(Press-News.org)
“[...] we discuss the implications of these novel findings on our understanding of how healthy aging affects verbal working memory processing.”
BUFFALO, NY- January 2, 2024 – A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 24, entitled, “Age-related alterations in the oscillatory dynamics serving verbal working memory processing.”
Working memory (WM) is a foundational cognitive function involving the temporary storage of information. Unfortunately, WM is also one of the most sensitive cognitive functions to the detrimental effects of aging. Expanding the field’s understanding of age-related WM changes is critical to advancing the development of strategies to mitigate age-related WM declines.
In this new study, researchers Seth D. Springer, Hannah J. Okelberry, Madelyn P. Willett, Hallie J. Johnson, Chloe E. Meehan, Mikki Schantell, Christine M. Embury, Maggie P. Rempe, and Tony W. Wilson from Boys Town National Research Hospital, University of Nebraska Medical Center, Washington University School of Medicine, and Creighton University investigated the neural mechanisms serving WM function in seventy-eight healthy aging adults (range: 20.2–65.2 years) using magnetoencephalography (MEG) and a Sternberg WM task with letter stimuli.
“We hypothesized that older adults would require stronger engagement of key left hemispheric frontal and parieto-occipital WM hubs. Additionally, we expected that prefrontal activity lateralization (i.e., stronger left hemispheric activity) during WM performance would diminish as a function of age, with older individuals tending to utilize a more bilaterally distributed WM network.”
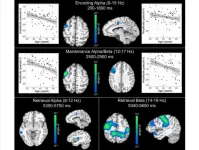
Neural activity during the different phases of the WM task (i.e., encoding, maintenance, and retrieval) were imaged using a time-frequency resolved beamformer and whole-brain statistics were performed. The researchers found stronger increases in theta activity and stronger decreases in alpha and beta activity (i.e., more negative relative to baseline) as a function of healthy aging. Specifically, age-related increases in theta activity were detected during the encoding period in the primary visual and left prefrontal cortices. Additionally, alpha and beta oscillations were stronger (i.e., more negative) during both encoding and maintenance in the left prefrontal cortex in older individuals. Finally, alpha and beta oscillations during the retrieval phase were stronger (i.e., more negative) in older participants within the prefrontal, parietal, and temporal cortices.
“Together, these results indicate that healthy aging strongly modulates the neural oscillatory dynamics serving WM function.”
Read the full study: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.205403
Corresponding Author: Tony W. Wilson - tony.wilson@boystown.org
Keywords: oscillation, magnetoencephalography, MEG, theta, alpha, aging
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article: https://aging.altmetric.com/details/email_updates?id=10.18632%2Faging.205403
About Aging:
Launched in 2009, Aging (Aging-US) publishes papers of general interest and biological significance in all fields of aging research and age-related diseases, including cancer—and now, with a special focus on COVID-19 vulnerability as an age-dependent syndrome. Topics in Aging go beyond traditional gerontology, including, but not limited to, cellular and molecular biology, human age-related diseases, pathology in model organisms, signal transduction pathways (e.g., p53, sirtuins, and PI-3K/AKT/mTOR, among others), and approaches to modulating these signaling pathways.
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
SoundCloud
Facebook
X, formerly known as Twitter
Instagram
YouTube
LabTube
LinkedIn
Reddit
Pinterest
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker Str., Suite 1B
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
###
END
In the quest to understand the potential for life beyond Earth, researchers are widening their search to encompass not only biological markers, but also technological ones. While astrobiologists have long recognized the importance of oxygen for life as we know it, oxygen could also be a key to unlocking advanced technology on a planetary scale.
In a new study published in Nature Astronomy, Adam Frank, the Helen F. and Fred H. Gowen Professor of Physics and Astronomy at the University ...
Plants have to be flexible to survive environmental changes, and the adaptive methods they deploy must often be as changeable as the shifts in climate and condition to which they adapt. To cope with drought, plant roots produce a water-repellent polymer called suberin that blocks water from flowing up towards the leaves, where it would quickly evaporate. Without suberin, the resulting water loss would be like leaving the tap running.
In some plants, suberin is produced by endodermal cells that line the vessels inside the roots. But in others, like tomatoes, suberin is produced in exodermal cells that sit just below ...
After the last embers of a campfire dim, the musky smell of smoke remains. Whiffs of that distinct smokey smell may serve as a pleasant reminder of the evening prior, but in the wake of a wildfire, that smell comes with ongoing health risks.
Wildfire smoke is certainly more pervasive than a small campfire, and the remnants can linger for days, weeks and months inside homes and businesses. New research from Portland State’s Elliott Gall, associate professor in Mechanical and Materials Engineering, examined how long harmful chemicals found in wildfire smoke can persist and the ...
LA JOLLA, CA—Identifying new ways to target proteins involved in human diseases is a priority for many researchers around the world. However, discovering how to alter the function of these proteins can be difficult, especially in live cells. Now, scientists from Scripps Research have developed a new method to examine how proteins interact with drug-like small molecules in human cells—revealing critical information about how to potentially target them therapeutically.
The strategy, published in Nature Chemical Biology on January 2, 2024, uses a combination of chemistry and analytical techniques to reveal the specific places where proteins and small molecules bind ...
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) vaccines recently approved for people 60 and older would dramatically reduce the disease’s significant burden of illness and death in the United States if they were widely adopted like annual influenza vaccines, a new study has found.
A high level of RSV vaccination would not only potentially reduce millions of dollars in annual outpatient and hospitalization costs but would also produce an economy of scale with individual shots being delivered at a relatively modest cost of between $117 and $245 per dose, the study said.
The vaccines are currently covered by most private insurers without ...
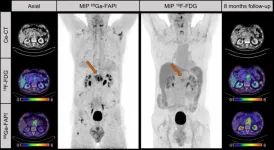
Reston, VA—PET imaging with 68Ga-FAPI can more effectively detect and stage pancreatic cancer as compared with 18F-FDG imaging or contrast-enhanced CT, according to new research published in the December issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine. In a head-to-head study, 68Ga-FAPI detected more pancreatic tumors on a per-lesion, per-patient, or per-region basis and led to major and minor changes to clinical management of patients. In addition to enhancing precise detection of pancreatic cancer, 68Ga-FAPI ...
Understanding Climate Mobilities: New study examines perspectives from South Florida practitioners
As climate change continues to impact people across South Florida, the need for adaptive responses becomes increasingly important.
A recent study led by researchers at the University of Miami Rosenstiel School of Marine, Atmospheric, and Earth Science, assessed the perspectives of 76 diverse South Florida climate adaptation professionals. The study titled, “Practitioner perspectives on climate mobilities in South Florida” was published in the December issue of the Journal Oxford Open Climate Change, and explores the expectations and concerns of practitioners from the ...
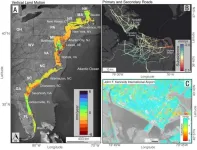
Major cities on the U.S. Atlantic coast are sinking, in some cases as much as 5 millimeters per year – a decline at the ocean’s edge that well outpaces global sea level rise, confirms new research from Virginia Tech and the U.S. Geological Survey.
Particularly hard hit population centers such as New York City and Long Island, Baltimore, and Virginia Beach and Norfolk are seeing areas of rapid “subsidence,” or sinking land, alongside more slowly sinking or relatively stable ground, increasing the risk to roadways, runways, building foundations, rail ...
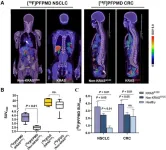
Reston, VA—A novel PET imaging tracer has been proven to safely and effectively detect a common cancer gene mutation that is an important molecular marker for tumor-targeted therapy. By identifying this mutation early, physicians can tailor treatment plans for patients to achieve the best results. This research was published in the December issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine.
Kirsten rat sarcoma (KRAS) is a commonly mutated oncogene that is present in approximately 20-70 percent of cancer cases. Patients with KRAS mutations usually respond poorly to standard therapies. As such, the National Comprehensive ...
Central features of human evolution may stop our species from resolving global environmental problems like climate change, says a new study led by the University of Maine.
Humans have come to dominate the planet with tools and systems to exploit natural resources that were refined over thousands of years through the process of cultural adaptation to the environment. University of Maine evolutionary biologist Tim Waring wanted to know how this process of cultural adaptation to the environment might influence the goal of solving global environmental problems. ...