(Press-News.org) The mini-halos of dark matter scattered throughout the Cosmos could function as highly sensitive probes of primordial magnetic fields. This is what emerges from a theoretical study conducted by SISSA and published in Physical Review Letters. Present on immense scales, magnetic fields are found everywhere in the Universe. However, their origin are still subjects of debate among scholars. An intriguing possibility is that magnetic fields originated near the birth of the universe itself, that is they are primordial magnetic fields. In the study, researchers showed that if magnetic fields are indeed primordial then it could cause an increase in dark matter density perturbations on small scales. The ultimate effect of this process would be the formation of mini-halos of dark matter, which, if detected would hint towards a primordial nature of magnetic fields. Thus, in an apparent paradox, the invisible part of our Universe could be useful in resolving the nature of a component of the visible one.
Shedding light on the formation of Magnetic Fields
"Magnetic fields are ubiquitous in the Cosmos," explains Pranjal Ralegankar of SISSA, the author of the research. "A possible theory regarding their formation suggests that those observed so far could be produced in the early stages of our Universe. However, this proposition lacks explanation in the standard model of physics. To shed light on this aspect and find a way to detect “primordial” magnetic fields, with this work we propose a method that we could define as 'indirect.' Our approach is based on a question: What is the influence of magnetic fields on dark matter?". It is known that there is no direct interaction. Still, as Ralegankar explains, “there is an indirect one that occurs through gravity”.
Right from the primordial Universe
Primordial magnetic fields can enhance density perturbations of electrons and protons in the primordial Universe. When these become too large, they influence the magnetic fields themselves. The consequence is the suppression of fluctuations on a small scale. Ralegankar explains: "In the study, we show something unexpected. The growth in baryon density gravitationally induces the growth of dark matter perturbations without the possibility of subsequent cancellation. This would result in their collapse on small scales, producing mini-halos of dark matter." The consequence, continues the author, is that although fluctuations in the density of baryonic matter are cancelled, they would leave traces through the mini-halos, all solely through gravitational interactions.
"These theoretical findings", concludes Pranjal Ralegankar, "also suggest that the abundance of mini-halos is determined not by the present presence of primordial magnetic fields but rather by their strength in the primordial Universe. Thus, a detection of dark matter mini-halos would reinforce the hypothesis that magnetic fields formed very early, even within 1 second after the Big Bang."
END
Magnetic fields in the Cosmos: dark matter could help us discover their origin
We don't know how they formed. Now a new theoretical research tells how the invisible part of our Universe could help us discover it, suggesting a primordial genesis, even within a second of the Big Bang
2024-01-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Pusan National University researchers boost signal amplification in perovskite nanosheets
2024-01-03
Perovskite materials are still attracting a lot of interest in solar cell applications. Now, the nanostructures of perovskite materials are being considered as a new laser medium. Over the years, light amplification in perovskite quantum dots has been reported, but most of the works present inadequate quantitative analysis. To assess the light amplification ability, “gain coefficient” is necessary, whereby the essential characteristic of a laser medium is revealed. An efficient laser medium is one that has a large gain.
Scientists have been exploring ways to boost this gain. Now, in a recent study, a team of researchers, led by Professor ...
PolyU researchers develop nature-inspired advanced materials to achieve 99.6% solar reflectivity
2024-01-03
Scientific researchers draw inspiration from nature’s brilliance as they seek to develop transformative solutions to unresolved challenges. Prof. WANG Zuankai, Associate Vice President (Research and Innovation) and Chair Professor of the Department of Mechanical Engineering of The Hong Kong Polytechnic University (PolyU), has meticulously explored the intricacies of nature and made remarkable findings with very significant real-world applications. His recently published research on cooling ceramic successfully translates novel discovery into sustainable applications.
Findings from his research project “Hierarchically structured passive radiative cooling ceramic with high ...
Study: Acetaminophen use during pregnancy linked to language delays in children
2024-01-03
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Acetaminophen is considered the safest over-the-counter pain reliever and fever reducer available during pregnancy. Studies have shown that 50%-65% of women in North America and Europe take acetaminophen during pregnancy. A new study from researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign explored the relationship between acetaminophen use during pregnancy and language outcomes in early childhood. It found that increasing acetaminophen use was associated with language delays.
The findings are reported in the journal Pediatric ...
Some sea cucumbers like it hot
2024-01-03
Hydrothermal vents are an unlikely environment for animals to flourish, characterized by rapid changes in temperature and a challenging chemistry: acidic pH, rich in sulfur and methane. Not to mention the high hydrostatic pressure and the darkness of the deep sea. A team of scientists at the Sanya Institute of Deep-sea Science and Engineering (China) have now sequenced the full genome of a particularly unusual inhabitant of the hydrothermal vent environment: the sea cucumber Chiridota heheva. The research has been published in the Open Science ...
New reasons eating less fat should be one of your resolutions
2024-01-03
A UC Riverside study to motivate your new year’s resolutions: it demonstrates that high-fat diets affect genes linked not only to obesity, colon cancer and irritable bowels, but also to the immune system, brain function, and potentially COVID-19 risk.
While other studies have examined the effects of a high-fat diet, this one is unusual in its scope. UCR researchers fed mice three different diets over the course of 24 weeks where at least 40% of the calories came from fat. Then, they looked not only at the microbiome, but also at genetic changes in all four parts of the intestines.
One group of ...
Job ads with wide pay ranges can deter applicants
2024-01-03
PULLMAN, Wash. – As more states require employers to list compensation on job ads, a trending strategy to use very wide pay ranges could potentially harm recruitment, according to a Washington State University study.
The study, published in the Journal of Applied Psychology, found that participants in three different experiments were more likely to respond negatively to job ads with very wide pay ranges, viewing those employers as less trustworthy. Prior surveys have found that most people report they would trust organizations that include pay ranges in ...
What makes urine yellow? UMD scientists discover the enzyme responsible
2024-01-03
Researchers at the University of Maryland and National Institutes of Health have identified the microbial enzyme responsible for giving urine its yellow hue, according to a new study published in the journal Nature Microbiology on January 3, 2024.
The discovery of this enzyme, called bilirubin reductase, paves the way for further research into the gut microbiome’s role in ailments like jaundice and inflammatory bowel disease.
“This enzyme discovery finally unravels the mystery behind urine’s yellow color,” said the study’s lead author Brantley Hall, an assistant ...
Non-toxic quantum dots pave the way towards CMOS shortwave infrared image sensors for consumer electronics
2024-01-03
Invisible to our eyes, shortwave infrared (SWIR) light can enable unprecedented reliability, function and performance in high-volume, computer vision first applications in service robotics, automotive and consumer electronics markets. Image sensors with SWIR sensitivity can operate reliably under adverse conditions such as bright sunlight, fog, haze and smoke. Furthermore, the SWIR range provides eye-safe illumination sources and opens up the possibility of detecting material properties through molecular imaging.
Colloidal quantum ...
Complex, unfamiliar sentences make the brain’s language network work harder
2024-01-03
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- With help from an artificial language network, MIT neuroscientists have discovered what kind of sentences are most likely to fire up the brain’s key language processing centers.
The new study reveals that sentences that are more complex, either because of unusual grammar or unexpected meaning, generate stronger responses in these language processing centers. Sentences that are very straightforward barely engage these regions, and nonsensical sequences of words don’t do much for them either.
For ...
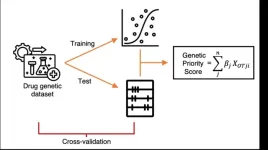
Novel genetic priority score unveiled to enhance target prioritization in drug development
2024-01-03
New York, NY [January 3, 2024]—Driven by the need for a better way to prioritize targets for drug development, the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai has led the development of a novel “genetic priority score” (GPS) that will integrate various types of human genetic data into a single easy-to-interpret score.
The findings were described in the January 3 online issue of Nature Genetics [DOI: 10.1038/s41588-023-01609-2].
Studies have shown that drugs have an increased likelihood of success in clinical trials when ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Learning makes brain cells work together, not apart
Engineers improve infrared devices using century-old materials
Physicists mathematically create the first ‘ideal glass’
Microbe exposure may not protect against developing allergic disease
Forest damage in Europe to rise by around 20% by 2100 even if warming is limited to 2°C
Rapid population growth helped koala’s recovery from severe genetic bottleneck
CAR-expressing astrocytes target and clear amyloid-β in mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
Unique Rubisco subunit boosts carbon assimilation in land plants
Climate change will drive increasing forest disturbances across Europe throughout the next century
Enhanced brain cells clear away dementia-related proteins
This odd little plant could help turbocharge crop yields
Flipped chromosomal segments drive natural selection
Whole-genome study of koalas transforms how we understand genetic risk in endangered species
Worcester Polytechnic Institute identifies new tool for predicting Alzheimer’s disease
HSS studies highlight advantages of osseointegration for people with an amputation
Buck Institute launches Healthspan Horizons to turn long-term health data into Actionable healthspan insights
University of Ottawa Heart Institute, the University of Ottawa and McGill University launch ARCHIMEDES to advance health research in Canada
The world’s largest brain research prize awarded for groundbreaking discoveries on how we sense touch and pain
Magnetofluids help to overcome challenges in left atrial appendage occlusion
Brain-clearing cells offer clues to slowing Alzheimer’s disease progression
mRNA therapy restores fertility in genetically infertile mice
Cloaked stem cells evade immune rejection in mice, pointing to a potential universal donor cell line
Growth in telemedicine has not improved mental health care access in rural areas, study finds
Pitt scientists engineer “living eye drop” to support corneal healing
Outcomes of older adults with advanced cancer who prefer quality of life vs prolonging survival
Lower music volume levels in fitness class and perceived exercise intensity
Of crocodiles, counting and conferences
AERA announces 2026 award winners in education research
Saving two lives with one fruit drop
Photonic chips advance real-time learning in spiking neural systems
[Press-News.org] Magnetic fields in the Cosmos: dark matter could help us discover their originWe don't know how they formed. Now a new theoretical research tells how the invisible part of our Universe could help us discover it, suggesting a primordial genesis, even within a second of the Big Bang