(Press-News.org) Climate change is the biggest global health threat in the 21st century, and the rising temperatures have undermined the health and safety of the working population, as well as caused labor losses, which are closely tied to social-economic development. Although the future temperatures increase in China has been forecasted by state-of-the-art climate change projections, to what extent the influence on labor has not been well studied. In a paper published in Science Bulletin, a Chinese research team presents evidence of future labor losses due to heat stress in China under climate change scenarios. This study was led by Cunrui Huang, a professor at the Vanke School of Public Health, Tsinghua University.
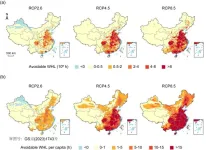
They found that climate change will exacerbate heat-related work hours lost (WHL) in China, even with a reduced working population in the future. The southern, eastern, and central provinces of China are the most affected, which is largely due to their higher temperature exposure, larger population size, and higher shares of vulnerable populations in total employment. However, limiting global warming to 1.5 °C would yield substantial gains. Compared to RCP2.6, RCP4.5 and RCP8.5, all provinces can avoid an average of 11.8%, 33.7%, and 53.9% of annual WHL if achieving the 1.5 °C target, which is equivalent to avoiding the losses of 0.1%, 0.6%, and 1.4% of annual GDP in China, respectively.
The research provides robust evidence for policymakers to understand the severity of future heat-related labor losses due to climate change in China. Stringent mitigation policies coupled with effective adaptation measures are therefore needed for protecting occupational health and work capacity in China. Each province should tailor occupational health protection measures to their circumstances. In addition, the findings are important for other developing countries with similar climate and demographic characteristics to China.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2023.09.044
END
Future labor losses due to heat stress in China under climate change scenarios
2023-12-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Acellular players in the high cryosphere: diversity, function and activity of the global supraglacial DNA viruses
2023-12-28
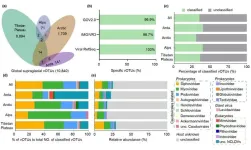
Supraglacial environments mainly consist of four main types of habitats for microbes and viruses, including snow, ice, meltwater, and cryoconites (the granular sediment on glacier surfaces). The paper revealed that there were more than 10,000 viral species in global supraglacial environments. This is a 15-fold expansion of DNA viral genomic inventory ever known. These viruses mainly belong to bacteriophages, viruses infecting bacteria. Liu et al., also found the viral communities showed a clear regional and habitat distribution pattern, with polar glacier samples separated from mountain ...
A carbon-lite atmosphere could be a sign of water and life on other terrestrial planets, MIT study finds.
2023-12-28
Scientists at MIT, the University of Birmingham, and elsewhere say that astronomers’ best chance of finding liquid water, and even life on other planets, is to look for the absence, rather than the presence, of a chemical feature in their atmospheres.
The researchers propose that if a terrestrial planet has substantially less carbon dioxide in its atmosphere compared to other planets in the same system, it could be a sign of liquid water — and possibly life — on that planet’s surface.
What’s more, this new signature is within the sights of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). While scientists have proposed ...
Insilico announces the expansion of its oncology pipelines and delivers the new generation FGFR2/3 inhibitor
2023-12-28
- The nomination of the new generation of FGFR2/3 inhibitor for the treatment of tissue-agnostic solid tumors, bringing the total number of PCCs nominated by Insilico in 2023 to six.
- ISM8001 is an oral, highly selective, covalent inhibitor that demonstrated superior potency in multiple FGFR2/3-driven efficacy models, and also in gatekeeper and molecular brake mutant resistant models.
- The program once again demonstrates Insilico's ability to efficiently generate novel molecules with high quality that are currently available for partnering.
Insilico Medicine ("Insilico"), a generative artificial intelligence (AI)-driven clinical-stage drug discovery ...
Liso-cel is a cost effective second-line treatment for common form of lymphoma
2023-12-28
(WASHINGTON, Dec. 28, 2023) – Lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel), a CAR T-cell therapy, is a cost effective second line treatment for relapsed and refractory (hard to treat) diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (r/r DLBCL), according to a study published today in Blood Advances. The study is the first of its kind to incorporate healthcare expenses, societal productivity losses, and patient quality of life in assessing the drug’s cost-effectiveness.
"In our study, we incorporated the often-overlooked societal costs associated with cancer treatment, which are typically neglected in ...
A team from the UPV and CSIC discovers a new method for generating metal nanoparticles for use as catalysts
2023-12-28
This new method is based on the exsolution process activated by microwave radiation. Exsolution is a method of generating metallic nanoparticles on the surface of ceramic materials. "At elevated temperatures and in a reducing atmosphere (usually hydrogen), metal atoms migrate from the structure of the material to its surface, forming metal nanoparticles anchored to the surface. This anchoring significantly increases the strength and stability of these nanoparticles, which positively impacts the efficiency of these catalysts," explains Beatriz García Baños, a researcher in the Microwave Area of the ITACA Institute at the UPV.
In the work now ...
Cancer test shows promise for bringing the benefits of immunotherapy to more patients
2023-12-28
Brigham researchers’ findings from next-generation sequencing suggest that revising current cancer care guidelines could allow approximately 6,000 more patients in the U.S. to benefit from immunotherapy treatment each year
Immunotherapy is a highly effective treatment for patients whose cancers harbor mismatch repair deficiency, and a new study identifies more cancer patients who could benefit from this form of therapy. Investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, found that nearly six percent of endometrial cancer patients and one percent of colorectal cancer patients with mismatch repair deficiency were ...
Medicaid coverage of physical, behavioral health together does not improve access, care
2023-12-28
Health care systems in the United States have gradually embraced the concept that mental health should be treated on par with physical health, especially in light of increased rates of anxiety and depression during and after the COVID-19 pandemic.
To improve access to mental health treatment, many Medicaid programs have required their managed care organizations to pay for behavioral health and physical health together. That’s in contrast to the traditional approach in which behavioral health, including treatment for substance use disorders, was “carved out” ...
Scientists discover new way to identify liquid water on exoplanets
2023-12-28
Scientists have devised a new way to identify habitable planets and potentially inhabited planets, by comparing the amount of carbon dioxide in their atmosphere, to neighbouring planets.
An international team of researchers from the University of Birmingham (UK), the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) (US) and elsewhere, have shown that if a planet has a reduced amount of CO2 in its atmosphere compared to neighbouring planets, it suggests there is liquid water on that planet’s surface. The drop in CO2 levels implies ...
Developing nanocatalysts to overcome limitations of water electrolysis technology
2023-12-28
Green hydrogen can be produced through water electrolysis technology, which uses renewable energy to split water into hydrogen and oxygen without emitting carbon dioxide. However, the production cost of green hydrogen is currently around $5 per kilogram, which is two to three times higher than gray hydrogen obtained from natural gas. For the practical use of green hydroten, the innovation in water electrolysis technology is required for the realization of hydrogen economy, especially for Korea where the utilization ...
Blood poisoning keeping many people out of work
2023-12-28
A few years ago, the World Health Organization estimated that blood poisoning, or sepsis, is involved in one in five deaths in the world. 11 million people die from sepsis each year, of which nearly 3 million are children.
This is also a problem in Norway, with thousands of people affected every year.
“Sepsis is a severe immunological overreaction to an infection. It causes the body’s organs to fail,” says Nina Vibeche Skei. She is a doctoral research fellow at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) and a senior anaesthetist ...