable-populations-face-flood-risk-in-most-african-countries
AGU press contact:
Liza Lester, +1 (202) 777-7494, news@agu.org (UTC-5 hours)
Contact information for the researchers:
Serena Ceola, University of Bologna, serena.ceola@unibo.it (GMT+1 hours)
WASHINGTON — In 80% of African countries, moved toward rivers and into cities during or following drought, increasing the number of people living in flood-risk areas in ...
The future of canine stem cell therapy: unprecedented, painless, and feeder-free
2023-12-21
Osaka, Japan – Dog owners may need to learn to appreciate their best friend’s urine. Scientists at Osaka Metropolitan University have devised an efficient, non-invasive, and pain-free method to reprogram canine stem cells from urine samples, bringing furry companions one step closer to veterinary regenerative treatment.
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) have been widely employed in studies on human generative medicine. With the growing importance of advanced medical care for dogs and cats, there is an expectation that new therapies utilizing iPSCs will ...
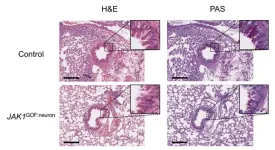
New insights revealed on tissue-dependent roles of JAK signaling in inflammation
2023-12-21
Researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have gained a deeper understanding of the nuanced roles of JAK inhibitors, or modulators, in inflammation across various cell types and tissues. Their findings suggest a more precise approach is required to potentially expand JAK inhibitor use to a wider range of allergy and inflammatory disorders. Details on the findings were published in the December 21, 2023, issue of the journal Cell.
JAK1 is a key protein in the body that supports cell communication and controls the immune system. It is part of ...
Researchers discover key to epithelial cell growth
2023-12-21
RESEARCHERS DISCOVER KEY TO EPITHELIAL CELL GROWTH
Australian researchers have discovered a new way that epithelial cells, which form layers in organs like the skin and stomach, attach to one another, and how they perceive growth signals at these attachments, helping them form tissues of the right size and shape.
Epithelial cells cover the surfaces of most organs in the body and must adhere to each other to form both a protective and permeable barrier. They are exquisitely designed to both be tightly sealed against pathogens like bacteria, and to also allow the transport of salts, fluids, and nutrients.
Researchers, led by Professor Kieran Harvey and Dr Benjamin Kroeger, at the ...
Race and ethnicity of infants enrolled in neonatal clinical trials
2023-12-21
About The Study: This systematic review of 120 studies with 14,000 participants found that Asian, Black, Hispanic, and Indigenous (e.g., Alaska Native, American Indian, and Native Hawaiian) participants were underrepresented in neonatal clinical trials, while white participants were overrepresented. There was wide variation in the terms used to report race and ethnicity data, and geographic representation was unevenly distributed, with some central and western U.S. regions underrepresented.
Authors: Elliott M. Weiss, M.D., M.S.M.E., of the University of Washington School of Medicine in Seattle, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For ...
Wearable biosensing to predict imminent aggressive behavior in psychiatric inpatient youths with autism
2023-12-21
About The Study: The results of this study involving 70 youths with autism across four psychiatric inpatient hospitals suggest that wearable biosensing and machine learning may hold promise for identifying objective indicators of impending aggressive behaviors in youths with autism who are psychiatric inpatients. The findings may lay the groundwork for developing just-in-time adaptive intervention mobile health systems that may enable new opportunities for preemptive intervention.
Authors: Matthew S. Goodwin, Ph.D., of Northeastern University in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: ...
Back to the future: Weizmann Institute scientists develop the first method to measure cellular changes in the body over time
2023-12-21
While physicists continue to argue about whether time is indeed an illusion, as Albert Einstein claimed, biologists have no doubt about its significance for understanding life as a dynamic system. In recent years, they have been gaining an increasingly deeper understanding of complex biological systems using tools enabling the simultaneous analysis of vast amounts of cellular and molecular data and the probing of cellular circuitry that drives disease. However, these in-depth investigations of how cells behave and interact have provided only separate snapshots of what happens inside complex organisms, without accounting ...
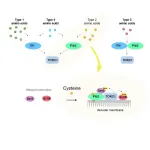
The key mechanism to cell growth has been elucidated
2023-12-21
Osaka, Japan – Amino acids are the building blocks of life. We obtain them from the food we eat, and the body uses them to make proteins, which in turn are used for growth, development, and a multitude of other functions. However, before the body can build with these blocks, it must first be able to sense their presence.
When amino acids are available, a master regulator protein called TORC1 is switched on, causing proteins to be manufactured and cells to grow. If no amino acids are available, TORC1 is switched off, and cells start to recycle themselves in a process known as autophagy. Until now, it was unclear exactly how amino acids triggered the TORC1 switch in yeast.
Now, in a study ...
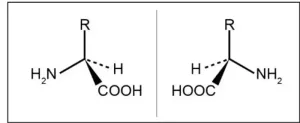
One of the keys to healthy sleep and blood sugar has been found
2023-12-21
Osaka, Japan – Only recently was it discovered that amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, exist in two different forms: L- and D-forms. While all natural proteins consist exclusively of L-amino acids, the function of D-amino acids remained poorly understood, despite being present in the food we eat every day.
Now, a multi-institutional research team led by Osaka University has revealed a function of one D-form amino acid: D-alanine. So, what does it do, and how did they uncover its function? To understand, we need a little background information.
The circadian clock, a natural ...