(Press-News.org) WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Large hypoxic zones low in oxygen long have been thought to have negative influences on aquatic life, but a Purdue University study shows that while these so-called dead zones have an adverse affect, not all species are impacted equally.
Tomas Höök, an assistant professor of forestry and natural resources, and former Purdue postdoctoral researcher Kristen Arend used output from a model to estimate how much dissolved oxygen was present in Lake Erie's hypoxic zone each day from 1987 to 2005. That information was compared with biological information for four fish species to assess the hypoxic zone's impact on the sustainability of their habitats.
"The term 'dead zone' sounds really scary," Höök said. "But in a lot of cases a hypoxic zone will not be negative for all fish species."
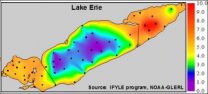
Lake Erie's hypoxic zone is very large - about the size of Rhode Island and Delaware combined. And while the Gulf of Mexico's dead zone has received more attention, during some years Lake Erie's zone may be greater in volume.
Hypoxia occurs when water has less than two parts per million of dissolved oxygen. Discharge of nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, leads to excess algae growth. When that algae settles to the bottom and decomposes, oxygen is consumed.
The team's findings, published in the Journal of Freshwater Biology, showed that hypoxia negatively affected habitat quality for all species, but to varying degrees. Yellow perch, for example, saw little decrease, while round goby and rainbow smelt were more significantly affected.
Despite a more positive outlook for habitats of some species, Höök said it's still unclear how the organisms themselves were affected.
"Invertebrates that are stuck on the bottom of the lake and can't tolerate a lack of oxygen will die," Höök said. "But other organisms may be able to tolerate lower levels of oxygen, move up in the water column or even benefit from increased algae growth, which could lead to more invertebrate prey for fish."
Höök used observed climatic conditions and U.S. Environmental Protection Agency data to estimate daily temperatures and oxygen levels at varying depths over 18 years. Then, researchers used bioenergetic models, which use data about each species' needs in order to survive, to determine when and at what depth fish species' habitats were affected by hypoxia.
Höök said more work is needed to understand the organisms' responses to changes in habitat quality. His research group is developing more complex models to see how hypoxia-induced movements by fish may affect predator-prey relationships and other issues related to hypoxia.
INFORMATION:
The U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Center of Sponsored Coastal Ocean Research funded the research. Höök collaborated with researchers from Lake Superior State University, University of Michigan, Ohio State University, Colorado State University and the NOAA Great Lakes Environmental Research Laboratory.
Writer: Brian Wallheimer, 765-496-2050, bwallhei@purdue.edu
Source: Tomas Höök, 765-496-6799, thook@purdue.edu
IMAGE CAPTION:
This image show interpolated bottom water oxygen concentrations in Lake Erie during September 2005. (Image by Stuart Ludsin)
http://news.uns.purdue.edu/images/2011/hook-hypoxia.jpg
Abstract on the research in this release is available at: http://www.purdue.edu/newsroom/research/2011/110110HookHypoxia.html
Lake Erie hypoxic zone doesn't affect all fish the same, study finds
2011-01-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Being poor can suppress children's genetic potentials
2011-01-11
AUSTIN, Texas — Growing up poor can suppress a child's genetic potential to excel cognitively even before the age of 2, according to research from psychologists at The University of Texas at Austin.
Half of the gains that wealthier children show on tests of mental ability between 10 months and 2 years of age can be attributed to their genes, the study finds. But children from poorer families, who already lag behind their peers by that age, show almost no improvements that are driven by their genetic makeup.
The study of 750 sets of twins by Assistant Professor Elliot ...
Possible missing link between young and old galaxies
2011-01-11
University of California, Berkeley, astronomers may have found the missing link between gas-filled, star-forming galaxies and older, gas-depleted galaxies typically characterized as "red and dead."
In a poster to be presented this week at the American Astronomical Society meeting in Seattle, UC Berkeley astronomers report that a long-known "early-type" galaxy, NGC 1266, is expelling molecular gas, mostly hydrogen, from its core.
Astronomers have long recognized the distinction between early-type red and dead galaxies, thought to be largely devoid of gas and dust and ...
Oxygen-free early oceans likely delayed rise of life on planet
2011-01-11
RIVERSIDE, Calif. – Geologists at the University of California, Riverside have found chemical evidence in 2.6-billion-year-old rocks that indicates that Earth's ancient oceans were oxygen-free and, surprisingly, contained abundant hydrogen sulfide in some areas.
"We are the first to show that ample hydrogen sulfide in the ocean was possible this early in Earth's history," said Timothy Lyons, a professor of biogeochemistry and the senior investigator in the study, which appears in the February issue of Geology. "This surprising finding adds to growing evidence showing ...
Does it hurt?
2011-01-11
It is well known that pain is a highly subjective experience. We each have a pain threshold, but this can vary depending on distractions and mood. A paper in the International Journal of Behavioural and Healthcare Research offers a cautionary note on measuring perceived pain in research.
There are many chronic illnesses and injuries that have no well-defined symptoms other than pain, but because of the subjectivity in a patient's reporting of their experience of the illness or injury, healthcare workers have difficulty in addressing the patient's needs. Moreover, when ...
New method takes snapshots of proteins as they fold
2011-01-11
People have only 20,000 to 30,000 genes (the number is hotly contested), but they use those genes to make more than 2 million proteins. It's the protein molecules that domost of the work in the human cell. After all, the word protein comes from the Greek prota, meaning "of primary importance."
Proteins are created as chains of amino acids, and these chains of usually fold spontaneously into what is called their "native form" in milliseconds or a few seconds.
A protein's function depends sensitively on its shape. For example, enzymes and the molecules they alter are ...
Universities miss chance to identify depressed students
2011-01-11
CHICAGO --- One out of every four or five students who visits a university health center for a routine cold or sore throat turns out to be depressed, but most centers miss the opportunity to identify these students because they don't screen for depression, according to new Northwestern Medicine research.
About 2 to 3 percent of these depressed students have had suicidal thoughts or are considering suicide, the study found.
"Depression screening is easy to do, we know it works, and it can save lives," said Michael Fleming, professor of family and community medicine ...
'Hot-bunking' bacterium recycles iron to boost ocean metabolism
2011-01-11
In the vast ocean where an essential nutrient—iron—is scarce, a marine bacterium that launches the ocean food web survives by using a remarkable biochemical trick: It recycles iron.
By day, it uses iron in enzymes for photosynthesis to make carbohydrates; then by night, it appears to reuse the same iron in different enzymes to produce organic nitrogen for proteins.
The bacterium, Crocosphaera watsonii, is one of the few marine microbes that can convert nitrogen gas into organic nitrogen, which (just as it does on land) acts as fertilizer to stimulate plant growth in ...
Men with macho faces attractive to fertile women, researchers find
2011-01-11
When their romantic partners are not quintessentially masculine, women in their fertile phase are more likely to fantasize about masculine-looking men than are women paired with George Clooney types.
But women with masculine-looking partners do not necessarily become more attracted to their partners, a recent study co-authored by a University of Colorado at Boulder researcher concludes.
Meanwhile, a man's intelligence has no effect on the extent to which fertile, female partners fantasize about others, the researchers found. They say the lack of an observed "fertility ...
GEN reports on biotech acquisition deals in 2010 that topped $1 billion
2011-01-11
New Rochelle, NY, January 10, 2011—The mega-mergers of 2009 did not continue into 2010. While the three biggest acquisitions in 2009 each had a price tag of more than $40 billion, only last year's top purchase got above that mark, according to an evaluation of reported deals conducted by Genetic Engineering & Biotechnology News (GEN) (http://www.genengnews.com/). The only other mega takeover for the year, sanofi-aventis' move to buy Genzyme, is still being worked out.
A look at 2010's buyouts that crossed the $1billion mark (http://www.genengnews.com/gen-news-highlights/acquisition-deals-in-2010-that-topped-1b/81244443/) ...
Abstinence, heavy drinking, binge drinking associated with increased risk of cognitive impairment
2011-01-11
Amsterdam, The Netherlands, January 10, 2011 -- Previous research regarding the association between alcohol consumption and dementia or cognitive impairment in later life suggests that mild to moderate alcohol consumption might be protective of dementia. However, most of the research has been conducted on subjects already rather elderly at the start of the follow-up. A new study published in the December issue of the Journal of Alzheimer's Disease addresses this problem with a follow-up of more than two decades.
The study, conducted at the University of Turku, University ...