(Press-News.org)
In this digital age, children are exposed to overwhelming amounts of information online, some of it unverified and increasingly generated by non-human sources, such as AI-driven language models. As children grow older, the ability to assess a source’s reliability is an important skill in cultivating critical thinking.
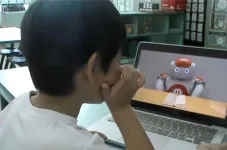
Children aged three to five years display selective trust based on the informant’s past accuracy when faced with both humans and robots, according to a study published in the journal Child Development titled, ‘Younger, not older, children trust an inaccurate human informant more than an inaccurate robot informant.’
“Children do not just trust anyone to teach them labels, they trust those who were reliable in the past. We believe that this selectivity in social learning reflects young children’s emerging understanding of what makes a good (reliable) source of information,” explained Li Xiaoqian, a research scholar at Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD) who co-authored the study with her PhD supervisor Professor Yow Wei Quin, a psychology professor and head of Humanities Arts and Social Sciences cluster at SUTD. “The question at stake is how young children use their intelligence to decide when to learn and whom to trust.”
In the study, participants from Singapore preschools such as ChildFirst, Red SchoolHouse and Safari House, aged between three and five, were split below and above the median age of 4.58 years old into ‘younger’ and ‘older’ cohorts respectively. They were paired with a robot or human informant, which either provided accurate or inaccurate labels to objects, such as ‘ball’ or ‘book’. The researchers then tested to see if the informant’s identity (human or robot) and track record as a reliable informant as well as the child’s age influenced the child’s trust in the informant to label things correctly in the future.
Participants were presented with only one informant during the study, and their trust was measured by their willingness to accept new information. The humanoid social robot by SoftBank Robotics, NAO, which has a human-like but robotic voice, was used as the robot informant. To keep conditions comparable, the human informant matched her movements to those of the robot. An experimenter was also seated next to the participant to ask the necessary questions, so that the participant would not feel pressured to agree with the informant.
The study revealed that children were willing to accept new information from both human and robot informants who had previously given accurate information, but not from a potentially unreliable informant who had made mistakes in the past—especially when the informant was a robot. As for the age effect, the authors reported that younger children were likelier to accept information from an unreliable human than an unreliable robot, but older children were found to distrust or reject information from an unreliable informant, human or robot.
“These results implicate that younger and older children may have different selective trust strategies, especially the way they use informants’ reliability and identity cues when deciding who to trust. Together with other research on children’s selective trust, we show that as children get older, they may increasingly rely on reliability cues to guide their trust behaviour,” said Dr Li.
Previous research has shown that children rely on factors such as age, familiarity, and language to figure out whether an informant is reliable or not. It may be that younger children rely on identity cues like these more than they do epistemic evidence. As they get older, children place more emphasis on “what you know” than “who you are” when deciding to trust an informant.
This is the first study to ask the questions: (1) Do children draw different inferences about robots with varying track records of accuracy? and (2) Are these inferences comparable to those about humans?
“Addressing these questions will provide a unique perspective on the development of trust and social learning among children who are growing up alongside various sources of information, including social robots,” described Prof Yow.
This research has significant implications for pedagogy, where robots and non-human educational tools are increasingly integrated into the classroom. Children today may not perceive robots as trustworthy as humans if they have not interacted much with robots. However, as children gain more exposure to smart machines, they could be inclined to see robots as intelligent and reliable sources of knowledge.
Future studies could explore the selective learning development theory beyond the scope of word learning, such as tool usage, emotional expression congruency, or episodic domains such as location learning. For now, the researchers hope that their findings are considered in the realm of design pedagogy.
“Designers should consider the impact of perceived competence when building robots and other AI-driven educational tools for young children. Recognising the developmental changes in children’s trust of humans versus robots can guide the creation of more effective learning environments, ensuring that the use of technologies aligns with children’s developing cognitive and social needs,” emphasised Prof Yow.
END
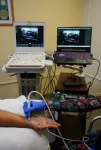
Researchers at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), in collaboration with Aster-CMI Hospital, have developed an AI tool that can identify the median nerve in ultrasound videos and detect carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS). The study was published in IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control.
CTS arises when the median nerve, which runs from the forearm into the hand, is compressed at the carpal tunnel part of the wrist, resulting in numbness, tingling or pain. It ...
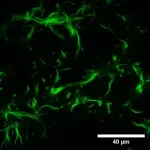
Tiny things matter – for instance, one amino acid can completely alter the architecture of the cell. Researchers at the Universities of Göttingen and Warwick investigated the structure and mechanics of the main component of the cytoskeleton of the cell: a protein known as actin. Actin is found in all living cells where it has a range of important functions – from muscle contraction to cell signalling and cell shape. This protein comes in two different varieties termed “isoforms”, which are known as gamma actin and beta actin. The difference between the two proteins is ...
For the first time, an instrument to find planets light years away was used on an object in the Solar System, in a study on Jupiter's winds.
We find ourselves at a time when it has become almost commonplace to discover planets orbiting another star, with more than 5,000 already registered. The first distant worlds to incorporate this list were mainly giant planets, similar to but also very different in many ways from Jupiter and Saturn.
Astrophysicists have already begun to obtain data on the atmospheres of exoplanets, but fundamental ...
Osaka, Japan - As the world grappled with lockdowns and restrictions brought by the COVID-19 pandemic, researchers at Osaka Metropolitan University conducted an extensive study to elucidate the link between changes in human mobility and the impact on medical costs associated with lifestyle-related diseases.
Dr. Haruka Kato and Professor Atsushi Takizawa of the Graduate School of Human Life and Ecology at Osaka Metropolitan University were concerned by the negative health effects resulting from the restriction of ...
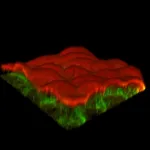
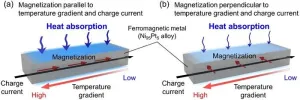
1. NIMS has succeeded in directly observing the "anisotropic magneto-Thomson effect," a phenomenon in which the heat absorption/release proportional to an applied temperature difference and charge current (i.e., Thomson effect) changes anisotropically depending on the magnetization direction in magnetic materials. This research is expected to lead to further development of basic physics and materials science related to the fusion area of thermoelectrics and spintronics, as well as to development of new functionalities to control thermal energy with magnetism.
2. The Thomson effect has long been known as one of the fundamental ...
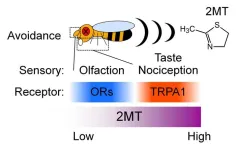
Okazaki, Japan – crop damage in agriculture and the transmission of vector-borne diseases by insect pests have become worldwide threat nowadays. Chemical treatments such as insecticides and repellents have been a major strategy against insect pests for centuries. Due to limited understanding of mechanisms of insect avoidance behavior, however, development of insect repellents has been delayed. To discover compounds that effectively repel insect pests, it is important to focus on key molecules associated with sensory, particularly aversive, responses. In this study, researchers ...
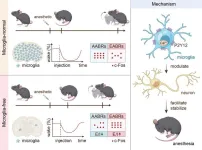
Though it may be a surprise to the millions of people who undergo general anesthesia every year for medical procedures, the biological mechanism for how different anesthetics block consciousness is still not fully understood. However, researchers may be one step closer after uncovering the way small immune cells in the brain called microglia are impacted by general anesthesia.
The research was presented in a paper published in eLife on 22/Dec/2023.
“We found that microglia play an important role in regulating the body’s response to general anesthesia. ...
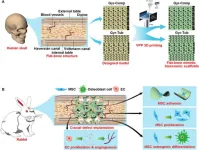
The cranial bone in the human body performs very important functions, such as protecting the brain and enabling the passage of the cranial nerves that are essential to physiological functioning. Critical-sized cranial defects can disrupt both the physical and psychological well-being of patients. Restoration of critical-sized cranial defects by cranioplasty is challenging for reconstructive surgeons, who prefer to use autologous bone grafts. The acquisition of autologous bone requires additional surgeries concomitant with risks such as free flap loss, infection, deep venous thrombosis, and nerve injury. These limitations necessitate the development ...
P. Hemachandra Reddy, Ph.D., a professor in the Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center (TTUHSC) School of Medicine’s Department of Internal Medicine who has researched healthy aging, dementia and other neurodegenerative diseases for more than 20 years, recently was named to the 2023 class of Fellows for the National Academy of Inventors (NAI).
The NAI is a member organization comprised of U.S. and international universities and governmental and nonprofit research institutes with more than 4,600 individual inventor members and fellows spanning more than 300 institutions worldwide. ...
Vision is a complex process. The visual perception of the environment is created by a combination of different wavelengths of light, which are decoded as colours and brightness in the brain. Photoreceptors in the retina first convert the light into electrical impulses: with sufficient light, the cones enable sharp, detailed, and coloured vision. Rods only contribute to vision in low light conditions allowing for different shades of grey to be distinguished but leaving vision much less precise. The electrical nerve impulses are finally transmitted to ganglion cells in the retina and then via the optic nerve to the visual cortex in the ...