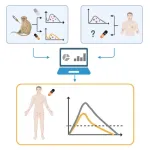
Despite use of tecovirimat since the beginning of the 2022 mpox outbreak, few data have been published on its antiviral effect in humans
This study predicts the impact of early tecovirimat administration on the time to viral clearance in patients with mpox infection, using an integrative modeling approach combining pre-clinical and clinical data
2023-12-21
(Press-News.org)
Despite use of tecovirimat since the beginning of the 2022 mpox outbreak, few data have been published on its antiviral effect in humans; this study predicts the impact of early tecovirimat administration on the time to viral clearance in patients with mpox infection, using an integrative modeling approach combining pre-clinical and clinical data
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002249
Article Title: Early administration of tecovirimat shortens the time to mpox clearance in a model of human infection
Author Countries: France, Spain, United Kingdom, United States, Papua New Ginea
Funding: BTN received funding from IAME UMR 137, Université Paris Cité, INSERM, F-75018, Paris, France (https://www.iame-research.center/). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-12-21
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A lot has changed in the world since the Endangered Species Act (ESA) was enacted 50 years ago in December 1973.
Two researchers at The Ohio State University were among a group of experts invited by the journal Science to discuss how the ESA has evolved and what its future might hold.
Tanya Berger-Wolf, faculty director of Ohio State’s Translational Data Analytics Institute, led a group that wrote on “Sustainable, trustworthy, human-technology partnership.” Amy Ando, professor and chair of the university’s Department of Agricultural, Environmental, and Development Economics, ...
2023-12-21
New research, publishing December 21st in the open access journal in PLOS Biology, shows that tears from women contain chemicals that block aggression in men. The study led by Shani Agron at the Weizmann Institute of Science, Israel, finds that sniffing tears leads to reduced brain activity related to aggression, which results is less aggressive behavior.
Male aggression in rodents is known to be blocked when they smell female tears. This is an example of social chemosignaling, a process that is common in animals but less common—or less understood—in humans. To determine whether tears have the same affect in people, ...
2023-12-21
Inspired by the structure of polar bear fur, researchers present a knittable aerogel fiber with exceptional thermal and mechanical properties. The fibers are washable, dyeable, durable, and well-suited to be used in advanced textiles. This allowed the researchers to test them in a sweater that demonstrated impressive thermal insulation, among other features. Aerogels are an ideal material for thermal insulation. They demonstrate high porosity and extremely low thermal conductivity. However, the application of ...
2023-12-21
Racial disparities related to health and physical well-being motivate Americans to take action for social change more than racial disparities related to other factors, like economics, a new study finds. This is because health-related racial inequalities are perceived to be more unjust. The results suggest that framing racial disparities to tap into feelings of moral injustice may motivate policy reform – a finding of potential interest to policymakers, social movements, and citizens seeking to gain support for actions to reduce racial inequality. “…this work can help us understand ...
2023-12-21
Genetic analyses of an Antarctic octopus show that the West Antarctic Ice Sheet (WAIS) collapsed during the Last Interglacial ~129,000 to 116,000 years ago when temperatures were only about 1 degree Celsius (°C) warmer than preindustrial levels. The findings suggest that WAIS collapse and resultant sea-level rise could be caused by even the minimal temperature rises projected by the most optimistic climate change mitigation plans. Climate change is driving unprecedented change to Earth’s cryosphere. The West Antarctic Ice Sheet is considered particularly vulnerable to warming ...
2023-12-21
In El Salvador, preference for cash and privacy fears deterred the widespread adoption of Bitcoin as an everyday currency, researchers report. The findings suggest that policies incentivizing cryptocurrency adoption as legal tender will likely fail unless populations are financially literate and already trust digital currencies. The introduction of digital currencies is one of the most important developments in monetary economics in the last decade. Unlike traditional digital currencies, which rely on central authorities such as governments or banks governed by regulations ...
2023-12-21
ROCHESTER, Minn. — Mayo Clinic researchers mapped how the measles virus mutated and spread in the brain of a person who succumbed to a rare, lethal brain disease. New cases of this disease, which is a complication of the measles virus, may occur as measles reemerges among the unvaccinated, say researchers.
Using the latest tools in genetic sequencing, researchers at Mayo Clinic reconstructed how a collective of viral genomes colonized a human brain. The virus acquired distinct mutations that drove the spread of the virus from the frontal cortex outward.
"Our study provides compelling data that ...
2023-12-21
Analysis of organic compounds – called polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) – extracted from the Ryugu asteroid and Murchison meteorite has found that certain PAHs likely formed in the cold areas of space between stars rather than in hot regions near stars as was previously thought. The findings open new possibilities for studying life beyond Earth and the chemistry of objects in space.
The only Australian members of an international research team, scientists from Curtin’s WA-Organic ...
2023-12-21
Researchers at the University of Chicago’s Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering (PME), Argonne National Laboratory, and the University of Modena and Reggio Emilia have developed a new computational tool to describe how the atoms within quantum materials behave when they absorb and emit light. The tool will be released as part of the open-source software package WEST, developed within the Midwest Integrated Center for Computational Materials (MICCoM) by a team led by Prof. Marco ...
2023-12-21
Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men other than skin cancer, and more than 288,000 new cases are diagnosed every year, according to the American Cancer Society. The disease’s fatality rate has decreased by more than half since the 1990s, but there is still room for progress—especially in treating or preventing advanced, metastatic disease, which is much more likely to be fatal.
A new paper published in Science Advances clarifies how an enzyme called SMYD3 may be involved in prostate ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Despite use of tecovirimat since the beginning of the 2022 mpox outbreak, few data have been published on its antiviral effect in humans
This study predicts the impact of early tecovirimat administration on the time to viral clearance in patients with mpox infection, using an integrative modeling approach combining pre-clinical and clinical data