(Press-News.org) ● KAT6 is an emerging target in hormone sensitive breast tumors and other cancers. Overexpression of KAT6A/B correlates with poor clinical outcomes in patients with ER+/HER2- breast cancer – the most common subtype.
● The molecule has demonstrated strong preclinical activity. Insilico Medicine presented data on the novel molecule at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium in early December.
● This agreement includes upfront and milestone payments with a combined potential value of over $500m and sales royalties.
FLORENCE, Italy and NEW YORK: The Menarini Group ("Menarini"), a leading international pharmaceutical and diagnostics company, and Stemline Therapeutics, Inc. ("Stemline"), a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Menarini Group focused on bringing transformational oncology treatments to cancer patients, along with clinical stage generative artificial intelligence (AI)-driven biotechnology company Insilico Medicine (“Insilico”), today announced that they have entered into an exclusive licensing agreement granting Stemline the global rights to develop and commercialize a novel, small molecule KAT6A inhibitor designed using Insilico’s AI platform, as a potential treatment for hormone sensitive cancers and other oncology indications.
Breast cancer is the most commonly diagnosed tumor type and the leading cause of cancer death among women, globally.1 Approximately 70% of breast cancers are estrogen receptor positive (ER+), and endocrine therapy remains the backbone of therapy for patients with ER+ breast cancer. However, tumors can develop a resistance to endocrine therapy, which in turn can lead to disease progression. This is a significant clinical challenge and highlights the urgent need for novel therapies to help overcome treatment resistance.
KAT6A is known to play an important role in several cancers. Overexpression of KAT6A correlates with poor clinical outcomes in patients with ER+/HER2- breast cancer, the most common subtype of breast cancer. In preclinical studies, the molecule has demonstrated potent inhibition against KAT6A in multiple CDX and PDX models with good efficacy and safety. Insilico presented data on the molecule at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium in early December.
“We are delighted to enter a collaboration with Insilico that harnesses the power of generative AI as a leader in the field, to explore a promising new treatment approach and potentially unlock transformative new cancer therapies,” said Elcin Barker Ergun, CEO of the Menarini Group. “Having brought the first innovation in endocrine therapy after almost 20 years to the U.S. and Europe with elacestrant for ER+, HER2- breast cancer patients, our aim is to further augment patient outcomes, and targeting KAT6A can potentially serve that in breast cancer and beyond.”
The novel molecule was designed by Insilico’s R&D team with the help of its end-to-end PharmaAI platform to inhibit KAT6A and block endocrine receptor (ER) at the transcriptional level, giving it the potential to overcome resistance to endocrine therapies due to mutation or ligand-independent constitutive activation of ER. Currently, endocrine therapy in combination with CDK4/6 inhibitors is the standard treatment for ER+/HER2- breast cancer patients with advanced or metastatic disease. Novel combinations with CDK4/6 inhibitors and/or new oral SERDs are needed to further extend outcomes.
“We are excited by the promise of our latest generative AI-designed therapy to provide a new potential treatment option for breast cancer patients,” says Alex Zhavoronkov, PhD, founder and co-CEO of Insilico Medicine. “With their innovative vision and deep focus in bringing transformational therapeutics in oncology, Stemline is the ideal partner to lead this molecule into development and through clinical trials.”
Under the terms of the agreement, Stemline will provide a $12 million upfront payment to Insilico. The combined value of the deal, including all development, regulatory, and commercial milestones, is over $500 million, followed by royalties up to double digits.
About The Menarini Group
The Menarini Group is a leading international pharmaceutical and diagnostics company, with a turnover of over $4.4 billion and over 17,000 employees. Menarini is focused on therapeutic areas with high unmet needs with products for cardiology, oncology, pneumology, gastroenterology, infectious diseases, diabetology, inflammation, and analgesia. With 18 production sites and 9 Research and Development centers, Menarini's products are available in 140 countries worldwide. For further information, please visit menarini.com.
About Stemline Therapeutics Inc.
Stemline Therapeutics, Inc. ("Stemline") a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Menarini Group, is a commercial-stage biopharmaceutical company focused on the development and commercialization of novel oncology therapeutics. Stemline commercializes ORSERDU® (elacestrant) in the U.S. and in the E.U., an oral endocrine therapy indicated for the treatment of postmenopausal women or adult men with estrogen receptor (ER)-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative, ESR1-mutated advanced or metastatic breast cancer with disease progression following at least one line of endocrine therapy. Stemline also commercializes ELZONRIS® (tagraxofusp-erzs), a novel targeted treatment directed to CD123 for patients with blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm (BPDCN), an aggressive hematologic cancer, in the United States and Europe, which is the only approved treatment for BPDCN in the US and EU to date. Stemline also commercializes NEXPOVIO® (selinexor) in Europe, an XPO1 inhibitor for multiple myeloma. Stemline also has an extensive clinical pipeline of small molecules and biologics in various stages of development for a host of solid and hematologic cancers.
About Insilico Medicine
Insilico Medicine, a global clinical stage biotechnology company powered by generative AI, is connecting biology, chemistry, and clinical trials analysis using next-generation AI systems. The company has developed AI platforms that utilize deep generative models, reinforcement learning, transformers, and other modern machine learning techniques for novel target discovery and the generation of novel molecular structures with desired properties. Insilico Medicine is developing breakthrough solutions to discover and develop innovative drugs for cancer, fibrosis, immunity, central nervous system diseases, infectious diseases, autoimmune diseases, and aging-related diseases. www.insilico.com
Media Contacts
Insilico Medicine
Brita Belli, Head of PR
brita@insilico.com
Menarini Stemline
Cheya Pope
media@menarinistemline.com
###
1 Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021 Feb 4. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 33538338.
END
Menarini Group and Insilico Medicine enter global exclusive license agreement for novel KAT6 inhibitor for potential breast cancer treatment and other oncology indications
2024-01-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New population risk prediction model for likelihood of ICU admission and survival
2024-01-04
INDIANAPOLIS – A significant obstacle to improving care and outcomes for intensive care unit (ICU) patients is the unexpected nature of becoming seriously ill. Which groups of patients are likely to become severely ill and will they survive their ICU stay?
In a first step in creating infrastructure for further studies to identify and follow cohorts of patients who may become critically ill, researchers including Sikandar Khan, D.O, M.S., of Regenstrief Institute and Indiana University School of Medicine, have developed and conducted ...
Chung-Ang University study reveals a higher market valuation of cash holdings of firms adopting electronic voting
2024-01-04
Firms worldwide are increasingly adopting electronic voting, enabling shareholders to cast their votes online, instead of attending shareholder meetings in-person. Shareholders can enjoy superior accessibility to the meetings with electronic voting, compared to those with traditional and in-person setups. Despite the emerging popularity of electronic voting in recent years, however, there is limited evidence of its impact on governance.
To address this gap in research, Associate Professor Wonsuk Ha from the School of Business Administration, Chung-Ang University, along ...
Women undergoing fertility treatment who are stressed may have heart health issues during pregnancy
2024-01-04
WASHINGTON—A new Journal of the Endocrine Society study among women attending a fertility center found that those with more stress before pregnancy had higher blood sugar levels during pregnancy, which is a sign of weaker cardiovascular health.
People’s stress levels have continued to rise over the years, particularly in the last few years due to the COVID-19 pandemic, putting them at risk for serious health issues such as heart disease. Research shows women may experience more stress than men, especially those going through infertility. Maintaining a healthy pregnancy ...
Study finds preconception stress may affect health of women undergoing fertility treatment
2024-01-04
Stress during pregnancy is known to influence health outcomes, but a new study from Mass General Brigham researchers suggests that stress levels before pregnancy are also important to evaluate. Investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital and Brigham and Women’s Hospital analyzed the link between self-reported stress immediately before conception among women seeking fertility care and blood glucose levels, a marker of heart health. The team found that maternal stress during preconception ...
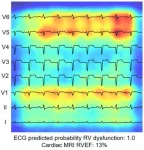
AI-driven study redefines right heart health assessment with novel predictive model
2024-01-04
New York, NY [January 4, 2023]—In a milestone study, researchers from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have harnessed the power of artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance the assessment of the heart’s right ventricle, which sends blood to the lungs.
Conducted by a team using AI-enabled electrocardiogram (AI-ECG) analysis, the research demonstrates that electrocardiograms can effectively predict right-side heart issues, offering a simpler alternative to complex imaging technologies and potentially enhancing patient outcomes.
The findings were described in the December 29 online ...
Better mental, physical health in older people tied to living near nature
2024-01-04
SPOKANE, Wash. – Even small differences in the availability of urban green and blue spaces may be associated with better mental and physical health in older adults, according to a Washington State University study.
The study’s findings showed that having just 10% more forest space in a person’s residential ZIP code was associated with reduced serious psychological distress, which covers mental health problems that require treatment and interfere with people’s social lives, work or school. Similarly, a 10% increase in green space, tree cover, water bodies ...
100 years of Science Changing Life: Scripps Research celebrates a century of transforming human health
2024-01-04
100 years of Science Changing Life: Scripps Research celebrates a century of transforming human health
LA JOLLA, CA—Scripps Research, a nonprofit biomedical institute ranked one of the most influential in the world for its impact on innovation, will celebrate its 100-year history throughout 2024. This significant milestone marks a century of seminal discoveries in immunology, infectious diseases (such as COVID-19, flu, HIV), neuroscience, heart disease, cancer, and more. The institute has also made strides in groundbreaking chemistry advances, drug development and educational ...
JAMA names seven academic physicians and nurses to new Editorial Fellowship Program
2024-01-04
Chicago, January 4, 2024 — The JAMA Network today announces a new class of seven academic physicians and nurses selected for a new program to provide junior faculty and current research fellows opportunities to learn about biomedical journals and scientific publication. This inaugural group of fellows will spend six months immersed as part of the JAMA editorial team to obtain direct exposure to the editorial review process and enhance their skills in scientific communication.
Fellows will be assigned to a current JAMA editor for mentorship, attend manuscript meetings, participate in discussions about research design, data validity, potential clinical importance, and conduct ...
New technique could improve liver fibrosis treatment
2024-01-04
Chronic liver disease, a growing threat to global health, often progresses silently in its early stages. Detecting its precursor, steatotic liver disease (SLD), and advanced liver fibrosis before complications arise is crucial to prevent devastating outcomes. The newly developed Chronic Liver Disease (CLivD) score offers a promising non-invasive approach to this challenge.
In a recent study involving a US general population sample, researchers explored the CLivD score’s ability to identify SLD and advanced fibrosis, assessed using liver stiffness measurement (LSM). The study also evaluated the potential ...
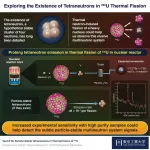
Hunting for the elusive tetraneutrons with thermal fission
2024-01-04
Tetraneutron is an elusive atomic nucleus consisting of four neutrons, whose existence has been highly debated by scientists. This stems primarily from our lack of knowledge about systems consisting of only neutrons, since most atomic nuclei are usually made of a combination of protons and neutrons. Scientists believe that the experimental observation of a tetraneutron could be the key to exploring new properties of atomic nuclei and answering the age-old question: Can a charge-neutral multineutron system ever exist?
Two recent experimental studies reported the presence of tetraneutrons in bound state and resonant state (a state that decays ...