(Press-News.org) As the world moves away from gas towards electricity as a greener power source, the to-do list goes beyond cars. The vast global manufacturing network that makes everything from our batteries to our fertilizers needs to flip the switch, too.
A study from UChicago chemists found a way to use electricity to boost a type of chemical reaction often used in synthesizing new candidates for pharmaceutical drugs.
Published Jan. 2 in Nature Catalysis, the research is an advance in the field of electrochemistry and shows a path forward to designing and controlling reactions—and making them more sustainable.
“What we want to do is understand what’s happening at the fundamental level at the electrode interface, and use that to predict and design more efficient chemical reactions,” said Anna Wuttig, UChicago Neubauer Family Assistant Professor and the senior author on the paper. “This is a step towards that eventual goal.”
Chemical complexity
In certain chemical reactions, electricity can boost the output—and because you can get the needed electricity from renewable sources, it could be part of making the worldwide chemical industry greener.
But electrochemistry, as the field is known, is especially complex. There is much scientists don’t know about the molecular interactions, especially because you have to insert a conductive solid (an electrode) into the mix to provide the electricity, which means the molecules interact with that electrode as well as with each other. To a scientist trying to untangle the roles each molecule is playing and in what order, this makes an already complicated process even more complicated.
Wuttig, however, wants to turn this into an advantage. “What if you think about it as electrochemistry providing us with a unique design lever that’s not possible in any other system?” she said.
In this case, she and her team focused on the surface of the electrode that provides the electricity to the reaction.
“There were hints that the surface itself is catalytic, that it plays a role,” Wuttig said, “but we don’t know how to systematically control those interactions at the molecular level.”
They tinkered with a type of reaction that is commonly used in manufacturing chemicals for medicine, to form a bond between two carbon atoms.
According to theoretical predictions, when this reaction is performed using electricity, the yield from the reaction should be 100%—that is, all the molecules that went in are made into a single new substance. But when you actually run the reaction in the lab, the yield is lower.
The team thought the presence of the electrode was tempting some of the molecules away from where they were needed during the reaction. They found that adding a key ingredient could help: a chemical known as a Lewis acid added to the liquid solution redirected those molecules.
“You get a near-clean reaction,” Wuttig said.
Catalyzing change
Moreover, the team was able to use special imaging techniques to watch the reactions unfold at the molecular level. “You can see that the presence of the modulator has a profound effect on the interfacial structure,” she said. “This allows us to visualize and understand what’s happening, rather than regard it as a black box.”
This is a crucial step, Wuttig said, because it shows a path forward towards being able to not only use the electrode in chemistry, but also to predict and control its effects.
Another benefit is that the electrode can be re-used for more reactions. (In most reactions, the catalyst is dissolved in the liquid and is drained away during the purification process to get the final product).
“This is a step towards sustainable synthesis,” she said. “Moving forward, my group is very excited to use these types of concepts and strategies to map out and address other synthetic challenges.”
END
Using electricity, scientists find promising new method of boosting chemical reactions
UChicago chemists hope to lay foundation for greener chemistry
2024-01-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Combine mindfulness with exercise for mental health boost in 2024 – study
2024-01-02
For people looking to start 2024 with a new routine to feel fitter and happier, a new study from the University of Bath suggests that combining mindfulness with exercise could be your key to success.
A study, published in the academic journal Mental Health and Physical Activity, suggests that life changes which combine both physical activity and mindfulness are most effective at lifting mood and improving health and wellbeing.
Both physical activity and mindfulness practice have well established psychological benefits. However, ...
New AI tool brings precision pathology for cancer and beyond into quicker, sharper focus
2024-01-02
A new artificial intelligence tool that interprets medical images with unprecedented clarity does so in a way that could allow time-strapped clinicians to dedicate their attention to critical aspects of disease diagnosis and image interpretation.
The tool, called iStar (Inferring Super-Resolution Tissue Architecture), was developed by researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, who believe they can help clinicians diagnose and better treat cancers that might otherwise go undetected. The imaging technique provides both highly detailed views of individual cells and a broader look of the ...
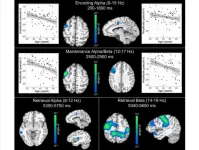
Age-related alterations in the oscillatory dynamics serving verbal working memory processing
2024-01-02
“[...] we discuss the implications of these novel findings on our understanding of how healthy aging affects verbal working memory processing.”
BUFFALO, NY- January 2, 2024 – A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 24, entitled, “Age-related alterations in the oscillatory dynamics serving verbal working memory processing.”
Working memory (WM) is a foundational cognitive function involving the temporary storage of information. Unfortunately, WM ...
Is oxygen the cosmic key to alien technology?
2024-01-02
In the quest to understand the potential for life beyond Earth, researchers are widening their search to encompass not only biological markers, but also technological ones. While astrobiologists have long recognized the importance of oxygen for life as we know it, oxygen could also be a key to unlocking advanced technology on a planetary scale.
In a new study published in Nature Astronomy, Adam Frank, the Helen F. and Fred H. Gowen Professor of Physics and Astronomy at the University ...
How tomato plants use their roots to ration water during drought
2024-01-02
Plants have to be flexible to survive environmental changes, and the adaptive methods they deploy must often be as changeable as the shifts in climate and condition to which they adapt. To cope with drought, plant roots produce a water-repellent polymer called suberin that blocks water from flowing up towards the leaves, where it would quickly evaporate. Without suberin, the resulting water loss would be like leaving the tap running.
In some plants, suberin is produced by endodermal cells that line the vessels inside the roots. But in others, like tomatoes, suberin is produced in exodermal cells that sit just below ...
Targeted household cleaning can reduce toxic chemicals post-wildfire, Portland State research shows
2024-01-02
After the last embers of a campfire dim, the musky smell of smoke remains. Whiffs of that distinct smokey smell may serve as a pleasant reminder of the evening prior, but in the wake of a wildfire, that smell comes with ongoing health risks.
Wildfire smoke is certainly more pervasive than a small campfire, and the remnants can linger for days, weeks and months inside homes and businesses. New research from Portland State’s Elliott Gall, associate professor in Mechanical and Materials Engineering, examined how long harmful chemicals found in wildfire smoke can persist and the ...
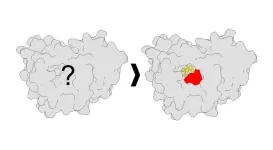
New method illuminates druggable sites on proteins
2024-01-02
LA JOLLA, CA—Identifying new ways to target proteins involved in human diseases is a priority for many researchers around the world. However, discovering how to alter the function of these proteins can be difficult, especially in live cells. Now, scientists from Scripps Research have developed a new method to examine how proteins interact with drug-like small molecules in human cells—revealing critical information about how to potentially target them therapeutically.
The strategy, published in Nature Chemical Biology on January 2, 2024, uses a combination of chemistry and analytical techniques to reveal the specific places where proteins and small molecules bind ...
RSV vaccines would greatly reduce illness if implemented like flu shots
2024-01-02
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) vaccines recently approved for people 60 and older would dramatically reduce the disease’s significant burden of illness and death in the United States if they were widely adopted like annual influenza vaccines, a new study has found.
A high level of RSV vaccination would not only potentially reduce millions of dollars in annual outpatient and hospitalization costs but would also produce an economy of scale with individual shots being delivered at a relatively modest cost of between $117 and $245 per dose, the study said.
The vaccines are currently covered by most private insurers without ...
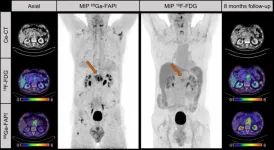
Ga-68 FAPI PET improves detection and staging of pancreatic cancer
2024-01-02
Reston, VA—PET imaging with 68Ga-FAPI can more effectively detect and stage pancreatic cancer as compared with 18F-FDG imaging or contrast-enhanced CT, according to new research published in the December issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine. In a head-to-head study, 68Ga-FAPI detected more pancreatic tumors on a per-lesion, per-patient, or per-region basis and led to major and minor changes to clinical management of patients. In addition to enhancing precise detection of pancreatic cancer, 68Ga-FAPI ...
Understanding climate mobilities: New study examines perspectives from South Florida practitioners
2024-01-02
Understanding Climate Mobilities: New study examines perspectives from South Florida practitioners
As climate change continues to impact people across South Florida, the need for adaptive responses becomes increasingly important.
A recent study led by researchers at the University of Miami Rosenstiel School of Marine, Atmospheric, and Earth Science, assessed the perspectives of 76 diverse South Florida climate adaptation professionals. The study titled, “Practitioner perspectives on climate mobilities in South Florida” was published in the December issue of the Journal Oxford Open Climate Change, and explores the expectations and concerns of practitioners from the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
[Press-News.org] Using electricity, scientists find promising new method of boosting chemical reactionsUChicago chemists hope to lay foundation for greener chemistry