(Press-News.org) Researchers at the UCLA Health Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center have received a five-year, $3 million grant from the National Cancer Institute to identify novel cancer biomarkers and develop AI that can detect and predict aggressive prostate cancer to help avoid unnecessary treatments and their associated negative side effects.
Despite recent advancements, prostate cancer remains a common and serious health issue for men, and current methods of screening and risk assessment can often lead to overdiagnosis and overtreatment. About 90% of people diagnosed with prostate cancer receive treatment, even though up to 60% of them could be candidates for active surveillance.
The project will be led by Corey Arnold, professor of radiology and pathology and laboratory medicine, and includes Paul Boutros, professor of human genetics and urology; Dr. Leonard Marks, professor of urology; Dr. Anthony Sisk, assistant professor of pathology and laboratory medicine; and Dr. Steven Raman, professor of radiology. The team will collaborate with investigators at Washington University in St. Louis to integrate magnetic resonance imaging, digital histology images, genetic information, and biomarkers in a computational model that can more precisely capture a patient’s current cancer state and forecast outcomes.
“We expect this approach to be able to provide more accurate information about the nature of the cancer, helping doctors to distinguish between aggressive and less threatening forms,” said Arnold, director of the UCLA Computational Diagnostics team. “It will also allow for more personalized and targeted treatment plans, reducing unnecessary interventions and their associated negative effects on patients’ quality of life.”
The project complements ongoing prostate cancer-focused grants in radiology led by faculty members Kyung Sung and Holden Wu.
END
Researchers awarded $3 million to develop AI to better detect aggressive prostate cancer
2023-12-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
GPCR structure: Research reveals molecular origins of function for a key drug target
2023-12-21
Through an international collaboration, scientists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital leveraged data science, pharmacology and structural information to conduct an atomic-level investigation into how each amino acid in the receptor that binds adrenaline contributes to receptor activity in the presence of this natural ligand. They discovered precisely which amino acids control the key pharmacological properties of the ligand. The adrenaline receptor studied is a member of the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) family, and this family is the target of one-third of all Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved drugs. Thus, understanding how ...
Structures of Parkinson’s disease-linked proteins offer a framework for understanding how they work together
2023-12-21
Scientists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital revealed the complex structure of two Parkinson’s disease-related proteins, both of which are implicated in late-onset cases. Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) is a protein kinase that modifies other proteins in a process called phosphorylation; Rab29, a member of the Rab GTPase family that regulates cellular trafficking, modulates the activity of LRRK2. How Rab29 and LRRK2 work synergistically to cause Parkinson’s disease remains ...
Male breast cancer diagnosis fuels groundbreaking treatment tool
2023-12-21
Doctors diagnosed Christopher Gregg, Ph.D., member of the Nuclear Control of Cell Growth and Differentiation Program at Huntsman Cancer Institute at the University of Utah (the U) and neuroscientist and professor of neurobiology and human genetics at the U, with stage 4 metastatic breast cancer in 2018. At that point, he started thinking of ways to improve his treatment.
“The core problem of metastatic cancer is it evolves,” says Gregg. “There may be a treatment that works today but eventually ...
NASA’s Hubble watches ‘spoke season’ on Saturn
2023-12-21
This photo of Saturn was taken by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope on October 22, 2023, when the ringed planet was approximately 850 million miles from Earth. Hubble's ultra-sharp vision reveals a phenomenon called ring spokes.
Saturn's spokes are transient features that rotate along with the rings. Their ghostly appearance only persists for two or three rotations around Saturn. During active periods, freshly-formed spokes continuously add to the pattern.
In 1981, NASA's Voyager 2 first photographed the ring spokes. NASA's Cassini orbiter also saw the spokes during its 13-year-long mission that ended in 2017.
Hubble continues ...
Astronomers detect seismic ripples in ancient galactic disk
2023-12-21
A new snapshot of an ancient, far-off galaxy could help scientists understand how it formed and the origins of our own Milky Way.
At more than 12 billion years old, BRI 1335-0417 is the oldest and furthest known spiral galaxy in our universe.
Lead author Dr Takafumi Tsukui said a state-of-the-art telescope called ALMA allowed them to look at this ancient galaxy in much greater detail.
“Specifically, we were interested in how gas was moving into and throughout the galaxy,” Dr Tsukui said.
“Gas is a key ingredient for forming stars and can give ...
Exercise prescription: Pioneering the "third pole" for clinical health management
2023-12-21
Professor Chen Shiyi's team at Huashan Hospital of Fudan University commented on the concept, policy, development and prospect of exercise prescription in the context of " Health for All", which was published in Research (10.34133/research.0284) under the title of " Exercise Prescription: Pioneering the “Third Pole” for Clinical Health Management".
Modern lifestyles have led to reduced physical activity and a rise in chronic diseases from a young age. Exercise ...
Inside the matrix: Nanoscale patterns revealed within model research organism
2023-12-21
Species throughout the animal kingdom feature vital interfaces between the outermost layers of their bodies and the environment. Intricate microscopic structures—featured on the outer skin layers of humans, as one example—are known to assemble in matrix patterns.
But how these complex structures, known as apical extracellular matrices (aECMs) are assembled into elaborately woven architectures has remained an elusive question.
Now, following years of research and the power of a technologically advanced instrument, University of California San Diego scientists have unraveled the underpinnings ...
Urology treatment studies show increased reporting of harmful effects
2023-12-21
Waltham — December 11, 2023 —
In recent years, clinical trial reports in major urology journals have been more likely to include data on harmful effects of treatments, reports a study in the January issue of The Journal of Urology®, an Official Journal of the American Urological Association (AUA). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"Our analysis finds a marked increase in reporting of potential harms in randomized treatment trials ...
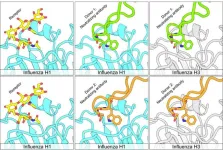
New type of antibody shows promise against multiple forms of flu virus
2023-12-21
Researchers have identified a previously unrecognized class of antibodies—immune system proteins that protect against disease—that appear capable of neutralizing multiple forms of flu virus. These findings, which could contribute to development of more broadly protective flu vaccines, will publish December 21st by Holly Simmons of the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, US, and colleagues in the open access journal PLOS Biology.
A flu vaccine prompts the immune system to make antibodies that can bind to a viral protein ...
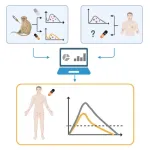
Despite use of tecovirimat since the beginning of the 2022 mpox outbreak, few data have been published on its antiviral effect in humans
2023-12-21
Despite use of tecovirimat since the beginning of the 2022 mpox outbreak, few data have been published on its antiviral effect in humans; this study predicts the impact of early tecovirimat administration on the time to viral clearance in patients with mpox infection, using an integrative modeling approach combining pre-clinical and clinical data
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002249
Article Title: Early administration of tecovirimat shortens the time to mpox clearance ...